Back to article: Variants of the human RAD52 gene confer defects in ionizing radiation resistance and homologous recombination repair in budding yeast
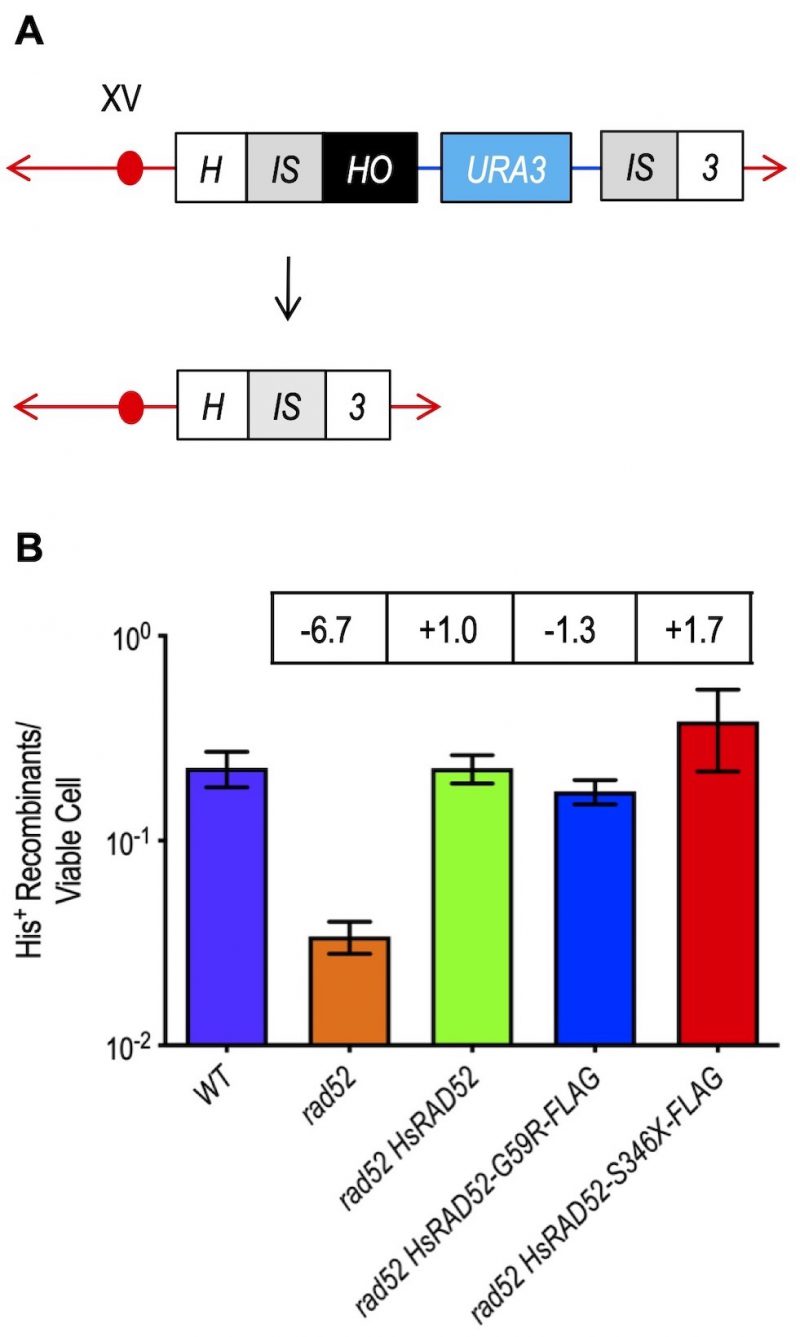
FIGURE 4: The adh1::HsRAD52-G59R-FLAG and adh1::HsRAD52-S346X-FLAG alleles complement the loss of DSB repair by SSA in rad52 mutant yeast cells. (A) Cartoon depicting DSB repair by recombination between non-tandem direct repeats. At the HIS3 locus on chromosome XV, DSB formation by HO endonuclease cutting at a HO cut site (black box) inserted at the right edge of the left duplication of a segment of the HIS3 coding sequence (left gray IS box) initiates bidirectional exonucleolytic processing. Processing reveals complementary single-stranded sequences at the left and right repeats (left and right gray IS boxes) that anneal, creating non-homologous tails whose removal deletes intervening plasmid sequences (blue line and aqua URA3 marker box) enroute to creating an intact HIS3 gene. (B) The adh1::HsRAD52-G59R-FLAG and adh1::HsRAD52-S346X-FLAG alleles complement the defects in DSB repair by DRR. Single colonies of haploid wild-type (ABM325), rad52 (ABM326), rad52 adh1::HsRAD52 (ABM507), rad52 adh1::HsRAD52-G59R-FLAG (ABX3970-88A), and rad52 adh1::HsRAD52-S346X (ABX3975-15A) strains were used to inoculate at least 10 one milliliter YPGL cultures and grown overnight. After a period of expression of HO endonuclease, appropriate dilutions were plated onto solid YPD medium to determine viability, and onto medium lacking histidine to select for recombinants. Following incubation for three days at 30° colonies were counted and frequencies of DRR determined by dividing the number of His+ recombinants by the number of viable cells plated. Mean frequencies of DRR and 95% confidence intervals were plotted against genotype. Fold differences above (+) and below (-) wild-type are indicated in the boxes above the bar for each mean frequency.