Back to article: Plant and fungal products that extend lifespan in Caenorhabditis elegans
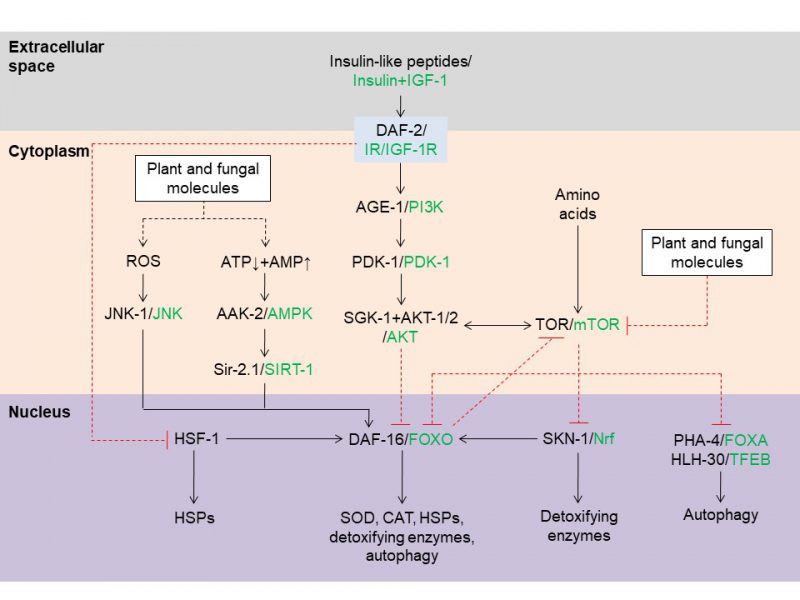
FIGURE 2: Aging-related pathways modulated by plant and fungal molecules in C. elegans. Plant and fungal molecules extend nematode lifespan by inducing the formation of ROS, by activating AAK-2/AMPK, or by inhibiting the insulin or TOR pathway. General cellular pathways are shown here, but variations may occur between cells of different tissues. Human protein homologs are given in green. Abbreviations: AGE-1, phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase age 1; AMP, adenosine monophosphate; ATP, adenosine triphosphate; AAK-2, 5' adenosine-monophosphate-activated protein kinase catalytic subunit alpha 2; AMPK, 5' adenosine-monophosphate-activated protein kinase; CAT, catalase; DAF, abnormal dauer formation protein; FOX, forkhead box; HLH-30, basic helix-loop-helix protein 30; HSF-1, heat-shock factor 1; HSPs, heat-shock proteins; IGF-1, insulin-like growth factor 1; IGF-1R, insulin-like growth factor 1 receptor; IR, insulin receptor; JNK, c-Jun N-terminal kinase; mTOR, mammalian target of rapamycin; Nrf, nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor; PDK-1, 3' phosphoinositide-dependent protein kinase 1; PHA-4, defective pharyngeal development protein 4; PI3K, phosphoinositide 3-kinase; ROS, reactive oxygen species; SGK-1, serum and glucocorticoid-regulated kinase-1; Sir-2.1, sirtuin 2.1; SIRT-1, sirtuin 1; SKN-1, skinhead 1; SOD, superoxide dismutase; TFEB, HLH transcription factor EB; TOR, target of rapamycin.