Back to article: Milestones in Bacillus subtilis sporulation research
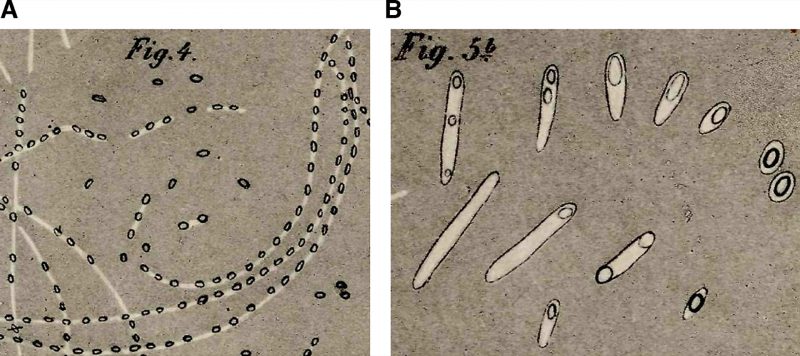
FIGURE 1: Early depictions of sporulation and germination in Bacillus spp. In one of his most well-known studies [6], Robert Koch investigated the etiology of anthrax. (A) Koch followed the sporulation process in B. anthracis. He placed a slice of spleen containing the Bacillus into cow sera or aqueous humor, and incubated the specimens at 35-37°C in an incubator that he himself had constructed. During the incubation, he observed the cells growing into string-like structures. After 10-15 h, these strings contained light refracting bodies, which he identified as spores. Koch depicted the structures in this sketch and likened them to fragile strings of pearls. The strings gradually decomposed, the spores were released and sank to the bottom of the droplet where they accumulated and could be kept for weeks. (B) Koch followed spore germination and outgrowth, and determined that spores can form viable cells. He fixed dried spores on a slide and incubated the sample with aqueous humor. After 3-4 hours, he observed various stages of germination and outgrowth, which are depicted in Cohn's sketch. Koch described spores as egg-shaped structures, enclosed by a thin layer of protoplasm that he called bright matter. He hypothesized that during outgrowth this bright matter stretched and became the vegetative cell, whereas the spore remained at one cell pole, lightened, and shrank, before it dissociated and disappeared. He proposed that the spore core consists of an oily substance necessary for the cell to resume vegetative growth.
6. Koch R (1876). Untersuchungen über Bakterien V. Die Aetiologie der Milzbrand-Krankheit, begründent auf die Entwicklungsgeschichte des Bacillus Anthracis. Beitrage zur Biol der Pflanz 277–310.