Back to article: Lipid and fatty acid metabolism in trypanosomatids
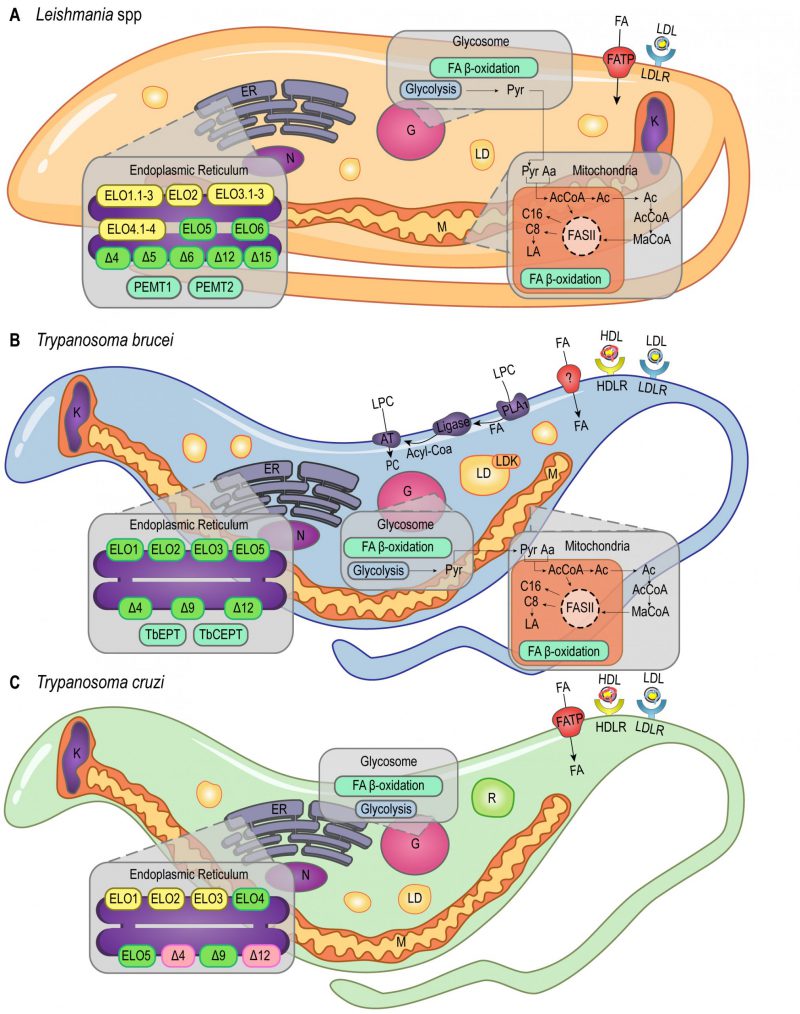
FIGURE 1: Lipid and FA pathways in Leishmania spp., T. brucei and T. cruzi. Schematic illustration of lipid and FA acquisition and metabolic pathways identified in Leishmania spp. (A), T. brucei (B) and T. cruzi (C). Aa – Aminoacid; AcCoA – Acetyl CoA; AT – Acetyltransferase; C8 – Octanoic acid; C16 – Palmitic acid; ELO1.1-3, ELO2, ELO3.1-3, ELO4.1-4, ELO5, ELO6 – Elongases; ER – Endoplasmic Reticulum; FA – Fatty Acid; FASII – Fatty Acid Synthase II; FAT – Fatty Acid Transporter; G – Glycosome; HDL – High Density Lipoprotein; HDLR – High Density Lipoprotein Receptor; K – Kinetoplast; LA – Lipoic acid; LD – Lipid Droplets; LDK – Lipid Droplet Kinase; LDL – Low Density Lipoprotein; LDLR – Low Density Lipoprotein Receptor; LPC – Lysophosphatidylcholine; M – Mitochondria; MaCoA – Malonyl-CoA; N – Nucleus; PC – Phosphatidylcholine; PEMT1 – Phosphatidylethanolamine Methyltransferase 1; PEMT2 – Phosphatidylethanolamine Methyltransferase 2; PLA1 – Phospholipase 1; Pyr – Pyruvate; R – Reservosomes; TbCEPT – Choline/Ethanolamine Phosphotransferase; TbEPT – Ethanolamine Pphosphotransferase; Δ4-6, Δ9, Δ12, Δ15 – Desaturases. Yellow boxes, Leishmania spp. putative genes (ELO1.1-3, ELO2, ELO3.1-3, ELO4.1-4 in A). Green boxes, characterized proteins (ELO5, ELO6 and desaturases in A; ELO1, ELO2, ELO3, ELO5 and desaturases in B; ELO5 and Δ9 in C). Pink boxes, protein activity detected in T. cruzi (Δ4 and Δ12 in C).