Back to article: Mechanisms underlying lactic acid tolerance and its influence on lactic acid production in Saccharomyces cerevisiae
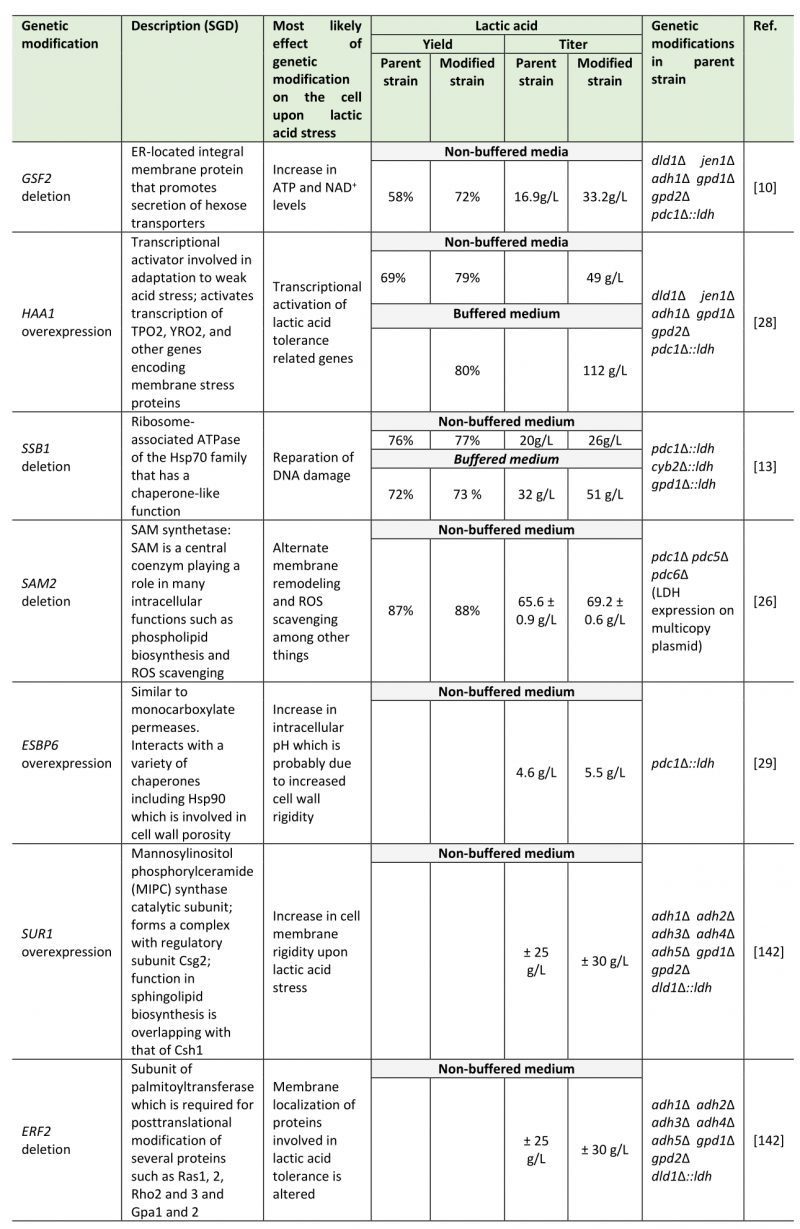
TABLE 1. List of genetic modifications linked to lactic acid tolerance that have been shown to increase lactic acid production in metabolically engineered S. cerevisiae strains.
10. Baek SH, Kwon EY, Kim SY, Hahn JS (2016). GSF2 deletion increases lactic acid production by alleviating glucose repression in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Sci Rep 6: 34812. 10.1038/srep34812
13. Lee JJ, Crook N, Sun J, Alper HS (2016). Improvement of lactic acid production in Saccharomyces cerevisiae by a deletion of ssb1. J Ind Microbiol Biotechnol 43(1): 87-96. 10.1007/s10295-015-1713-7
26. Dato L, Berterame NM, Ricci MA, Paganoni P, Palmieri L, Porro D, Branduardi P (2014). Changes in SAM2 expression affect lactic acid tolerance and lactic acid production in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Microb Cell Fact 13: 147. 10.1186/s12934-014-0147-7
28. Baek SH, Kwon EY, Kim YH, Hahn JS (2016). Metabolic engineering and adaptive evolution for efficient production of D-lactic acid in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 100(6): 2737-2748. 10.1007/s00253-015-7174-0
29. Sugiyama M, Akase SP, Nakanishi R, Kaneko Y, Harashima S (2016). Overexpression of ESBP6 improves lactic acid resistance and production in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Biosci Bioeng 122(4): 415-420. 10.1016/j.jbiosc.2016.03.010
142. Baek SH, Kwon EY, Bae SJ, Cho BR, Kim SY, Hahn JS (2017). Improvement of D?lactic acid production in Saccharomyces cerevisiae under acidic conditions by evolutionary and rational metabolic engineering. Biotechnol J 12(10). 10.1002/biot.201700015