Back to article: Barcode sequencing and a high-throughput assay for chronological lifespan uncover ageing-associated genes in fission yeast
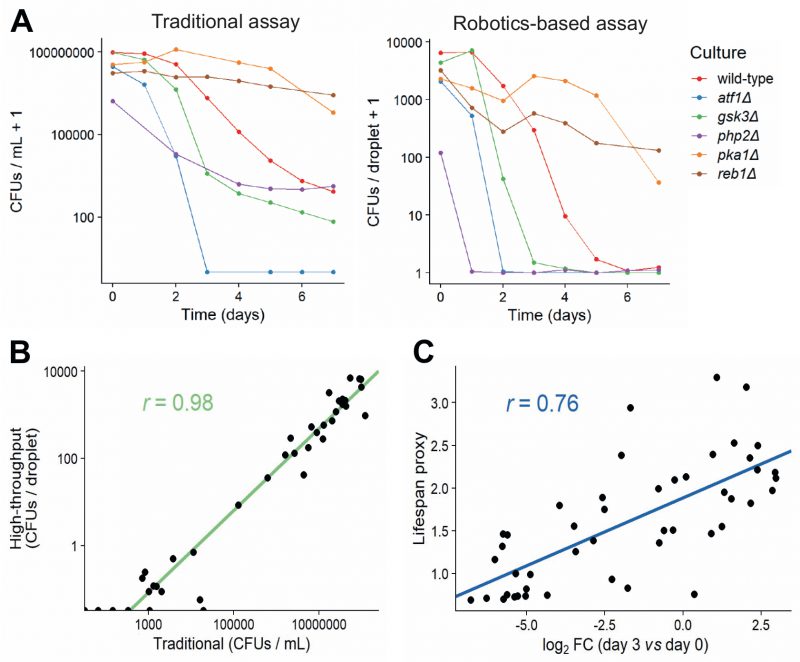
FIGURE 4: Comparison of traditional and high-throughput lifespan assays.(A) Comparison of traditional and robotics-based assays to determine CFUs. Lifespan curves for six mutants with different lifespans were measured in parallel using both the traditional (left) and robotics-based (right) assays. Both methods capture differences in lifespan between short-lived mutants (atf1Δ, gsk3Δ, php2Δ) and long-lived mutants (pka1Δ, reb1Δ). (B) CFUs determined for various cultures (different mutants grown under different conditions) at different timepoints, using both the traditional and robotics-based method. Scatter plot shows the agreement between the two methods. Green: linear regression of log-transformed CFU values (traditional vs robotics-based), along with Pearson correlation coefficient. (C) Scatter plot showing the agreement of CLS estimates between Bar-seq and the robotics-based lifespan assay for the 47 validated mutants. The log2 fold change (FC) of barcode abundance (Day 3 relative to Day 0) is plotted against the lifespan proxy based on maximum-likelihood estimates from the robotics-based method. Blue: linear regression between log2 FC and lifespan proxy, along with Pearson correlation coefficient.