Back to article: Genome, transcriptome and secretome analyses of the antagonistic, yeast-like fungus Aureobasidium pullulans to identify potential biocontrol genes
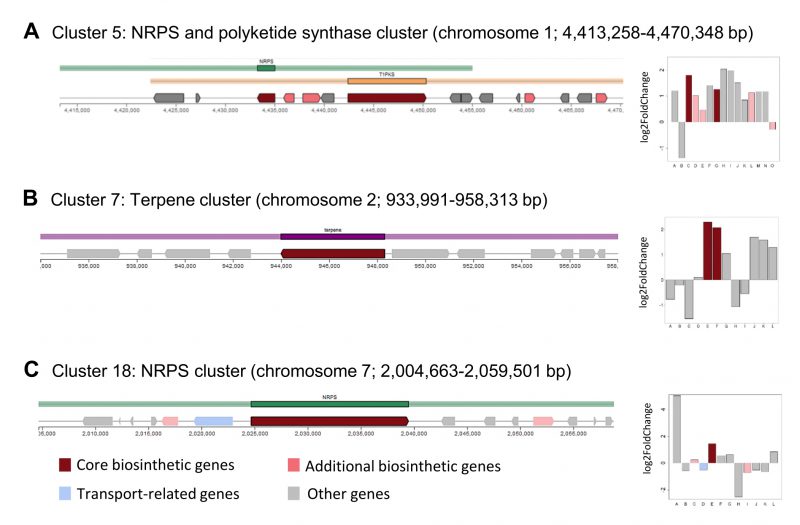
FIGURE 5: Identification of secondary metabolite clusters in the A. pullulans NBB 7.2.1 genome with the fungal antiSMASH v.5.1.2 online tool [41][42]. Core biosynthetic genes of three A. pullulans NBB 7.2.1 secondary metabolite clusters were upregulated in response to co-cultuvation with F. oxysporum NRRL 26381/CL57. The core biosynthetic genes (dark red colour) of cluster 5 (NRPS and polyketide synthase cluster) (A), 7 (terpene cluster) (B), and 18 (NRPS cluster) (C) were upregulated after one day of interaction with F. oxysporum NRRL 26381/CL57.
41. Blin K, Shaw S, Steinke K, Villebro R, Ziemert N, Lee SY, Medema MH, and Weber T (2019). antiSMASH 5.0: updates to the secondary metabolite genome mining pipeline. Nucleic Acids Res 47(W1): W81–W87. 10.1093/nar/gkz310
42. Medema MH, Blin K, Cimermancic P, de Jager V, Zakrzewski P, Fischbach MA, Weber T, Takano E, and Breitling R (2011). antiSMASH: rapid identification, annotation and analysis of secondary metabolite biosynthesis gene clusters in bacterial and fungal genome sequences. Nucleic Acids Res 39: W339–W346. 10.1093/nar/gkr466