Back to article: Infinity war: Trichomonas vaginalis and interactions with host immune response
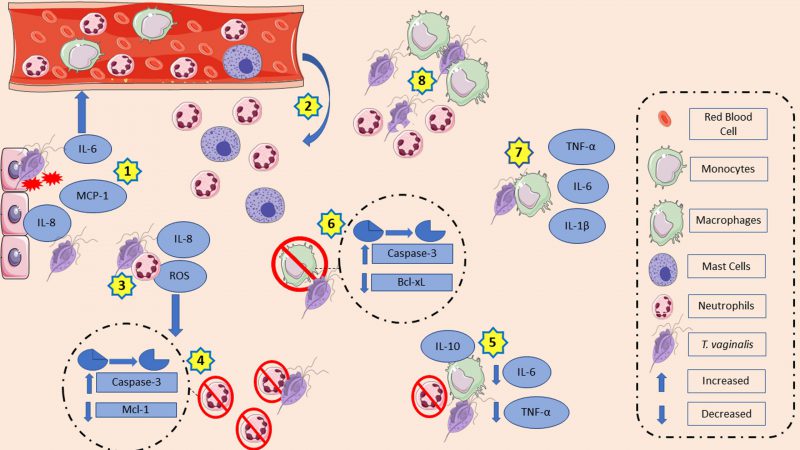
FIGURE 1: T. vaginalis and the interaction with host immune cells. T. vaginalis stimulates vaginal, ectocervical, and endocervical epithelial cells to release IL-6, MCP-1 and IL-8 (1), resulting in the migration of mast cells and neutrophils to the site of infection (2). There, neutrophils in contact with trichomonads release IL-8 and ROS (3), which activate caspase-3 and decrease Mcl-1, an anti-apoptotic protein (4). Macrophages in contact with neutrophils killed by parasite-induced apoptosis decrease IL-6 and TNF-α and increase IL-10 (5). The interaction between macrophages and T. vaginalis can lead to their apoptosis by caspase-3 activation and downregulation of Bcl-xL (6) or can result in the release of TNF-α, IL-6, and IL-1β (7). Finally, monocytes can kill the protozoan through extracellular traps, while neutrophils use a mechanism known as trogocytosis (8).