Back to article: Extracellular DNA secreted in yeast cultures is metabolism-specific and inhibits cell proliferation
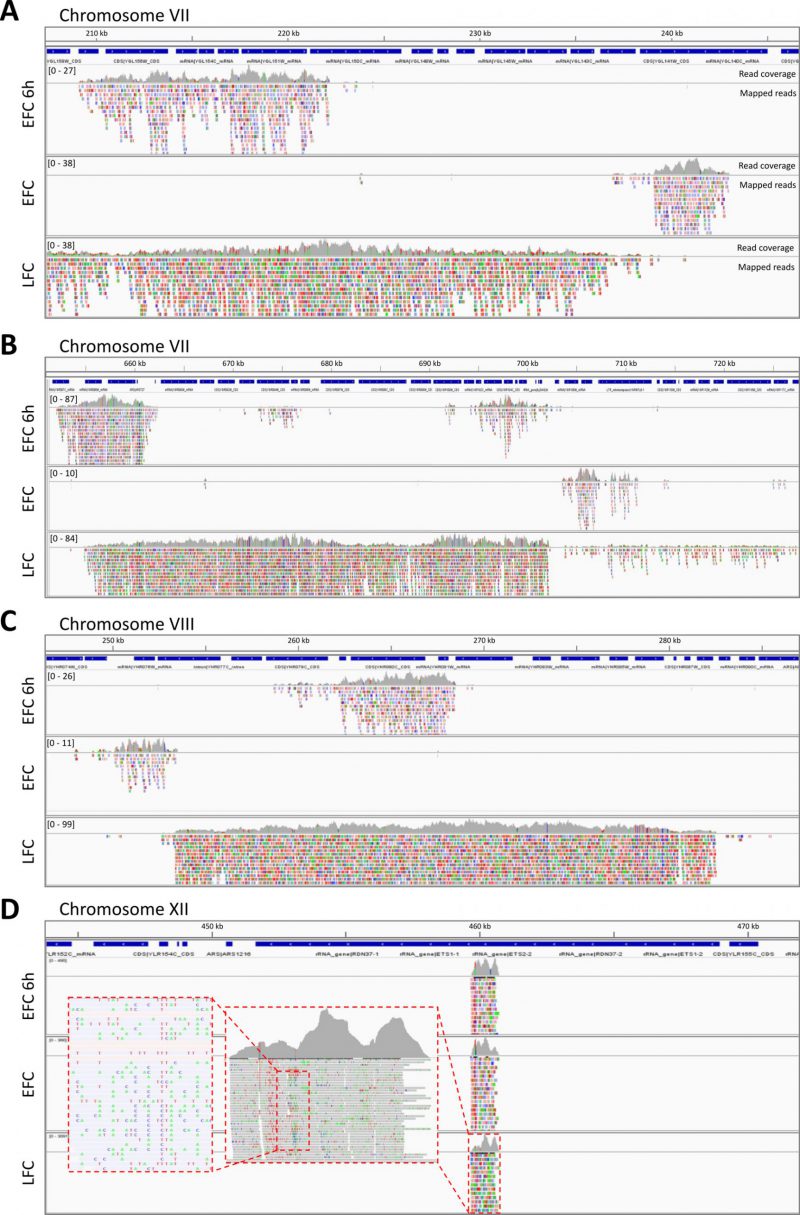
FIGURE 3: ExDNA sequencing from yeast culture media reveals specific differences associated to active metabolism. Examples of nucleotide reads mapped to the S288C S. cerevisiae reference genome. Shown are samples of sequenced exDNA collected from media of early respiratory EFC (EFC-6h), late fermentative EFC (EFC), and respiratory LFC (LFC). The reads are aligned on the corresponding parts of genomic regions of different chromosomes: chromosome VII (A, B), chromosome VIII (C), and chromosome XII (D). Blue bars refer to specific sequence features of the mapped regions. Grey histograms represent mapped reads coverage. Coloured boxes indicate individual reads nucleotide mismatches, with respect to the reference genome sequences. Magnification of a portion of chromosomes XII, showing the high degree of mismatch rate, is shown in the inset (D).