Back to article: Ribose 5-phosphate: the key metabolite bridging the metabolisms of nucleotides and amino acids during stringent response in Escherichia coli?
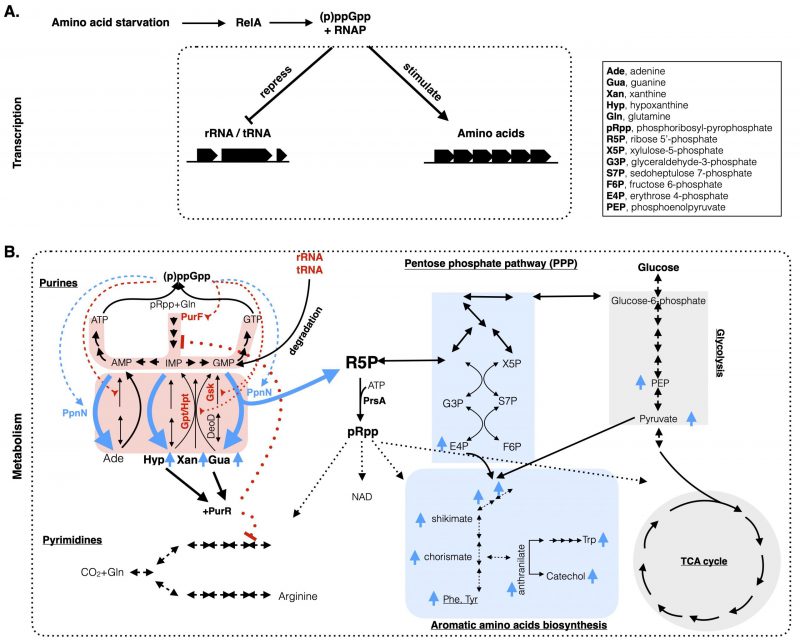
FIGURE 1: A comprehensive model integrating both the metabolic and transcriptional coordination of nucleotide and amino acid metabolisms upon stringent response in E. coli. (A) Amino acid starvation in E. coli leads to the activation of RelA to produce (p)ppGpp, which binds to the RNA polymerase (RNAP) to downregulate stable RNA (rRNA, tRNA) and upregulate amino acid biosynthesis genes at the transcriptional level. (B) At the metabolic level, (p)ppGpp directly inhibits (in red broken lines) the de novo and the salvage pathways (highlighted in red shadow) of purine nucleotides synthesis by targeting the PurF and Gpt/Hpt/Gsk proteins, respectively (in red font). Meanwhile, (p)ppGpp binds to PpnN (light blue font) and stimulates its activity (in blue broken lines) to degrade excess nucleotides, from both the redundant nucleotides and the degraded rRNAs/tRNAs. Degraded nucleotides lead to increased nucleobases (Gua, Xan, Hyp) (in blue up arrows) and R5P. The former ones bind to PurR to repress expression of genes (in red dotted lines) in the de novo purine and pyrimidine biosynthesis pathways. R5P, used to produce pRpp, enters the pentose phosphate pathway and culminates with the synthesis of (aromatic) amino acids and the intermediate metabolites. Metabolites highlighted with light blue up arrows are the ones that increased their concentrations upon amino acid starvation in the wild type E. coli, but not in the ΔppnN mutant strain [10]. The list of abbreviated metabolites is included in the inset.
10. Zhang YE, Baerentsen RL, Fuhrer T, Sauer U, Gerdes K, Brodersen DE (2019). (p)ppGpp Regulates a Bacterial Nucleosidase by an Allosteric Two-Domain Switch. Mol Cell 74(6): 1239-1249 e1234. 10.1016/j.molcel.2019.03.035