Back to article: The role of invariant surface glycoprotein 75 in xenobiotic acquisition by African trypanosomes
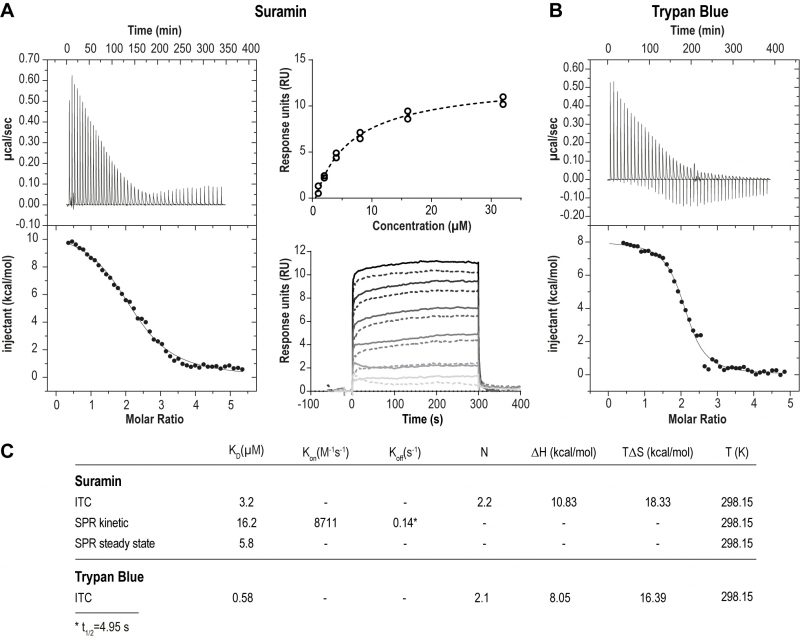
FIGURE 1: ISG75 binds suramin and trypan blue directly. (A) Left panel – Isothermal titration calorimetry of the interaction of suramin with ISG75. 400 µM suramin was titrated into 16 µM ISG75 solution within the calorimetric cell. The upper left panel shows the raw data of sequential suramin injections, the lower panel the integral after subtraction of the heat of suramin dilution (dots) together with the fit (line). Right panel – Surface plasmon resonance of the ISG75:suramin interaction. Avi-tagged ISG75, site-specifically biotinylated at the C-terminus was used as ligand and immobilised onto the CAPture sensor chip surface. Suramin was used as analyte and flowed over the chip at 1, 2, 4, 8, 16 and 32 µM. Data were reference-subtracted and fitted using steady state (upper right) and one-to-one kinetic analysis (lower right). For fitting, data points from two independent measurements (circles, upper panel; solid/dashed lines, lower panel) were used. (B) Isothermal titration calorimetry of the interaction of trypan blue with ISG75. 500 µM trypan blue was titrated into 16 µM ISG75 solution within the calorimetric cell. The upper left panel shows the raw data of sequential trypan blue injections, the lower panel the integrated heats after subtraction of the heat of trypan blue dilution (dots) together with the fit (line). (C) Kinetic and thermodynamic parameters of the ISG75:suramin and ISG75:trypan blue interaction. KD, dissociation constant; Kon, association rate; Koff, dissociation rate; N, stoichiometry; ΔH, change in enthalpy; ΔS, change in entropy; T, temperature in Kelvin; t1/2=complex half-life time.