Back to article: The metabolites of lactic acid bacteria: classification, biosynthesis and modulation of gut microbiota
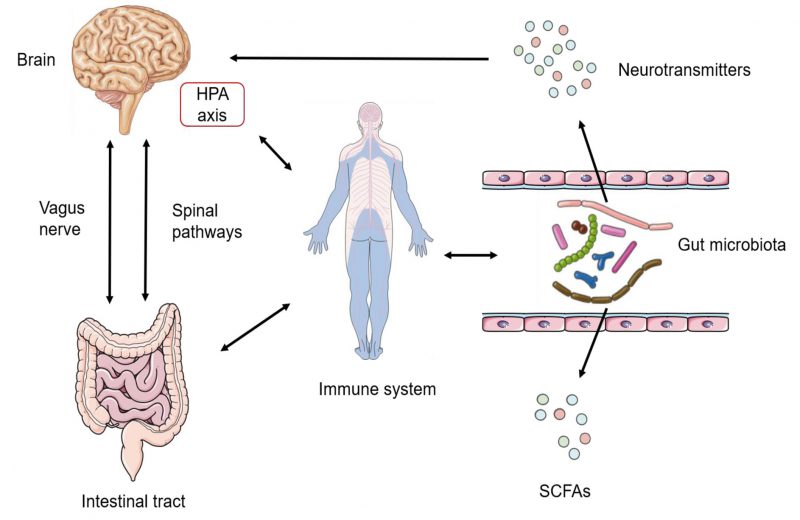
FIGURE 2: Routes of communication in the gut-brain-axis (GBA). The Gut microbiota is one of the key regulators of gut-brain function. Communication within the occurs through these three ways: the immune pathway, the neuroendocrine pathway (neurotransmitters), and the vagus pathway, involving microbial metabolites such as SCFAs. LAB maintain homeostasis and affect host behaviors via the microbiota–gut–brain axis. HPA, hypothalamic–pituitary–adrenal axis, is central to homeostasis, stress responses, energy metabolism, and neuropsychiatric function.