Back to article: Understanding the molecular mechanisms of human diseases: the benefits of fission yeasts
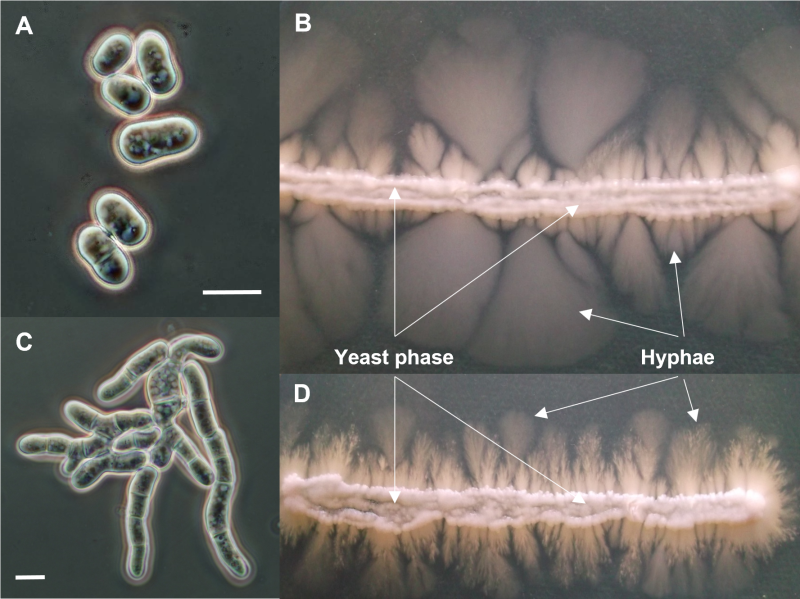
FIGURE 4: Microscopic and macroscopic morphologies of different Schizosaccharomyces japonicus strains. Microscopic morphology of the wild-type S. japonicus cells (A) and colony morphology of the yeast phase and hyphae on agar plate (indicated with white arrows and labels) (B). Cell morphology of a yet unidentified cell separation mutant strain (C) and its yeast phase and hyphae production (D). Cell sizes in (A) and (C) are not to scale, the images concentrate on the cell morphology. Scale bars represent 10 µm. Microscopic images were captured with an Olympus DX-40 microscope and an Olympus DP-70 camera. Photos were taken in different focal planes and stacked with the program Combine ZP.