Back to article: Polyadenylated versions of small non-coding RNAs in Saccharomyces cerevisiae are degraded by Rrp6p/Rrp47p independent of the core nuclear exosome
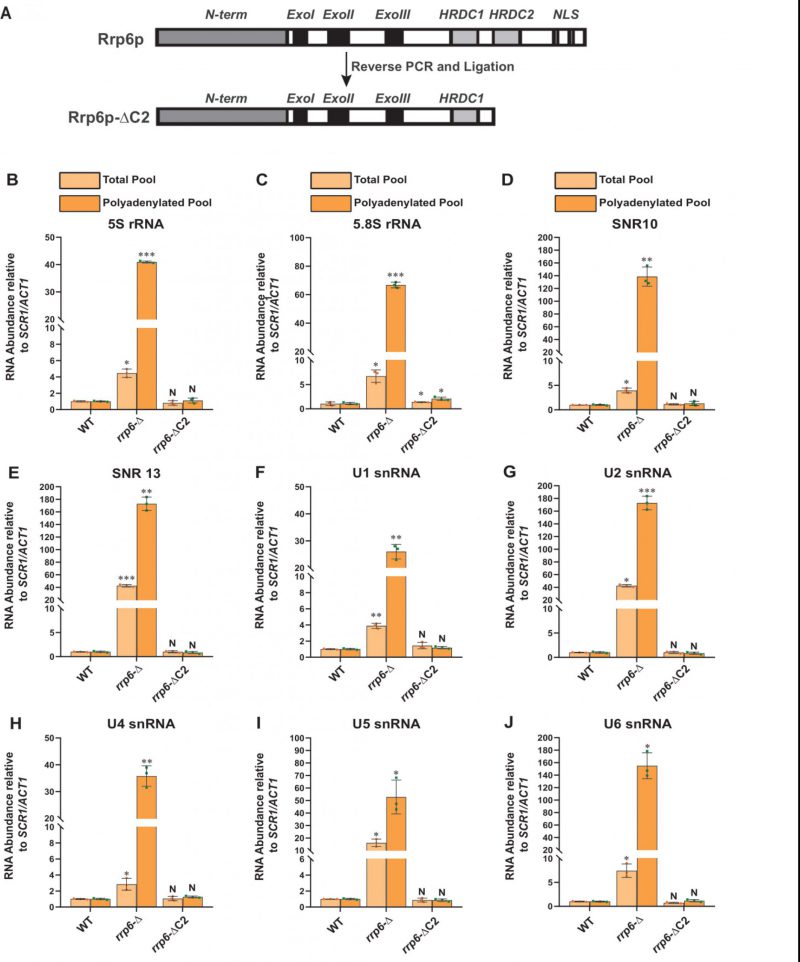
FIGURE 4: A truncated version of Rrp6p consisting of a deletion of the C-terminal domain that abolishes its interaction with the core exosome is equally competent in maintaining the steady-state levels of the polyadenylated version of mature populations of all sncRNAs like its native full-length counterpart. (A) Cartoon showing the various functional domains of native full-length Rrp6p and Rrp6p-ΔC2 lacking its entire C-terminal domain. (B-J) Scattered/Bar plots revealing the steady-state levels of various low molecular weight ncRNAs estimated from the 2 ng cDNA samples prepared using random hexanucleotide primers (pale yellow histograms) or oligo-dT30 anchor primer (dark yellow histograms) by RT-qPCR from the WT strain (yBD-117), yeast strains carrying either a complete deletion of RRP6 (rrp6-Δ; yBD-129) or a deletion of its C-terminal domain (rrp6-ΔC2: yBD-527). SCR1 (in the case of RT-qPCR assays using random primer) and ACT1 mRNA (in the case of RT-qPCR assays using oligo dT30 primer) were used as the internal loading control. Normalized values of each of the ncRNAs in the WT yeast strain were set to 1. Three independent cDNA preparations (biological replicates, n = 3) were used to determine the levels of various ncRNAs. The statistical significance of difference reflected in the ranges of P values estimated from Student’s two-tailed t-tests for a given pair of test strains for every message are presented with the following symbols, *<0.05, **<0.005, and ***<0.001; N, not significant.