Back to article: Fat storage-inducing transmembrane (FIT or FITM) proteins are related to lipid phosphatase/phosphotransferase enzymes
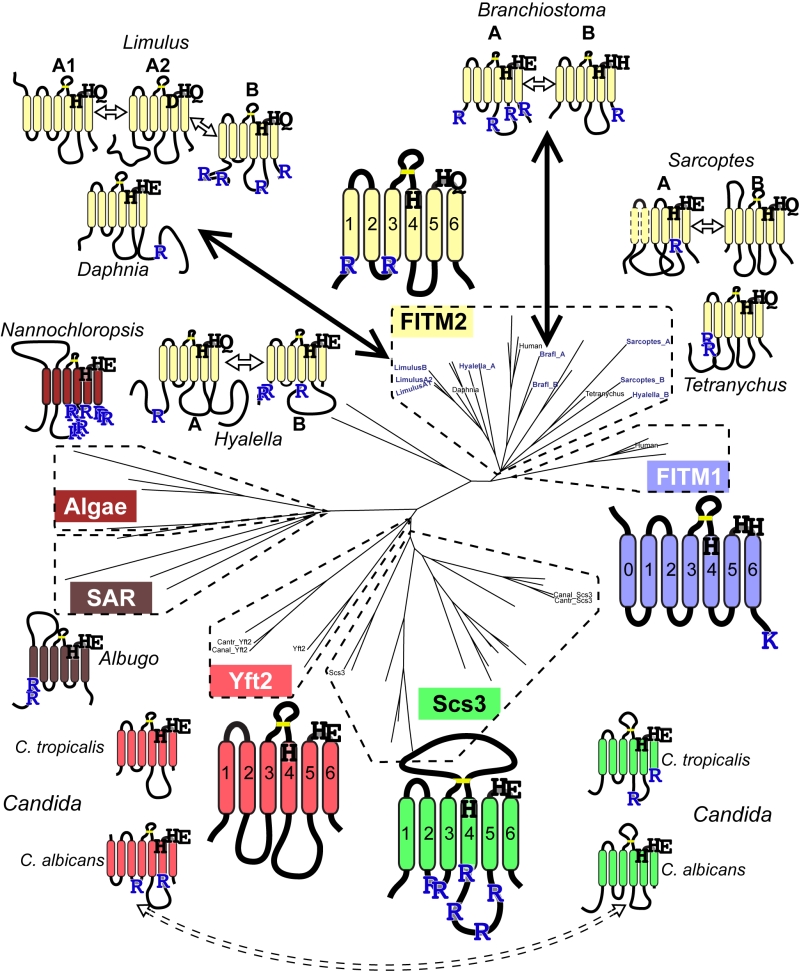
FIGURE 6: Catalytic triad residues and di-arginine motifs diverge at multiple duplications across FITM evolution. Sequence features of main FITMs and those in recent divergent duplications. Examples from the major groups of FITMs (FITM1 in vertebrates, FITM2 in animals, Yft2p and Scs3p in fungi) and from the two groups of FITMs in protists and algae are shown to indicate the residues that align with the catalytic triad in LPTs and their ER retention motifs (R = diarginine, K = KK(x)xx). Also shown are the recently duplicated sequences and their closest related sequences, as described in the text, colour coded to indicate what group of FITMs they belong to. Other features indicated: size of loops between TMDs, disulphide bridge predicted for loop 3/4 (yellow bar), and the position of each protein on the overall tree of FITMs (see Figure S2). Sequences from Candida species C. tropicalis and C. albicans show high levels of conservation, but the di-arginine motifs are swapped (see Discussion).