Back to article: Mutational analysis of fructose-1,6-bis-phosphatase FBP1 indicates partially independent functions in gluconeogenesis and sensitivity to genotoxic stress
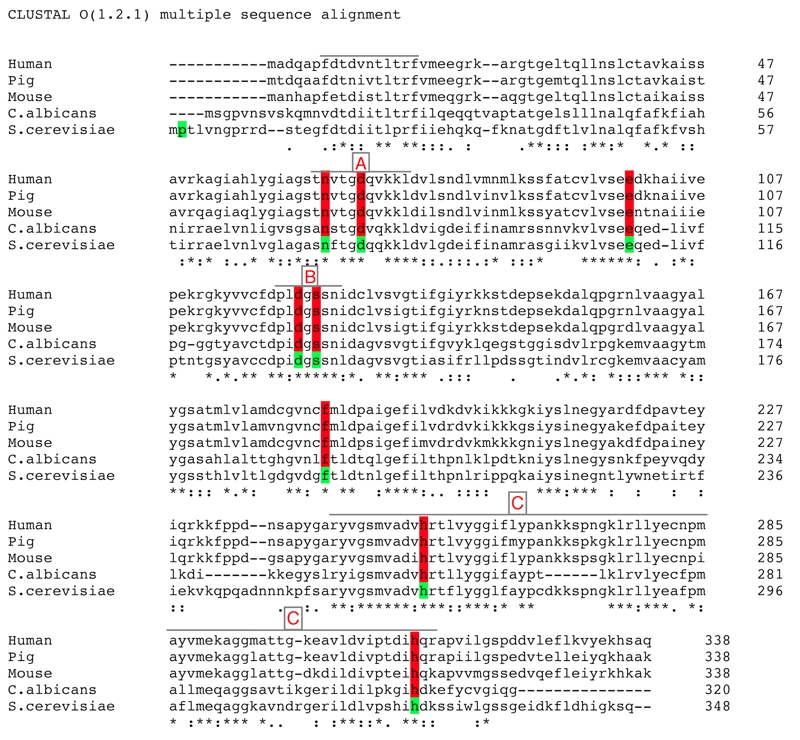
FIGURE 1: Multiple global-alignment of FBP1 amino-acid sequences of Saccharomyces cerevisiae and several species using the online-available ClustalW2 multiple sequence alignment tool, provided by EMBL-EBI.
Identical residues are marked with (|) ; similarities (:) and totally different ones with (.). Residues included in the mutational analysis are highlighted. Three regions (a, b and c) of sequence homology are indicated: (A) representing the mostly conserved part of the regulatory loop, (B) the conserved metal binding site, and (C) the largest homology domain on the c-terminus containing the active site.