Back to article: Shutdown of interferon signaling by a viral-hijacked E3 ubiquitin ligase
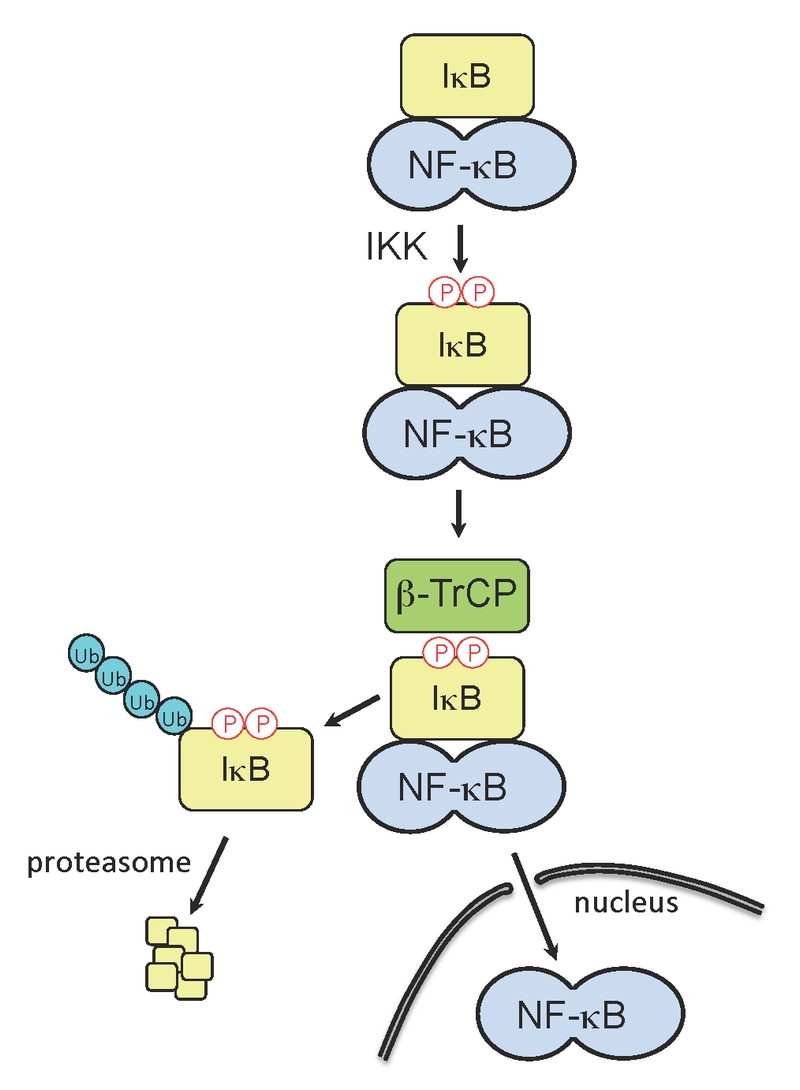
FIGURE 1: Activation of NF-κB. Upon detection of RNA-virus infection by the host cell, signaling cascades are induced which can trigger IFN expression and the establishment of an antiviral state. The inducible IκB kinase (IKK) plays critical role in IFN signaling cascades, as its activity is responsible for phosphorylation of the IκB degron. The phosphorylated IκB degron is recognized by β-TrCP, a substrate-specific adaptor of an E3 ubiquitin ligase complex, SCFβTrCP, leading to IκB ubiquitination and degradation. IκB degradation releases NF-κB, allowing the transcription factor to translocate to the nucleus and upregulate IFN genes.