Back to article: Specific mutations in the permease domain of septal protein SepJ differentially affect functions related to multicellularity in the filamentous cyanobacterium Anabaena
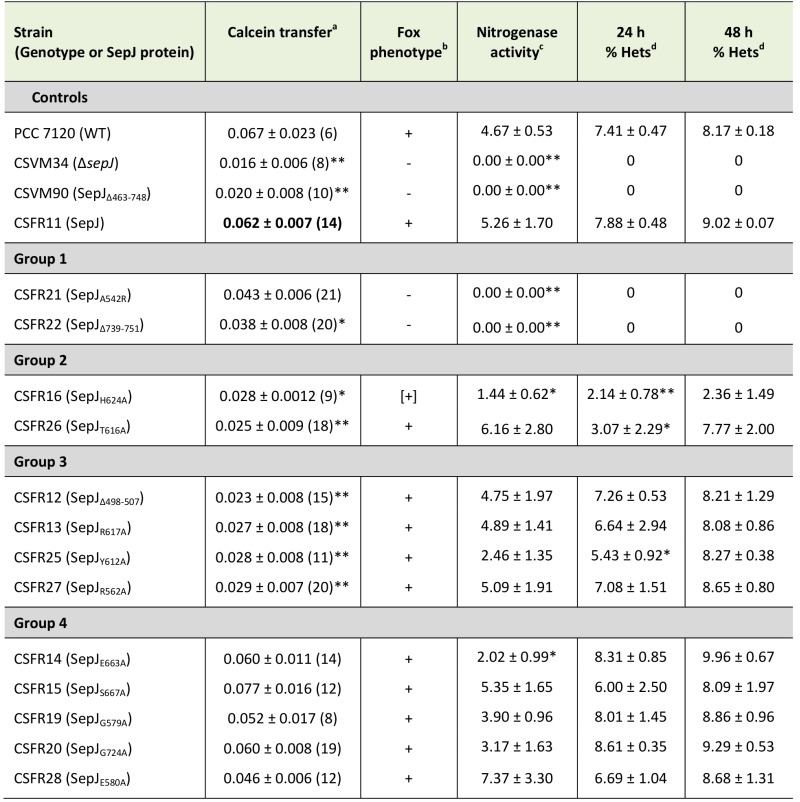
TABLE 1. Calcein transfer, Fox phenotype, nitrogenase activity and heterocysts in sepJ mutant strains.
a Intercellular transfer of calcein was determined by FRAP analysis performed with filaments that had been grown in BG11 medium (supplemented with antibiotics for the CSFR mutants). Data presented as the recovery constant R (s-1), mean ± SEM of 12-29 filaments from 3 independent cultures. The difference between each strain and the complemented CSFR11 mutant (used for reference) was assessed with the Student’s t test (*, p < 0.05; **, p < 0.01).
b Fox phenotype (growth on solid BG110 medium as shown in Fig. 5): +, positive; -, negative; [+], weak positive.
c Nitrogenase activity was determined as acetylene reduction in assays performed under oxic conditions with filaments that had been grown in BG11 medium (with antibiotics for the CSFR mutants) and incubated in BG110 medium (without antibiotics) for 48 h. Data presented as μmol (mg Chl)-1 h-1, mean ± SEM of 2 (for strains which do not develop heterocysts), 3 or 4 (for CSFR11) independent cultures. The significance of the difference between mutant and strain CSFR11 assessed with the Student’s t test (*, p ≤ 0.05; **, p < 0.01).
d Heterocysts were visualized in filaments grown in BG11 medium (with antibiotics for the CSFR mutants) and incubated in BG110 medium without antibiotics for 24 or 48 h, as indicated. The percentage of hetero-cysts was determined for each of three independent cultures. When present, at least 100 heterocysts from each culture were counted. Data are mean ± SD (n =3). The significance of the difference between each mutant and strain CSFR11 was assessed with the Student’s t test (*, p ≤ 0.05; **, p < 0.01).