Back to article: Sulfur transfer and activation by ubiquitin-like modifier system Uba4•Urm1 link protein urmylation and tRNA thiolation in yeast
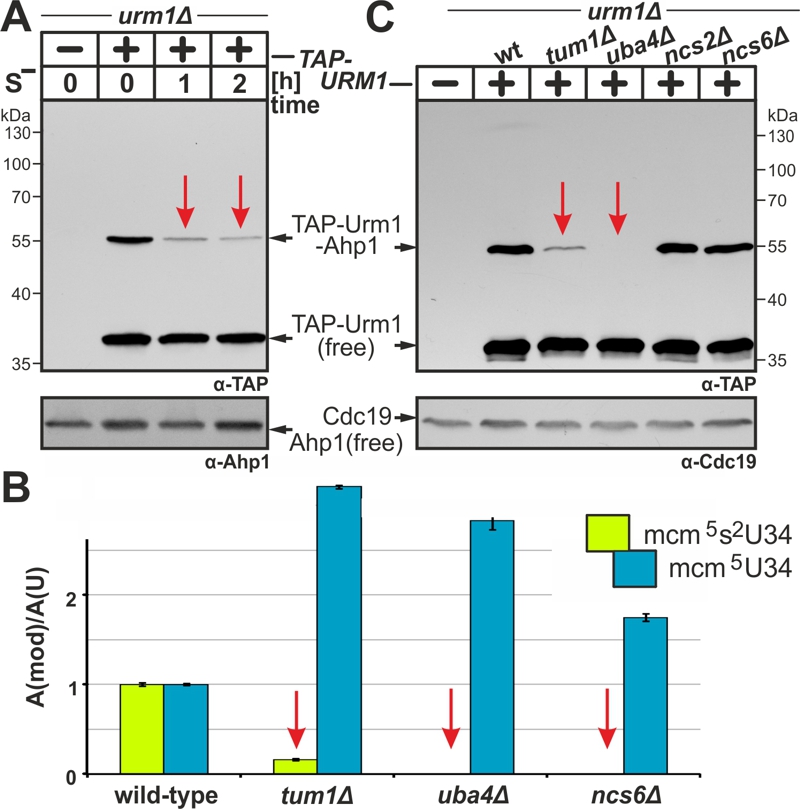
FIGURE 3: Sulfur supply, transfer and activation are critical for the tRNA thiolation and urmylation branches of the URM1 pathway.
(A) Urmylation is sulfur sensitive. TAP-URM1 expressing cells (see Fig. 2) were grown in Met containing media prior to S-starvation (S–) for two hours (h) in media without Met. Analysis of Ahp1 urmylation was as described (see Fig. 2).
(B) LC-MS/MS-based tRNA (thio)modification analysis of modified U34 nucleoside content in tRNAs from wild-type and indicated URM1 pathway mutants. In each case, the modified nucleoside signal was normalized using total uridine content to allow comparison of the different samples. Inset: mcm5 (blue) and mcm5s2 (green) modifications at U34.
(C) Urmylation of Ahp1 is normal in thiolase-minus (ncs2∆, ncs6∆) cells but drastically reduced in the absence of S-transferase Tum1 (tum1∆). Protein extracts from TAP-URM1 expressors of the indicated backgrounds (i.e. wild-type (wt) and URM1 pathway mutants) were subjected to Ahp1 urmylation assays as described (see Fig. 2). Non-conjugated (free) forms of TAP-Urm1 and Ahp1 as well as TAP-Urm1 conjugated to Ahp1 and loading control Cdc19 are indicated by arrows (A, C).