Back to article: The copper transport-associated protein Ctr4 can form prion-like epigenetic determinants in Schizosaccharomyces pombe
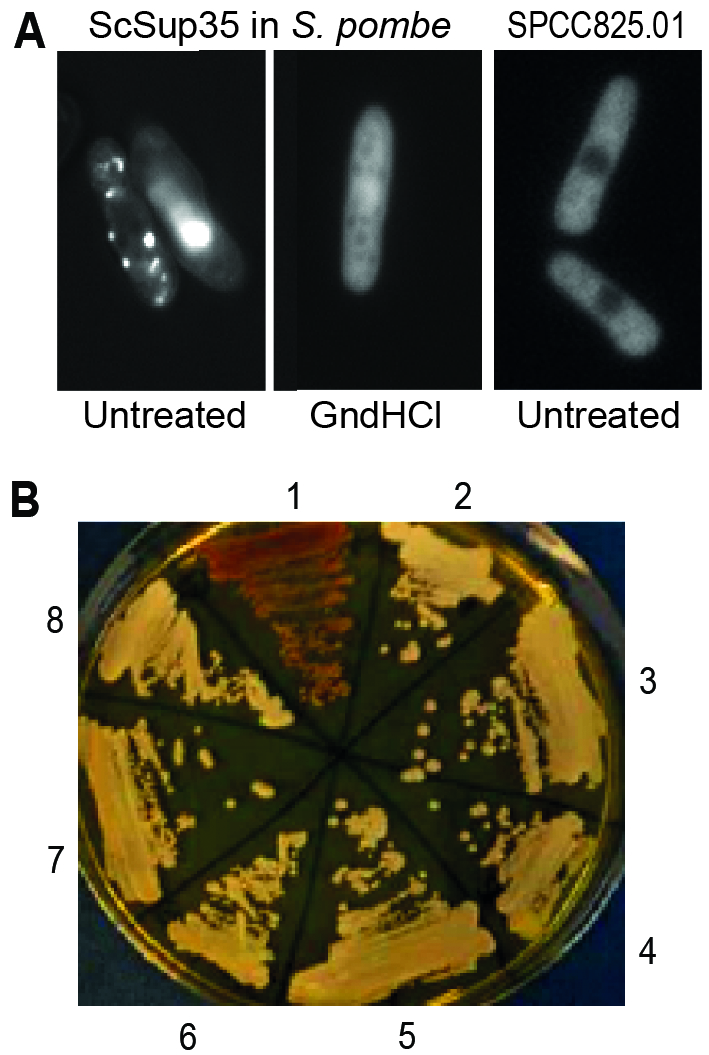
FIGURE 1: Fission yeast can support formation and propagation of the budding yeast [PSI+] prion.
(A) Left: Fluorescent foci in S. pombe resulting from overexpression of S. cerevisiae Sup35-GFP, using the medium-strength, regulatable nmt41 promoter under activating conditions from a high-copy plasmid. This result resembles the patterns seen when ScSup35-GFP is overexpressed from a high-copy plasmid in S. cerevisiae [47]. Middle: The foci are absent from cells grown for 35-40 generations in 3 mM guanidine hydrochloride (GndHCl). Right: Most GFP-tagged S. pombe proteins do not show fluorescent foci when overexpressed (see also [54]); the uncharacterized protein SPCC825.01(predicted ATPase) serves as an example for such a negative control, showing diffuse cytoplasmic localization.
(B) Transformation of S. pombe cell extract containing ScSup35-GFP aggregates can convert S. cerevisiae [psi–] cells (red, streak 1) to [PSI+] cells (white, streaks 2-4 and 6-8). Streaks 1 and 5 show control [psi–] and [PSI+] strains, respectively.
47. Zhou P, Derkatch IL, Liebman SW (2001). The relationship between visible intracellular aggregates that appear after overexpression of Sup35 and the yeast prion-like elements [PSI(+)] and [PIN(+)]. Mol Microbiol 39(1): 37-46. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/?term=11123686
54. Matsuyama A, Arai R, Yashiroda Y, Shirai A, Kamata A, Sekido S, Kobayashi Y, Hashimoto A, Hamamoto M, Hiraoka Y, Horinouchi S, Yoshida M (2006). ORFeome cloning and global analysis of protein localization in the fission yeast Schizosaccharomyces pombe. Nat Biotechnol 24(7): 841-847. https://doi.org/10.1038/nbt1222