Back to article: The interplay between transcription and mRNA degradation in Saccharomyces cerevisiae
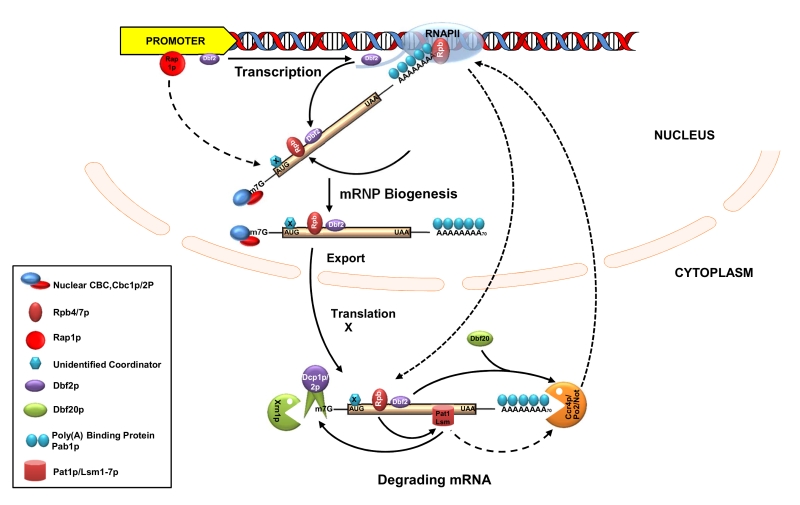
FIGURE 3: The interplay between the transcription and mRNA degradation in S. cere-visiae. Schematic diagram showing the functional coupling between the mRNA synthesis and degradation. Functional cou-pling is achieved by marking of the transcribing and maturing messages by various coordinators either through the Rpb1-CTD of RNAPII in a transcription-dependent manner (such as those of Rpb4/7p and Dbf2p) or in a transcription factor (Rap1p)/promoter-dependent manner (such as that of a hitherto unidentified coordinator(s), coded X). The effect of various elements on the recruitment of diverse coordinators is indicated either by the solid (demonstrated) of dashed (postulated) arrow. Export-competent mRNPs undergo translation after arriving in the cytoplasm and are subsequently degraded via the general default decay pathway. During this stage, the Rpb4/7p dependent recruitment of Pat1/Lsm1-7p and influence of Dbf2p together with Dbf20 on the CCR4/NOT complex to further stimulate decay via the activation of other decay components are indicated by the solid arrow. Note that the demonstrated influence of Pat1/Lsm1-7p on the decapping complex is shown by the solid arrow, whereas its potential but questionable impact on CCR4/NOT is indicated by a dashed arrow. Mutual influence of each process on the other is indicated by dashed arrows. Only relevant components are shown by annotated symbols. Other proteins which remain associated to translating/degrading mRNAs (such as eIF4E) during translation and decay are not shown.