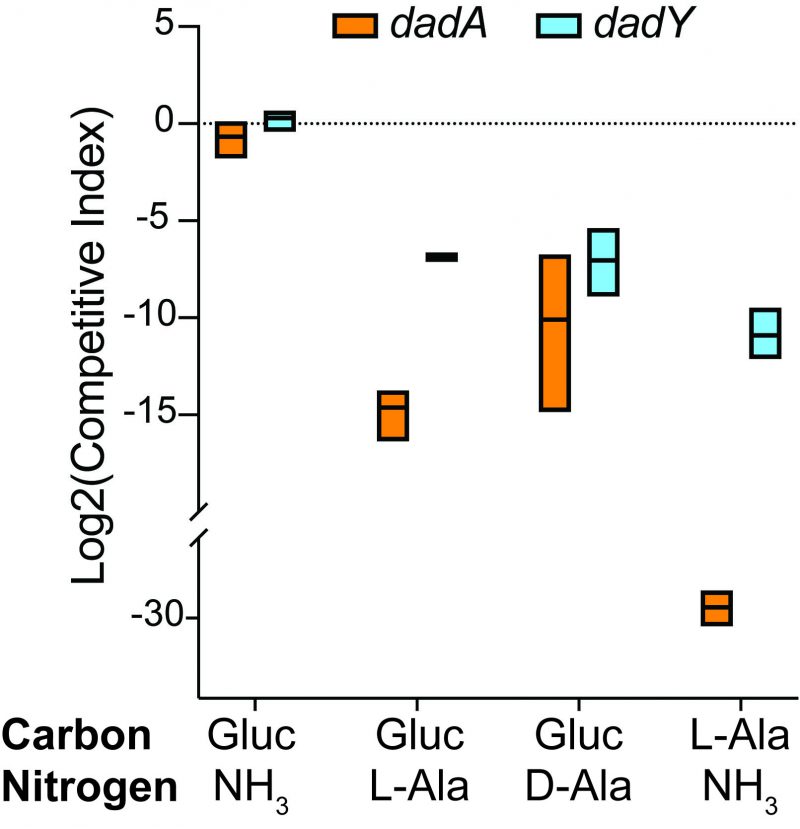
FIGURE 5: dadA and dadY mutants are outcompeted by wild-type when alanine catabolism is required. Cells of mutant strain DMPA39 (dadA GmR, orange) or DMPA40 (dadY GmR, blue) were combined with an equal number of DMPA4 (wild-type) cells (final OD650 = 0.02) in minimal media with the indicated sources of carbon (11 mM glucose or 20 mM Ala) and nitrogen (10 mM ammonia or 5 mM Ala). Co-cultures were grown to stationary phase at 37°C with shaking. Colony forming units (CFU) were determined by serial dilution and spot plating onto LB Gm30 (dadA or dadY mutants) and LB without drug (total cells) at the onset of the experiment, and after cultures reached stationary phase. The number of wild-type cells was determined by subtracting the number of each mutant from the total number of cells. The Competitive Index (CI) was calculated as the ratio of mutant to wild-type P. aeruginosa after co-incubation, divided by the ratio of mutant to wild-type in the inoculum. Data shown are mean and standard deviation of three independent biological replicates. Experiments were performed three times with similar results.
By continuing to use the site, you agree to the use of cookies. more information
The cookie settings on this website are set to "allow cookies" to give you the best browsing experience possible. If you continue to use this website without changing your cookie settings or you click "Accept" below then you are consenting to this. Please refer to our "privacy statement" and our "terms of use" for further information.