Back to article: pH homeostasis links the nutrient sensing PKA/TORC1/Sch9 ménage-à-trois to stress tolerance and longevity
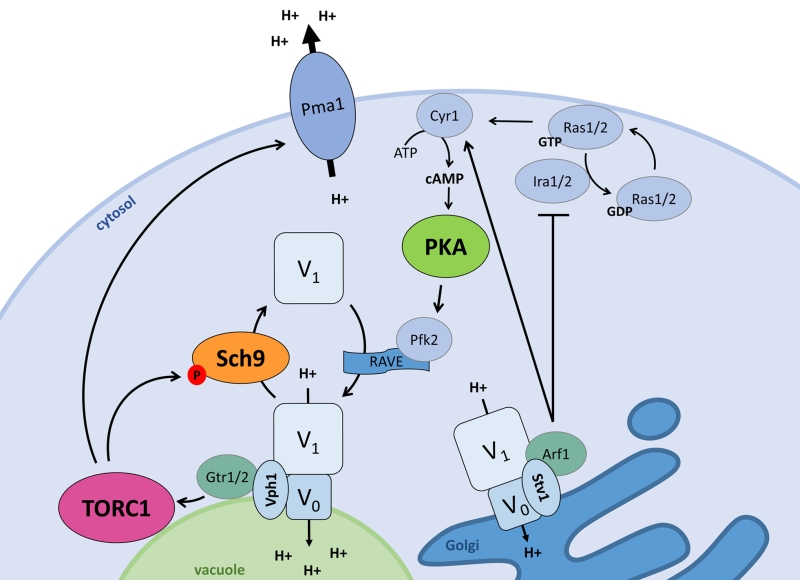
FIGURE 2: The interplay between signalling and pH control. Pma1 and the V-ATPase, the two main players in pH control, both impact and are regulated by the ménage-à-trois. When stimulated by glucose or cytosolic protons, the vacuolar Vph1-containing V-ATPase stimulates TORC1 via the EGOC-components Gtr1/2. The Golgi-specific Stv1-containing V-ATPase stimulates PKA via Ira1/2 inhibition by Arf1, pushing Ras1/2 towards the GTP-bound state and in turn activating Cyr1 to produce cAMP. Active TORC1 and PKA each regulate the vacuolar V-ATPase assembly state. TORC1 stimulates disassembly via Sch9, while PKA aids V-ATPase assembly presumably via Pfk2 which impacts on the V-ATPase scaffolding complex RAVE. Additionally, the vacuolar V-ATPase subunit Vph1 acts as a proton sensor to induce V-ATPase activity, and this may also be the case for the Stv1-containing V-ATPase. Additionally, active TORC1 also stimulates Pma1 activity.