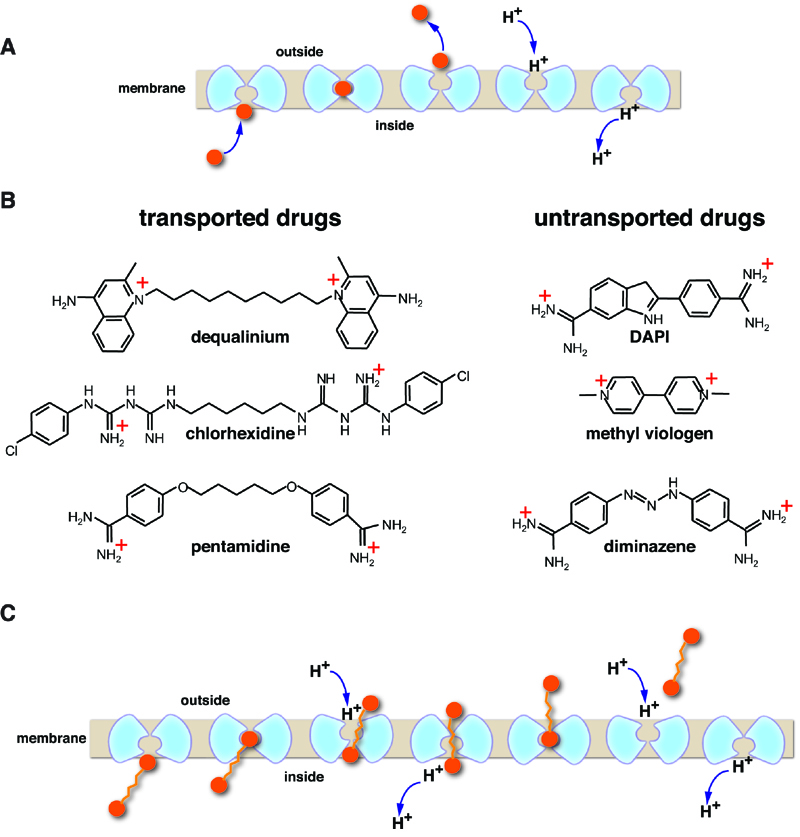
FIGURE 1:
(A) General mechanism for H+-coupled solute antiport. Note that most transporters have an internal 2-fold symmetry axis and a monomeric transporter is represented here by two symmetrical parts, shown in light blue. The substrate is indicated by orange sphere. The occluded state is second from the left.
(B) Chemical structure of divalent cationic drugs that are transported or untransported by MdfA.
(C) Illustration of the suggested processive antiport mechanism.