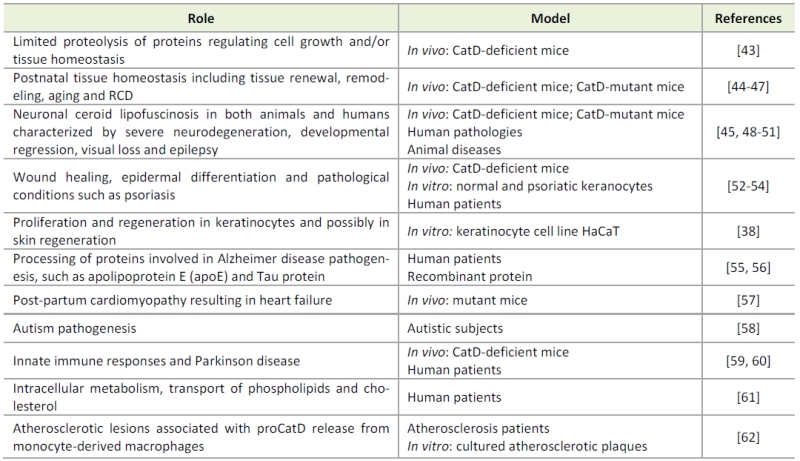
TABLE 1. Cellular roles of cathepsin D in physiological and pathological processes.
38. Vashishta A, Saraswat Ohri S, Vetvickova J, Fusek M, Ulrichova J, and Vetvicka V (2007). Procathepsin D secreted by HaCaT keratinocyte cells – A novel regulator of keratinocyte growth. Eur J Cell Biol 86(6): 303–313. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.ejcb.2007.03.008
43. Saftig P, Hetman M, Schmahl W, Weber K, Heine L, Mossmann H, Köster A, Hess B, Evers M, and von Figura K (1995). Mice deficient for the lysosomal proteinase cathepsin D exhibit progressive atrophy of the intestinal mucosa and profound destruction of lymphoid cells. EMBO J 14(15): 3599–3608. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/?term=7641679
44. Koike M, Shibata M, Ohsawa Y, Nakanishi H, Koga T, Kametaka S, Waguri S, Momoi T, Kominami E, Peters C, Figura K von, Saftig P, and Uchiyama Y (2003). Involvement of two different cell death pathways in retinal atrophy of cathepsin D-deficient mice. Mol Cell Neurosci 22(2): 146–161. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/s1044-7431(03)00035-6
45. Koike M, Nakanishi H, Saftig P, Ezaki J, Isahara K, Ohsawa Y, Schulz-Schaeffer W, Watanabe T, Waguri S, Kametaka S, Shibata M, Yamamoto K, Kominami E, Peters C, von Figura K, and Uchiyama Y (2000). Cathepsin D deficiency induces lysosomal storage with ceroid lipofuscin in mouse CNS neurons. J Neurosci Off J Soc Neurosci 20(18): 6898–6906. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/s0168-0102(00)81020-2
46. Koike M, Shibata M, Waguri S, Yoshimura K, Tanida I, Kominami E, Gotow T, Peters C, von Figura K, Mizushima N, Saftig P, and Uchiyama Y (2005). Participation of autophagy in storage of lysosomes in neurons from mouse models of neuronal ceroid-lipofuscinoses (Batten disease). Am J Pathol 167(6): 1713–1728. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/S0002-9440(10)61253-9
47. Zhang D, Brankov M, Makhija MT, Robertson T, Helmerhorst E, Papadimitriou JM, and Rakoczy PE (2005). Correlation between inactive cathepsin D expression and retinal changes in mcd2/mcd2 transgenic mice. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 46(9): 3031–3038. http://dx.doi.org/10.1167/iovs.04-1510
48. Steinfeld R, Reinhardt K, Schreiber K, Hillebrand M, Kraetzner R, Bruck W, Saftig P, and Gartner J (2006). Cathepsin D deficiency is associated with a human neurodegenerative disorder. Am J Hum Genet 78(6): 988–998. http://dx.doi.org/10.1086/504159
49. Siintola E, Partanen S, Strömme P, Haapanen A, Haltia M, Maehlen J, Lehesjoki A-E, and Tyynelä J (2006). Cathepsin D deficiency underlies congenital human neuronal ceroid-lipofuscinosis. Brain J Neurol 129(Pt 6): 1438–1445. http://dx.doi.org/10.1093/brain/awl107
50. Tyynelä J, Sohar I, Sleat DE, Gin RM, Donnelly RJ, Baumann M, Haltia M, and Lobel P (2001). Congenital ovine neuronal ceroid lipofuscinosis–a cathepsin D deficiency with increased levels of the inactive enzyme. Eur J Paediatr Neurol EJPN Off J Eur Paediatr Neurol Soc 5 Suppl A: 43–45. http://dx.doi.org/10.1053/ejpn.2000.0433
51. Awano T, Katz ML, O’Brien DP, Taylor JF, Evans J, Khan S, Sohar I, Lobel P, and Johnson GS (2006). A mutation in the cathepsin D gene (CTSD) in American Bulldogs with neuronal ceroid lipofuscinosis. Mol Genet Metab 87(4): 341–348. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.ymgme.2005.11.005
52. Egberts F, Heinrich M, Jensen J-M, Winoto-Morbach S, Pfeiffer S, Wickel M, Schunck M, Steude J, Saftig P, Proksch E, and Schütze S (2004). Cathepsin D is involved in the regulation of transglutaminase 1 and epidermal differentiation. J Cell Sci 117(Pt 11): 2295–2307. http://dx.doi.org/10.1242/jcs.01075
53. Chen SH, Arany I, Apisarnthanarax N, Rajaraman S, Tyring SK, Horikoshi T, Brysk H, and Brysk MM (2000). Response of keratinocytes from normal and psoriatic epidermis to interferon-gamma differs in the expression of zinc-alpha(2)-glycoprotein and cathepsin D. FASEB J Off Publ Fed Am Soc Exp Biol 14(3): 565–571. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/?term=10698972
54. Kawada A, Hara K, Kominami E, Hiruma M, Noguchi H, and Ishibashi A (1997). Processing of cathepsins L, B and D in psoriatic epidermis. Arch Dermatol Res 289(2): 87–93. http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s004030050160
55. Zhou W, Scott SA, Shelton SB, and Crutcher KA (2006). Cathepsin D-mediated proteolysis of apolipoprotein E: possible role in Alzheimer’s disease. Neuroscience 143(3): 689–701. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroscience.2006.08.019
56. Kenessey A, Nacharaju P, Ko LW, and Yen SH (1997). Degradation of tau by lysosomal enzyme cathepsin D: implication for Alzheimer neurofibrillary degeneration. J Neurochem 69(5): 2026–2038. http://dx.doi.org/10.1046/j.1471-4159.1997.69052026.x
57. Hilfiker-Kleiner D, Kaminski K, Podewski E, Bonda T, Schaefer A, Sliwa K, Forster O, Quint A, Landmesser U, Doerries C, Luchtefeld M, Poli V, Schneider MD, Balligand J-L, Desjardins F, Ansari A, Struman I, Nguyen NQN, Zschemisch NH, Klein G, Heusch G, Schulz R, Hilfiker A, and Drexler H (2007). A cathepsin D-cleaved 16 kDa form of prolactin mediates postpartum cardiomyopathy. Cell 128(3): 589–600. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2006.12.036
58. Sheikh AM, Li X, Wen G, Tauqeer Z, Brown WT, and Malik M (2010). Cathepsin D and apoptosis related proteins are elevated in the brain of autistic subjects. Neuroscience 165(2): 363–370. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroscience.2009.10.035
59. Conus S, Perozzo R, Reinheckel T, Peters C, Scapozza L, Yousefi S, and Simon H-U (2008). Caspase-8 is activated by cathepsin D initiating neutrophil apoptosis during the resolution of inflammation. J Exp Med 205(3): 685–698. http://dx.doi.org/10.1084/jem.20072152
60. Cullen V, Lindfors M, Ng J, Paetau A, Swinton E, Kolodziej P, Boston H, Saftig P, Woulfe J, Feany MB, Myllykangas L, Schlossmacher MG, and Tyynelä J (2009). Cathepsin D expression level affects alpha-synuclein processing, aggregation, and toxicity in vivo. Mol Brain 2: 5. http://dx.doi.org/10.1186/1756-6606-2-5
61. Haidar B, Kiss RS, Sarov-Blat L, Brunet R, Harder C, McPherson R, and Marcel YL (2006). Cathepsin D, a lysosomal protease, regulates ABCA1-mediated lipid efflux. J Biol Chem 281(52): 39971–39981. http://dx.doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M605095200
62. Durán MC, Martín-Ventura JL, Mohammed S, Barderas MG, Blanco-Colio LM, Mas S, Moral V, Ortega L, Tuñón J, Jensen ON, Vivanco F, and Egido J (2007). Atorvastatin modulates the profile of proteins released by human atherosclerotic plaques. Eur J Pharmacol 562(1-2): 119–129. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.ejphar.2007.01.077