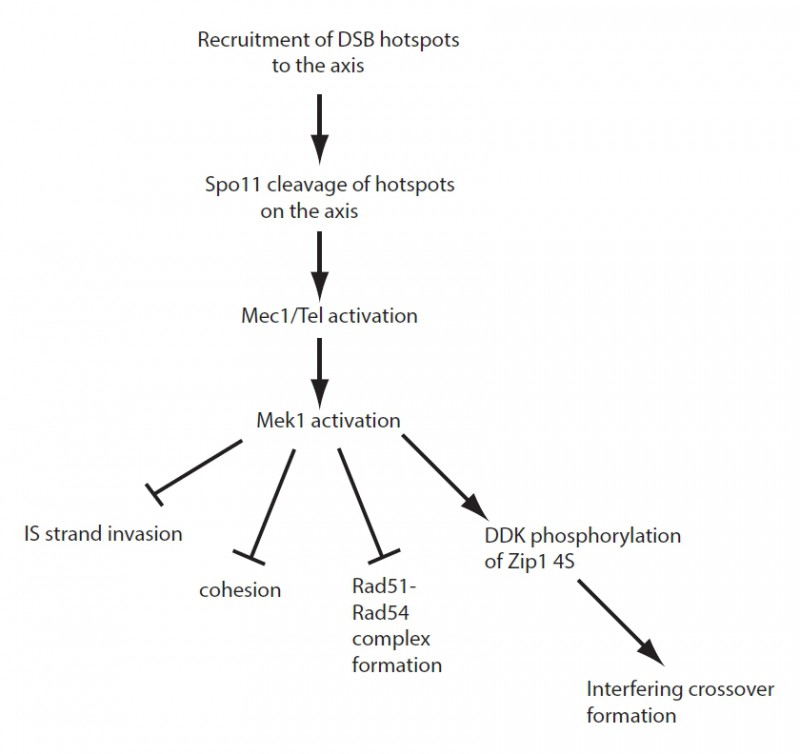
FIGURE 1: Activation of Mek1 activity at meiotic DSBs globally regulates different aspects of recombination. DSBs occur in preferred regions of the genome called “hotspots” and are created by Spo11 cleavage after the hotspot regions have been tethered to chromosome axes. DSB formation and resection activate the Tel1 and Mec1 checkpoint kinases, respectively, which in turn activate the meiosis-specific kinase Mek1 locally at DSBs. Mek1 kinase activity then represses intersister strand invasion by phosphorylation of unknown substrates. It is proposed to locally antagonize cohesion, although the mechanism for this remains to be determined. Mek1 phosphorylation of Rad54 decreases Rad51-Rad54 complex formation, helping to maintain Rad51 in an inactive state while Dmc1 mediates interhomolog recombination. In addition, Mek1 allows DDK phosphorylation of Zip1 4S which is required for interhomolog engagement, chromosome synapsis, and the interfering crossover pathway of recombination.
By continuing to use the site, you agree to the use of cookies. more information
The cookie settings on this website are set to "allow cookies" to give you the best browsing experience possible. If you continue to use this website without changing your cookie settings or you click "Accept" below then you are consenting to this. Please refer to our "privacy statement" and our "terms of use" for further information.