
Regulation of extracellular vesicles for protein secretion in Aspergillus nidulans
This study reveals that Aspergillus nidulans boosts extracellular vesicle production when ER-trafficked enzymes are induced, uncovering how fungi remodel their secretome through vesicle-mediated secretion to adapt to changing environments and biofilm formation.

Transcriptomic response to different heme sources in Trypanosoma cruzi epimastigotes
This study uncovers how the Chagas disease parasite adapts to changes in heme, an essential molecule for its survival, providing transcriptional clues to heme metabolism and identifying a previously unreported heme-binding protein in T. cruzi.

Luminal acetylation of microtubules is not essential for Plasmodium berghei and Toxoplasma gondii survival
Acetylation of α-tubulin at lysine 40 is not essential for cytoskeletal stability in Plasmodium berghei or Toxoplasma gondii, suggesting redundancy and plasticity in microtubule regulation in these parasites.

The dual-site agonist for human M2 muscarinic receptors Iper-8-naphtalimide induces mitochondrial dysfunction in Saccharomyces cerevisiae
S. cerevisiae is a model to study human GPCRs. N-8-Iper, active against glioblastoma via M2 receptor, causes mitochondrial damage in yeast by binding Ste2, highlighting evolutionary conservation of GPCRs.

Integrative Omics reveals changes in the cellular landscape of peroxisome-deficient pex3 yeast cells
To uncover the consequences of peroxisome deficiency, we compared Saccharomyces cerevisiae wild-type with pex3 cells, which lack peroxisomes, employing quantitative proteomics and transcriptomics technologies.

Regulation of extracellular vesicles for protein secretion in Aspergillus nidulans
Rebekkah E. Pope1, Patrick Ballmann2, Lisa Whitworth3 and Rolf A. Prade1,*
This study reveals that Aspergillus nidulans boosts extracellular vesicle production when ER-trafficked enzymes are induced, uncovering how fungi remodel their secretome through vesicle-mediated secretion to adapt to changing environments and biofilm formation.

Transcriptomic response to different heme sources in Trypanosoma cruzi epimastigotes
Evelyn Tevere1,a, María G. Mediavilla1,a, Cecilia B. Di Capua1, Marcelo L. Merli1, Carlos Robello2,3, Luisa Berná2,4 and Julia A. Cricco
This study uncovers how the Chagas disease parasite adapts to changes in heme, an essential molecule for its survival, providing transcriptional clues to heme metabolism and identifying a previously unreported heme-binding protein in T. cruzi.
Sir2 regulates selective autophagy in stationary-phase yeast cells
Ji-In Ryua, Juhye Junga, and Jeong-Yoon Kim
This study establishes Sir2 as a previously unrecognized regulator of selective autophagy during the stationary phase and highlight how cells dynamically control organelle degradation.
Protein oxidation in the intermembrane space of mitochondria is substrate-specific rather than general
Valentina Peleh1, Jan Riemer2, Andrew Dancis3 and Johannes M. Herrmann1
In this work, the authors suggest that in Saccharomyces cerevisiae, the Mia40-dependent oxidation of proteins in the intermembrane space only takes place in specific proteins and presumably relies on the presence of Mia40-binding sites.
Deletion of AIF1 but not of YCA1/MCA1 protects Saccharomyces cerevisiae and Candida albicans cells from caspofungin-induced programmed cell death
Christopher Chin1,2,#, Faith Donaghey1,#, Katherine Helming1,3,#, Morgan McCarthy1,#, Stephen Rogers1, and Nicanor Austriaco1
This work suggests that deleting AIF1 but not YCA1/MCA1 protects S. cerevisiae and Candida albicans from caspofungin-induced cell death. This is not only the first time that AIF1 has been specifically tied to cell death in Candida but also the first time that caspofungin resistance has been linked to the cell death machinery in yeast.
Reduced TORC1 signaling abolishes mitochondrial dysfunctions and shortened chronological lifespan of Isc1p-deficient cells
Vitor Teixeira1,2, Tânia C. Medeiros1, Rita Vilaça1,2, Pedro Moradas-Ferreira1,2, and Vítor Costa1,2
Overall, this article shows that the TORC1-Sch9p axis is deregulated in Isc1p-deficient Saccharomyces cerevisiae cells, contributing to mitochondrial dysfunction, enhanced oxidative stress sensitivity and premature aging of isc1Δ cells.
Early manifestations of replicative aging in the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae.
Maksim I. Sorokin1,3, Dmitry A. Knorre2,3, and Fedor F. Severin2,3
The data preseted herein suggest that retrograde signaling starts to malfunction in relatively young cells, leading to accumulation of heterogeneous mitochondria within one cell. The latter may further contribute to a decline in stress resistances.
Tracking autophagy during proliferation and differentiation of Trypanosoma brucei
William R. Proto1, Nathaniel G. Jones1, Graham H. Coombs2, and Jeremy C. Mottram1
This article provides insights into the function of autophagy, a cellular degradation and recycling pathway, in the protozoan parasite Trypanosoma brucei.
A roadmap for designing narrow-spectrum antibiotics targeting bacterial pathogens
Xinyun Cao1,*, Robert Landick1,2, Elizabeth A. Campbell3
This comment discusses the article “Basis of narrow-spectrum activity of fidaxomicin on Clostridioides difficile” by Cao et al. (2022, Nature).
Breaking the clip for cargo unloading from motor proteins: mechanism and significance
Keisuke Obara1, and Takumi Kamura1
The mitochondrion is an essential organelle involved in ATP generation, lipid metabolism, regulation of calcium ions, etc. Therefore, it should be inherited properly by newly generated cells. In the budding yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae, mitochondria are passed on to daughter cells by the motor protein, Myo2, on the actin cable. The mitochondria and Myo2 are connected via the adaptor protein Mmr1. After reaching daughter cells, mitochondria are released from the actin-myosin machinery and move dynamically. In our recent paper (Obara K et al. (2022), Nat Commun, doi:10.1038/s41467-022-29704-8), we demonstrated that the regulated proteolysis of Mmr1 is required for the unloading of mitochondria from Myo2 in daughter cells. Sequential post-translational modifications of Mmr1, i.e., phosphorylation followed by ubiquitination, are essential for Mmr1 degradation and mitochondrial release from Myo2. Defects in Mmr1 degradation cause stacking and deformation of mitochondria at the bud-tip and bud-neck, where Myo2 accumulates. Compared to wild-type cells, mutant cells with defects in Mmr1 degradation possess an elevated mitochondrial membrane potential and produce higher levels of reactive oxygen species (ROS), along with hypersensitivity to oxidative stress.
Pirates of the haemoglobin
Daniel Akinbosede1, Robert Chizea1 and Stephen A. Hare1,†
Not all treasure is silver and gold; for pathogenic bacteria, iron is the most precious and the most pillaged of metallic elements. Iron is essential for the survival and growth of all life; however free iron is scarce for bacteria inside human hosts. As a mechanism of defence, humans have evolved ways to store iron so as to render it inaccessible for invading pathogens, such as keeping the metal bound to iron-carrying proteins. For bacteria to survive within humans, they must therefore evolve counters to this defence to compete with these proteins for iron binding, or directly steal iron from them. (…)
An ionophore breaks the multi-drug-resistance of Acinetobacter baumannii
David M.P. De Oliveira1 and Mark J. Walker1
Within intensive care units, multi-drug resistant Acinetobacter baumannii outbreaks are a frequent cause of ventilator-associated pneumonia. During the on-going COVID-19 pandemic, patients who receive ventilator support experience a 2-fold increased risk of mortality when they contract a secondary A. baumannii pulmonary infection. In our recent paper (De Oliveira et al. (2022), Mbio, doi: 10.1128/mbio.03517-21), we demonstrate that the 8-hydroxquinoline ionophore, PBT2 breaks the resistance of A. baumannii to tetracycline class antibiotics. In vitro, the combination of PBT2 and zinc with either tetracycline, doxycycline, or tigecycline was shown to be bactericidal against multi-drug-resistant A. baumannii, (…)
Endomembrane remodeling and dynamics in Salmonella infection
Ziyan Fang1 and Stéphane Méresse1
Salmonellae are bacteria that cause moderate to severe infections in humans, depending on the strain and the immune status of the infected host. These pathogens have the particularity of residing in the cells of the infected host. They are usually found in a vacuolar compartment that the bacteria shape with the help of effector proteins. Following invasion of a eukaryotic cell, the bacterial vacuole undergoes maturation characterized by changes in localization, composition and morphology. In particular, membrane tubules stretching over the microtubule cytoskeleton are formed from the bacterial vacuole. Although these tubules do not occur in all infected cells, they are functionally important and promote intracellular replication. This review focuses on the role and significance of membrane compartment remodeling observed in infected cells and the bacterial and host cell pathways involved.
The small bowel microbiome changes significantly with age and aspects of the ageing process
Gabriela Leite1, Mark Pimentel1,2, Gillian M. Barlow1 and Ruchi Mathur1,3
Gut microbiome changes have been associated with human ageing and implicated in age-related diseases including Alzheimer’s disease and Parkinson’s disease. However, studies to date have used stool samples, which do not represent the entire gut. Although more challenging to access, the small intestine plays critical roles in host metabolism and immune function. In this paper (Leite et al. (2021), Cell Reports, doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2021.109765), we demonstrate significant differences in the small intestinal microbiome in older subjects, (…)
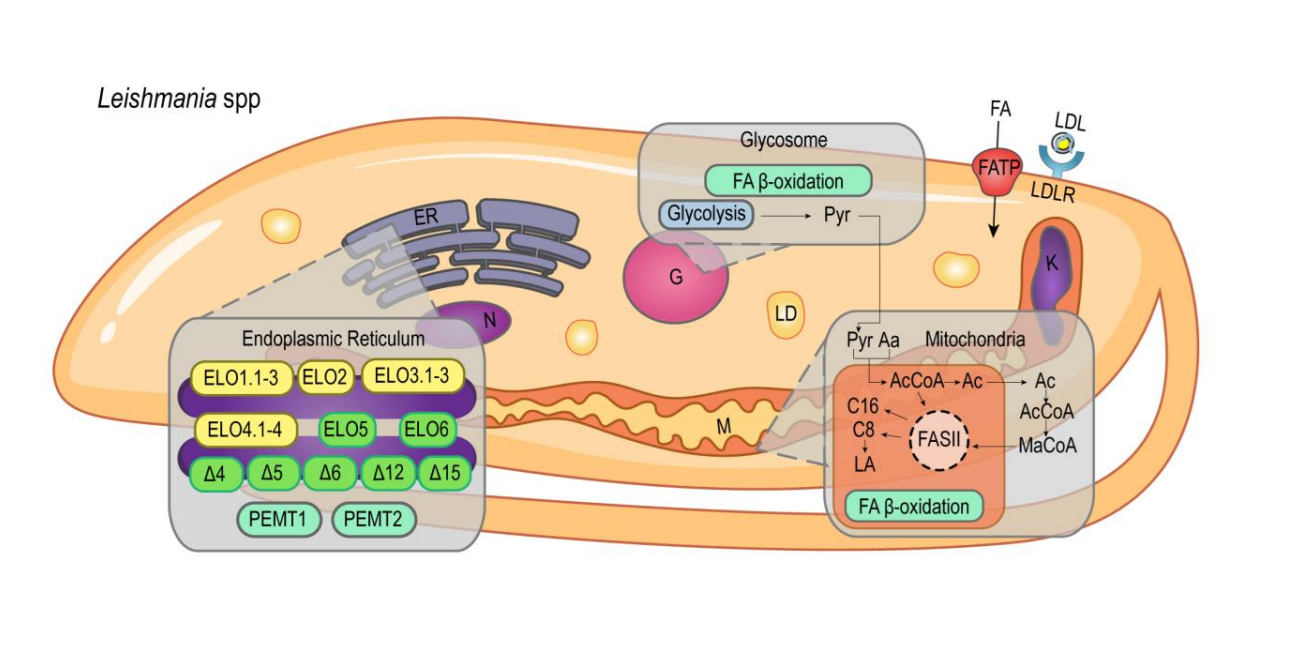
Lipid and fatty acid metabolism in trypanosomatids
Giovana Parreira de Aquino1,#, Marco Antonio Mendes Gomes1,#, Roberto Köpke Salinas2 and Maria Fernanda Laranjeira-Silva1
This work reviews specific aspects of lipid and fatty acid metabolism in the protozoan parasites T. brucei, T. cruzi, and Leishmania spp., as well as the pathways that have been explored for the development of new chemotherapies.
Starting with a degron: N-terminal formyl-methionine of nascent bacterial proteins contributes to their proteolytic control
R. Jürgen Dohmen
In this article, the author comments on the study “Formyl-methionine as a degradation signal at the N-termini of bacterial proteins.” by Piatkov et al. (Microbial Cell, 2015), discussing a novel N-terminal degradation signal (N-degron) that targets nascent proteins for degradation in Escherichia coli by a new branch of the bacterial N-end rule pathway, termed the fMet/N-end rule pathway
Elongation factor-P at the crossroads of the host-endosymbiont interface
Andrei Rajkovic1, Anne Witzky2, William Navarre3, Andrew J. Darwin4 and Michael Ibba5
Elongation factor P (EF-P) is an ancient bacterial translational factor that aids the ribosome in polymerizing oligo-prolines. EF-P structurally resembles tRNA and binds in-between the exit and peptidyl sites of the ribosome to accelerate the intrinsically slow reaction of peptidyl-prolyl bond formation. Recent studies have identified in separate organisms, two evolutionarily convergent EF-P post-translational modification systems (EPMS), split predominantly between gammaproteobacteria, and betaproteobacteria. Here, the authors highlight the recent discoveries made regarding EPMSs, with a focus on how these incomplete modification pathways shape or have been shaped by the endosymbiont-host relationship.
Feelin’ it: Differential oxidative stress sensing mediated by Cyclin C
W. Scott Moye-Rowley
Microbial cells that live exposed directly to their environmental milieu are faced with the challenge of adapting to the dynamic stress conditions that will inevitably be encountered. These stress conditions may vary over wide ranges and the most efficient responses would be tuned to produce a proportional buffering change. A mild stress would most efficiently be dealt with by a mild metabolic reprogramming that would prevent serious damage. A more severe environmental challenge would demand a more dramatic cellular compensatory response.
Subverting lysosomal function in Trypanosoma brucei
Sam Alsford
This article discusses Koh et al. (2015) “The lysosomotropic drug LeuLeu-OMe induces lysosome disruption and autophagy-independent cell death in Trypanosoma brucei (Microbial Cell 2(8): 288-298).
Entamoeba histolytica – tumor necrosis factor: a fatal attraction
Serge Ankri
This article comments on the study “In Entamoeba histolytica, a BspA family protein is required for chemotaxis toward tumour necrosis factor” by Silvestre et al. (Microbial Cell, 2015).
Toxoplasma control of host apoptosis: the art of not biting too hard the hand that feeds you
Sébastien Besteiro
Toxoplasma gondii is an obligate intracellular parasite that is able to infect a multitude of different vertebrate hosts and can survive in virtually any nucleated cell. Here, the authors discuss the article “Toxoplasma gondii inhibits cytochrome c-induced caspase activation in its host cell by interference with holo-apoptosome assembly” by Graumann et al. (2015, Microbial Cell).
A safety catch for ornithine decarboxylase degradation
Christof Taxis
Feedback inhibition is a common mechanism to adjust the activity of an enzyme in accordance with the abundance of a product. This article comments on the study “Polyamines directly promote antizyme-mediated degradation of ornithine decarboxylase by the proteasome” by Beenukumar et al. (2015), Microbial Cell.
Fancy a gene? A surprisingly complex evolutionary history of peroxiredoxins.
Alena Zíková1,2, Miroslav Oborník1,2,3 and Julius Lukeš1,2,4
In this comment, the authors discuss the article “Prokaryotic ancestry and gene fusion of a dual localized peroxiredoxin in malaria parasites” (Djuika et al., Microbial Cell 2015).
Quorum protection, growth and survival
Ian G . Macreadie
For the growth of a cell culture, one inoculates not with one cell but with a quorum of cells. This most often a requirement, not just a convenience, and most of us take this for granted without question. Here this observation is re-examined to understand why a quorum may be required to grow cells. The importance of quorums may be widespread in the aspects of microbiology they affect. It is very likely that quorums are connected with and have a large impact on the determination of Minimal Inhibitory Concentrations. It is also possible that low cell density may adversely affect cell survival, however, this is an area where even less is known. The need for a quorum might affect other aspects of microbial cell culture, cell isolation and cell preservation. Effects also extend to mammalian cell culture. Here I seek to review studies that have been documented and speculate on how the information might be utilized in the future.
Microbial Cell
is an open-access, peer-reviewed journal that publishes exceptionally relevant research works that implement the use of unicellular organisms (and multicellular microorganisms) to understand cellular responses to internal and external stimuli and/or human diseases.
you can trust
Can’t find what you’re looking for?
You can browse all our issues and published articles here.
FAQs
Peer-reviewed, open-access research using unicellular organisms (and multicellular microorganisms) to understand cellular responses and human disease.
The journal (founded in 2014) is led by its Editors-in-Chief Frank Madeo, Didac Carmona-Gutierrez, and Guido Kroemer
Microbial Cell has been publishing original scientific literature since 2014, and from the very beginning has been managed by active scientists through an independent Publishing House (Shared science Publishers). The journal was conceived as a platform to acknowledge the importance of unicellular organisms, both as model systems as well as in the biological context of human health and disease.
Ever since, Microbial Cell has very positively developed and strongly grown into a respected journal in the unicellular research community and even beyond. This scientific impact is reflected in the yearly number of citations obtained by articles published in Microbial Cell, as recorded by the Web of Science (Clarivate, formerly Thomson/Reuters):

The scientific impact of Microbial Cell is also mirrored in a series of milestones:
2015: Microbial Cell is included in the Emerging Sources Citation Index (ESCI), a selection of developing journals drafted by Clarivate Analytics based on the candidate’s publishing standards, quality, editorial content, and citation data. Note: As an ESCI-selected journal, Microbial Cell is currently being evaluated in a rigorous and long process to determine an inclusion in the Science Citation Index Expanded (SCIE), which allows the official calculation of Clarivate Analytics’ impact factor.
2016: Microbial Cell is awarded the so-called DOAJ Seal by the selective Directory of Open Access Journals (DOAJ). The DOAJ Seal is an exclusive mark of certification for open access journals granted by DOAJ to journals that adhere to outstanding best practice and achieve an extra high and clear commitment to open access and high publishing standards.
2017: Microbial Cell is included in Pubmed Central (PMC), allowing the archiving of all the journal’s articles in PMC and PubMed.
2019: Microbial Cell is indexed in the prestigious abstract and citation database Scopus after a thorough selection process. This also means that Microbial Cell obtains, for the first time, an official Scopus CiteScore as well as an official journal ranking in the Scimago Journal and Country Ranking.
2022: Microbial Cell’s CiteScore reaches a value of 7.2 for the year 2021, positioning Microbial Cell among the top microbiology journals (previously available CiteScores: 2019: 5.4; 2020: 5.1).
2022: Microbial Cell is indexed in the highly selective Science Citation Index Expanded™, which covers approx. 9,500 of the world’s most impactful journals across 178 scientific disciplines. In their journal selection and curation process, Clarivate´s editors apply 24 ‘quality’ criteria and four ‘impact’ criteria to select the most influential journals in their respective fields. This selection is also a pre-requisite for inclusion in the JCR, which features the impact factor.
2022: Microbial Cell is listed in the Journal Citation Reports™ (JCR), and obtains its first official Journal Impact Factor™ (JIF) for the year 2021: 5.316.Check Article Types and Manuscript Preparation guidelines. Submit online via Scholastica.

