
Regulation of extracellular vesicles for protein secretion in Aspergillus nidulans
This study reveals that Aspergillus nidulans boosts extracellular vesicle production when ER-trafficked enzymes are induced, uncovering how fungi remodel their secretome through vesicle-mediated secretion to adapt to changing environments and biofilm formation.

Transcriptomic response to different heme sources in Trypanosoma cruzi epimastigotes
This study uncovers how the Chagas disease parasite adapts to changes in heme, an essential molecule for its survival, providing transcriptional clues to heme metabolism and identifying a previously unreported heme-binding protein in T. cruzi.

Luminal acetylation of microtubules is not essential for Plasmodium berghei and Toxoplasma gondii survival
Acetylation of α-tubulin at lysine 40 is not essential for cytoskeletal stability in Plasmodium berghei or Toxoplasma gondii, suggesting redundancy and plasticity in microtubule regulation in these parasites.

The dual-site agonist for human M2 muscarinic receptors Iper-8-naphtalimide induces mitochondrial dysfunction in Saccharomyces cerevisiae
S. cerevisiae is a model to study human GPCRs. N-8-Iper, active against glioblastoma via M2 receptor, causes mitochondrial damage in yeast by binding Ste2, highlighting evolutionary conservation of GPCRs.

Integrative Omics reveals changes in the cellular landscape of peroxisome-deficient pex3 yeast cells
To uncover the consequences of peroxisome deficiency, we compared Saccharomyces cerevisiae wild-type with pex3 cells, which lack peroxisomes, employing quantitative proteomics and transcriptomics technologies.

Regulation of extracellular vesicles for protein secretion in Aspergillus nidulans
Rebekkah E. Pope1, Patrick Ballmann2, Lisa Whitworth3 and Rolf A. Prade1,*
This study reveals that Aspergillus nidulans boosts extracellular vesicle production when ER-trafficked enzymes are induced, uncovering how fungi remodel their secretome through vesicle-mediated secretion to adapt to changing environments and biofilm formation.

Transcriptomic response to different heme sources in Trypanosoma cruzi epimastigotes
Evelyn Tevere1,a, María G. Mediavilla1,a, Cecilia B. Di Capua1, Marcelo L. Merli1, Carlos Robello2,3, Luisa Berná2,4 and Julia A. Cricco
This study uncovers how the Chagas disease parasite adapts to changes in heme, an essential molecule for its survival, providing transcriptional clues to heme metabolism and identifying a previously unreported heme-binding protein in T. cruzi.
Sir2 regulates selective autophagy in stationary-phase yeast cells
Ji-In Ryua, Juhye Junga, and Jeong-Yoon Kim
This study establishes Sir2 as a previously unrecognized regulator of selective autophagy during the stationary phase and highlight how cells dynamically control organelle degradation.
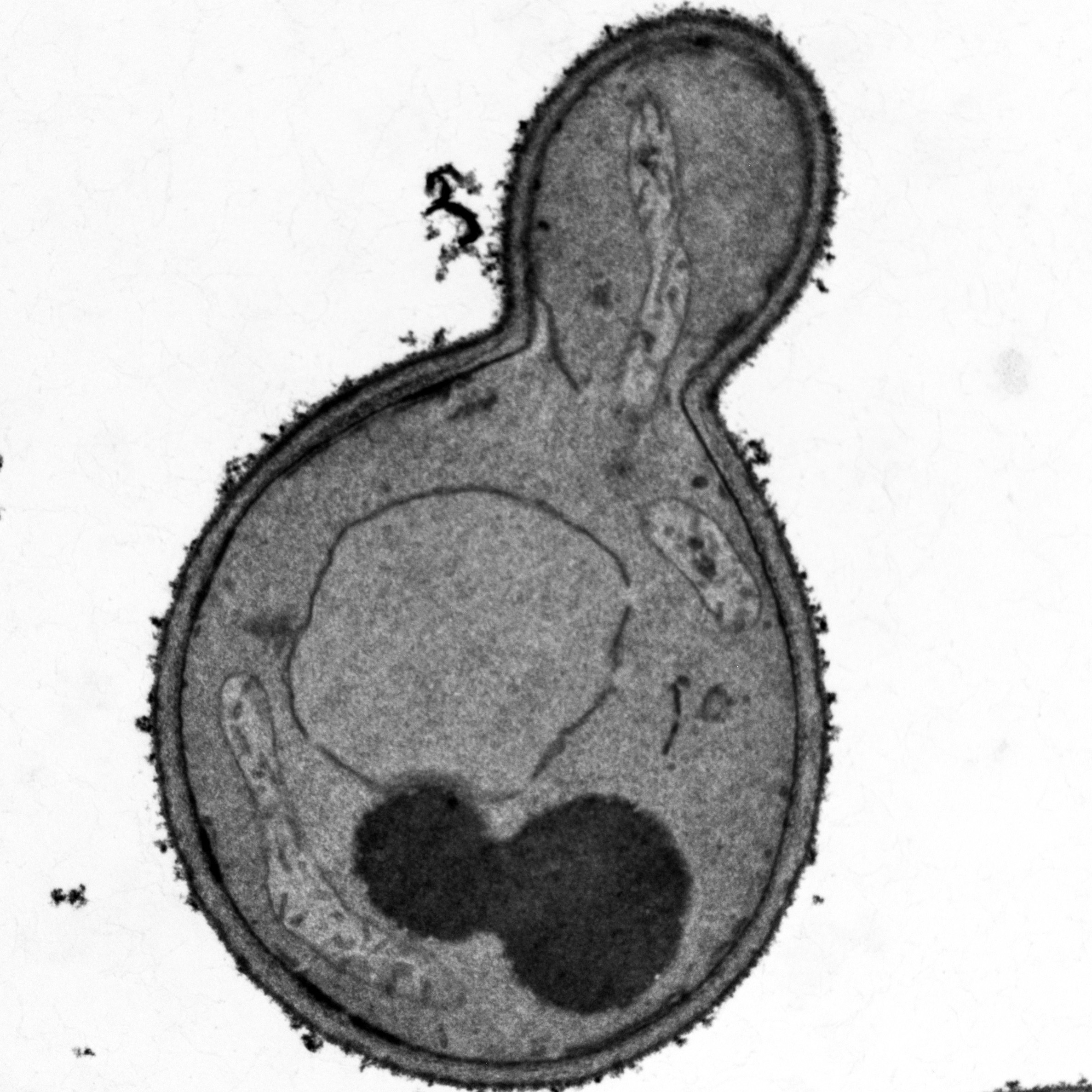
Microwave-assisted preparation of yeast cells for ultrastructural analysis by electron microscopy
Moritz Mayera, Christina Schuga, Stefan Geimer, Till Klecker and Benedikt Westermann
Budding yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae is widely used as a model organism to study the biogenesis and architecture of organellar membranes, which can be visualized by transmission electron microscopy (TEM).

A complex remodeling of cellular homeostasis distinguishes RSV/SARS-CoV-2 co-infected A549-hACE2 expressing cell lines
Claudia Vanetti1, Irma Saulle1,2, Valentina Artusa1,2, Claudia Moscheni1, Gioia Cappelletti1, Silvia Zecchini1, Sergio Strizzi1, Micaela Garziano1,2, Claudio Fenizia1,2, Antonella Tosoni1, Martina Broggiato1, Pasquale Ogno1, Manuela Nebuloni1, Mario Clerici2,3, Daria Trabattoni1, Fiona Limanaqi1 and Mara Biasin1
Given the common tropism of SARS-CoV-2 and RSV, and the unclear consequences of their mutual influence, we developed an in vitro lung epithelial cell model to study the molecular mechanisms and cellular pathways modulated in viral co-infection.

Fecal gelatinase does not predict mortality in patients with alcohol-associated hepatitis
Yongqiang Yang1,a, Philipp Hartmann2,3,a and Bernd Schnabl1,4
This study aimed to investigate the significance of fecal gelatinase on clinical outcomes in patients with alcohol-associated hepatitis. In conclusion, in our cohort, fecal gelatinase does not predict mortality and does not indicate higher disease severity in patients with alcohol-associated hepatitis.

Direct detection of stringent alarmones (pp)pGpp using malachite green
Muriel Schicketanz1, Magdalena Petrová2, Dominik Rejman2, Margherita Sosio3, Stefano Donadio3 and Yong Everett Zhang1
In this study, we demonstrate the surprising discovery of a commercially available, low-cost malachite green (MG) detection kit, originally designed for orthophosphate (Pi) detection, for detecting (p)ppGpp and its analogues, especially pGpp

Promoter methylation and increased expression of PD-L1 in patients with active tuberculosis
Yen-Han Tseng1,2, Sheng-Wei Pan1,2,3, Jhong-Ru Huang2,4, Chang-Ching Lee1, Jung-Jyh Hung2,5, Po-Kuei Hsu2,5, Nien-Jung Chen6, Wei-Juin Su2,7, Yuh-Min Chen1,2 and Jia-Yih Feng1,2,8
The PD-1/PD-L1 pathway plays a pivotal role in T cell activity and is involved in the pathophysiology of tuberculosis. Here we show that PD-L1 expression is increased in patients with active tuberculosis and is correlated with treatment outcomes.

Quantification methods of Candida albicans are independent irrespective of fungal morphology
Amanda B Soares1, Maria C de Albuquerque1, Leticia M Rosa1, Marlise I Klein 2, Ana C Paravina1, Paula A Barbugli1, Livia N Dovigo3 and Ewerton G de O Mima1
Our study demonstrated that the quantification methods of C. albicans (cells/mL, CFU/mL, and vPCR) did not agree, regardless of the fungal morphology/growth, even though a significant and strong correlation is observed.

Pathogenic Escherichia coli change the adhesion between neutrophils and endotheliocytes in the experimental bacteremia model
Svetlana N Pleskova1,2,*, Nikolay A Bezrukov1, Sergey Z Bobyk1, Ekaterina N Gorshkova1 and Dimitri V Novikov3
In this work, we have demonstrated that in the model of experimental septicemia there is a disruption of adhesion contacts between neutrophils and endothelial cells, manifested by a decrease in adhesion force and work upon exposure to E. coli.

Arsenite treatment induces Hsp90 aggregates distinct from conventional stress granules in fission yeast
Naofumi Tomimotoa, Teruaki Takasakia and Reiko Sugiura
Given the conserved role of Hsp90 as a molecular chaperone protein, our findings presented in this study may suggest a novel type of arsenite-induced biological condensates, wherein Hsp90 plays a key role in maintaining its integrity.
A Cinderella story: how the vacuolar proteases Pep4 and Prb1 do more than cleaning up the cell’s mass degradation processes
Winnie Kerstens1,2 and Patrick Van Dijck1,2
This review summarizes the expanded roles of the Saccharomyces cerevisiae vacuolar proteases Pep4 and Prb1 in non-vacuolar activities outside of autophagy, such as programmed cell death, protection from harmful protein forms, and gene expression regulation. The potential implications of these findings for fungal biology and drug target discovery, including insights for mammalian cell studies, are highlighted, emphasizing the need for a deeper understanding of these molecular processes.
The biosynthesis of pyoverdines
Michael T. Ringel1 and Thomas Brüser1
This review provides an overview of pyoverdine biosynthesis, emphasizing the distinctive fluorophore shared by various pyoverdines derived from ferribactins and the role of periplasmic processes in the maturation and modification of these siderophores, critical for the growth and colonization of hosts by fluorescent pseudomonads.
Toxin release mediated by the novel autolysin Cwp19 in Clostridium difficile
Imane El Meouche1 and Johann Peltier2,3
In this article, the authors comment on the study “Cwp19 is a novel lytic transglycosylase involved in stationary-phase autolysis resulting in toxin release in Clostridium difficile” by Wydau-Dematteis (MBio, 2018) that characterizes a novel peptidoglycan hydrolase, Cwp19, in Clostridioides difficile, highlighting its glucose-dependent mediation of toxins secretion and suggesting a potential role in the pathogenesis of this bacterium, contributing to the understanding of these enzymes in C. difficile and their implication in pathogenicity.
A global view of substrate phosphorylation and dephosphorylation during budding yeast mitotic exit
Sandra A. Touati1 and Frank Uhlmann1
In this article, the authors comment on the study “Phosphoproteome dynamics during mitotic exit in budding yeast” by Touati (EMBO J, 2018) that described a time-resolved global phosphoproteome analysis during a cell cycle phase known as mitotic exit in budding yeast revealed the principles of phosphoregulation governing the ordered sequence of events such as spindle elongation, chromosome decondensation, and completion of cell division.
Gammaretroviruses tether to mitotic chromatin by directly binding nucleosomal histone proteins
Madushi Wanaguru1 and Kate N. Bishop1
In this article, the authors comment on the study “Murine leukemia virus p12 tethers the capsid-containing pre-integration complex to chromatin by binding directly to host nucleosomes in mitosis” by Wanaguruet al. (PLoS Pathog, 2018) that highlights the essential role of the gammaretroviral gag cleavage product, p12, at both early and late stages of the virus life cycle, particularly in the integration of the viral DNA into the host cell chromatin to form a provirus. It also emphasizes the recent findings regarding the N- and C-terminal domains of p12, revealing their direct binding to the viral capsid lattice and nucleosomal histone proteins, respectively, thus elucidating the mechanism by which p12 links the viral pre-integration complex to mitotic chromatin.
Methodologies for in vitro and in vivo evaluation of efficacy of antifungal and antibiofilm agents and surface coatings against fungal biofilms
Patrick Van Dijck1,2,‡, Jelmer Sjollema3,‡, Bruno P.A. Cammue4,5, Katrien Lagrou6,7, Judith Berman8, Christophe d’Enfert9, David R. Andes10,11, Maiken C. Arendrup12-14, Axel A. Brakhage15, Richard Calderone16, Emilia Cantón17, Tom Coenye18,19, Paul Cos20, Leah E. Cowen21, Mira Edgerton22, Ana Espinel-Ingroff23, Scott G. Filler24, Mahmoud Ghannoum25, Neil A.R. Gow26, Hubertus Haas27, Mary Ann Jabra-Rizk28, Elizabeth M. Johnson29, Shawn R. Lockhart30, Jose L. Lopez-Ribot31, Johan Maertens32, Carol A. Munro26, Jeniel E. Nett33, Clarissa J. Nobile34, Michael A. Pfaller35,36, Gordon Ramage19,37, Dominique Sanglard38, Maurizio Sanguinetti39, Isabel Spriet40, Paul E. Verweij41, Adilia Warris42, Joost Wauters43, Michael R. Yeaman44, Sebastian A.J. Zaat45, Karin Thevissen4,*
This article highlights the critical importance of accurate susceptibility testing methods and the discovery of novel antifungal and antibiofilm agents in combating invasive fungal infections associated with biofilm formation on medical devices, thereby emphasizing the need for advancements in medical mycology research to address these complex diseases.
Shepherding DNA ends: Rif1 protects telomeres and chromosome breaks
Gabriele A. Fontana1, Julia K. Reinert1,2, Nicolas H. Thomä1, Ulrich Rass1
This review discusses the conserved mechanisms cells have evolved to protect DNA ends at chromosomal termini and DNA double-strand breaks (DSBs), focusing on the protein Rif1’s roles in telomere homeostasis and DSB repair in eukaryotes. It highlights the intriguing connection between Rif1’s involvement in both telomere maintenance and DSB repair, and suggests that excluding end-processing factors may underlie Rif1’s diverse biological functions at telomeres and chromosome breaks.
The CRISPR conundrum: evolve and maybe die, or survive and risk stagnation
Jesús García-Martínez1, Rafael D. Maldonado1, Noemí M. Guzmán1 and Francisco J. M. Mojica1,2
In this article García-Martínez et al. cover how the model bacterium Escherichia coli deals with CRISPR-Cas to tackle the major dilemma of evolution versus survival.
Transceptors as a functional link of transporters and receptors
George Diallinas
A relative newcomer in environment sensing are the so called transceptors, membrane proteins that possess both solute transport and receptor-like signaling activities. Now, the transceptor concept is further enlarged to include micronutrient sensing via the iron and zinc high-affinity transporters of Saccharomyces cerevisiae.
S. pombe placed on the prion map
Jacqueline Hayles
This article comments on work published by Sideri et al. (Microbial Cell, 2017), which identified the Ctr4 prion in S. pombe.
Using microbes as a key tool to unravel the mechanism of autophagy and the functions of the ATG proteins
Mario Mauthe1,2 and Fulvio Reggiori1,2
Microbes have served to discover and characterize unconventional functions of the ATG proteins, which are uncoupled from their role in autophagy. In our recent study, we have taken advantage of viruses as a screening tool to determine the extent of the unconventional functions of the ATG proteome and characterize one of them.
Autophagy: one more Nobel Prize for yeast
Andreas Zimmermann1, Katharina Kainz1, Aleksandra Andryushkova1, Sebastian Hofer1, Frank Madeo1,2 and Didac Carmona-Gutierrez1
The recent announcement of the 2016 Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine, awarded to Yoshinori Ohsumifor the discoveries of mechanisms governing autophagy, underscores the importance of intracellular degradation and recycling. Here we provide a quick historical overview that mirrors both the importance of autophagy as a conserved and essential process for cellular life and death as well as the crucial role of yeast in its mechanistic characterization.
Physiology, phylogeny, and LUCA
William F. Martin1,2, Madeline C. Weiss1, Sinje Neukirchen3, Shijulal Nelson-Sathi4, Filipa L. Sousa3
Genomes record their own history. But if we want to look all the way back to life’s beginnings some 4 billion years ago, the record of microbial evolution that is preserved in prokaryotic genomes is not easy to read. The classical approach has been to look for genes that are universally distributed. Another approach is to make all trees for all genes, and sift out the trees where signals have been overwritten by lateral gene transfer. What is left ought to be ancient. If we do that, what do we find?
Sexually transmitted infections: old foes on the rise
Didac Carmona-Gutierrez1,*, Katharina Kainz1 and Frank Madeo1,2,*
Sexually transmitted infections (STIs) are commonly spread via sexual contact. It is estimated that one million STIs are acquired every day worldwide. Besides their impact on sexual, reproductive and neonatal health, they can cause disastrous and life-threatening complications if left untreated. In addition to this personal burden, STIs also represent a socioeconomic problem, deriving in treatment costs of tremendous proportions. Despite a substantial progress in diagnosis, treatment and prevention, the incidence of many common STIs is increasing, and STIs continue to represent a global public health problem and a major cause for morbidity and mortality. With this Special Issue, Microbial Cell provides an in-depth overview of the eight major STIs, covering all relevant features of each infection.
Microbial Cell
is an open-access, peer-reviewed journal that publishes exceptionally relevant research works that implement the use of unicellular organisms (and multicellular microorganisms) to understand cellular responses to internal and external stimuli and/or human diseases.
you can trust
Can’t find what you’re looking for?
You can browse all our issues and published articles here.
FAQs
Peer-reviewed, open-access research using unicellular organisms (and multicellular microorganisms) to understand cellular responses and human disease.
The journal (founded in 2014) is led by its Editors-in-Chief Frank Madeo, Didac Carmona-Gutierrez, and Guido Kroemer
Microbial Cell has been publishing original scientific literature since 2014, and from the very beginning has been managed by active scientists through an independent Publishing House (Shared science Publishers). The journal was conceived as a platform to acknowledge the importance of unicellular organisms, both as model systems as well as in the biological context of human health and disease.
Ever since, Microbial Cell has very positively developed and strongly grown into a respected journal in the unicellular research community and even beyond. This scientific impact is reflected in the yearly number of citations obtained by articles published in Microbial Cell, as recorded by the Web of Science (Clarivate, formerly Thomson/Reuters):

The scientific impact of Microbial Cell is also mirrored in a series of milestones:
2015: Microbial Cell is included in the Emerging Sources Citation Index (ESCI), a selection of developing journals drafted by Clarivate Analytics based on the candidate’s publishing standards, quality, editorial content, and citation data. Note: As an ESCI-selected journal, Microbial Cell is currently being evaluated in a rigorous and long process to determine an inclusion in the Science Citation Index Expanded (SCIE), which allows the official calculation of Clarivate Analytics’ impact factor.
2016: Microbial Cell is awarded the so-called DOAJ Seal by the selective Directory of Open Access Journals (DOAJ). The DOAJ Seal is an exclusive mark of certification for open access journals granted by DOAJ to journals that adhere to outstanding best practice and achieve an extra high and clear commitment to open access and high publishing standards.
2017: Microbial Cell is included in Pubmed Central (PMC), allowing the archiving of all the journal’s articles in PMC and PubMed.
2019: Microbial Cell is indexed in the prestigious abstract and citation database Scopus after a thorough selection process. This also means that Microbial Cell obtains, for the first time, an official Scopus CiteScore as well as an official journal ranking in the Scimago Journal and Country Ranking.
2022: Microbial Cell’s CiteScore reaches a value of 7.2 for the year 2021, positioning Microbial Cell among the top microbiology journals (previously available CiteScores: 2019: 5.4; 2020: 5.1).
2022: Microbial Cell is indexed in the highly selective Science Citation Index Expanded™, which covers approx. 9,500 of the world’s most impactful journals across 178 scientific disciplines. In their journal selection and curation process, Clarivate´s editors apply 24 ‘quality’ criteria and four ‘impact’ criteria to select the most influential journals in their respective fields. This selection is also a pre-requisite for inclusion in the JCR, which features the impact factor.
2022: Microbial Cell is listed in the Journal Citation Reports™ (JCR), and obtains its first official Journal Impact Factor™ (JIF) for the year 2021: 5.316.Check Article Types and Manuscript Preparation guidelines. Submit online via Scholastica.


Staphylococcus aureus type I signal peptidase: essential or not essential, that’s the question
Wouter L.W. Hazenbos1, Elizabeth Skippington2 and Man-Wah Tan1
This article comments on work published by Morisaki et al. (mBio, 2016), which characterized a novel ABC transporter. This transporter apparently compensates for SpsB’s essential function by mediating alternative cleavage of a subset of proteins at a site distinct from the SpsB-cleavage site, leading to SpsB-independent secretion.