
Regulation of extracellular vesicles for protein secretion in Aspergillus nidulans
This study reveals that Aspergillus nidulans boosts extracellular vesicle production when ER-trafficked enzymes are induced, uncovering how fungi remodel their secretome through vesicle-mediated secretion to adapt to changing environments and biofilm formation.

Transcriptomic response to different heme sources in Trypanosoma cruzi epimastigotes
This study uncovers how the Chagas disease parasite adapts to changes in heme, an essential molecule for its survival, providing transcriptional clues to heme metabolism and identifying a previously unreported heme-binding protein in T. cruzi.

Luminal acetylation of microtubules is not essential for Plasmodium berghei and Toxoplasma gondii survival
Acetylation of α-tubulin at lysine 40 is not essential for cytoskeletal stability in Plasmodium berghei or Toxoplasma gondii, suggesting redundancy and plasticity in microtubule regulation in these parasites.

The dual-site agonist for human M2 muscarinic receptors Iper-8-naphtalimide induces mitochondrial dysfunction in Saccharomyces cerevisiae
S. cerevisiae is a model to study human GPCRs. N-8-Iper, active against glioblastoma via M2 receptor, causes mitochondrial damage in yeast by binding Ste2, highlighting evolutionary conservation of GPCRs.

Integrative Omics reveals changes in the cellular landscape of peroxisome-deficient pex3 yeast cells
To uncover the consequences of peroxisome deficiency, we compared Saccharomyces cerevisiae wild-type with pex3 cells, which lack peroxisomes, employing quantitative proteomics and transcriptomics technologies.

Regulation of extracellular vesicles for protein secretion in Aspergillus nidulans
Rebekkah E. Pope1, Patrick Ballmann2, Lisa Whitworth3 and Rolf A. Prade1,*
This study reveals that Aspergillus nidulans boosts extracellular vesicle production when ER-trafficked enzymes are induced, uncovering how fungi remodel their secretome through vesicle-mediated secretion to adapt to changing environments and biofilm formation.

Transcriptomic response to different heme sources in Trypanosoma cruzi epimastigotes
Evelyn Tevere1,a, María G. Mediavilla1,a, Cecilia B. Di Capua1, Marcelo L. Merli1, Carlos Robello2,3, Luisa Berná2,4 and Julia A. Cricco
This study uncovers how the Chagas disease parasite adapts to changes in heme, an essential molecule for its survival, providing transcriptional clues to heme metabolism and identifying a previously unreported heme-binding protein in T. cruzi.
Sir2 regulates selective autophagy in stationary-phase yeast cells
Ji-In Ryua, Juhye Junga, and Jeong-Yoon Kim
This study establishes Sir2 as a previously unrecognized regulator of selective autophagy during the stationary phase and highlight how cells dynamically control organelle degradation.

Unresolved mystery of cyclic nucleotide second messengers, periplasmic acid phosphatases and bacterial natural competence
Kristina Kronborg and Yong Everett Zhang
In this study we aimed to identify the promotors responsible for the expression of the non-specific acid phosphatase AphA during different starvation conditions, to confirm the requirement of the cAMP-dependent CRP regulon for aphA expression, and to finally identify regulators of its expression.

Polyadenylated versions of small non-coding RNAs in Saccharomyces cerevisiae are degraded by Rrp6p/Rrp47p independent of the core nuclear exosome
Anusha Chaudhuri1,#, Soumita Paul2,#, Mayukh Banerjea2 and Biswadip Das2
In this investigation, we unveiled a novel functional role of the major nuclear 3′→5′ exoribonuclease, Rrp6p, and its cofactor Rrp47p in the degradation of polyadenylated versions of several mature sncRNAs, including 5S, 5.8S rRNAs, all sn- and some select snoRNAs in the baker’s yeast S. cerevisiae.
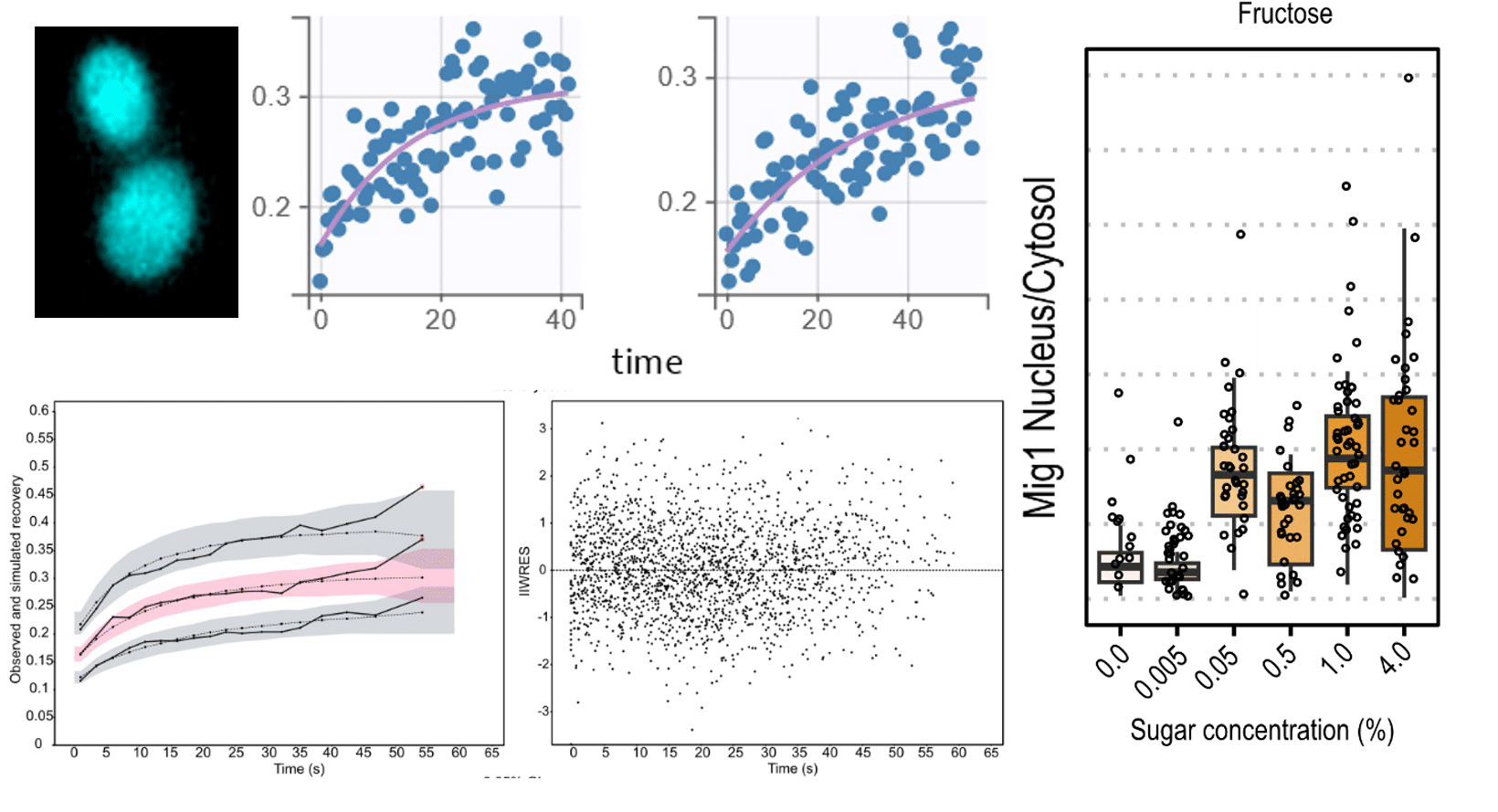
Exploring carbon source related localization and phosphorylation in the Snf1/Mig1 network using population and single cell-based approaches
Svenja Braam1, Farida Tripodi2, Linnea Österberg1,3, Sebastian Persson1, Niek Welkenhuysen1, Paola Coccetti2 and Marija Cvijovic1
In this work we set out to explore the relationship between the subcellular localization and regulation of kinases in the context of carbon source signaling. The data presented in this paper reinforce the notion that not only the activation/inactivation of kinases but also their subcellular localization and that of their targets influence fate decisions in response to environmental changes.

A Modular Cloning Toolkit for the production of recombinant proteins in Leishmania tarentolae
Katrin Hieronimus1,2,#, Tabea Donauer1,2,#, Jonas Klein1,#, Bastian Hinkel1,#, Julia Vanessa Spänle1,#, Anna Probst1,#, Justus Niemeyer1,#, Salina Kibrom1, Anna Maria Kiefer1, Luzia Schneider2, Britta Husemann2, Eileen Bischoff2, Sophie Möhring2, Nicolas Bayer1, Dorothée Klein1, Adrian Engels1, Benjamin Gustav Ziehmer2, Julian Stieß3, Pavlo Moroka1, Michael Schroda1, and Marcel Deponte2
Modular Cloning (MoClo) is based on libraries of standardized genetic parts that can be directionally assembled via Golden Gate cloning in one-pot reactions into transcription units and multigene constructs. We established a MoClo toolkit and exemplified its application for the production of recombinant proteins in L. tarentolae.
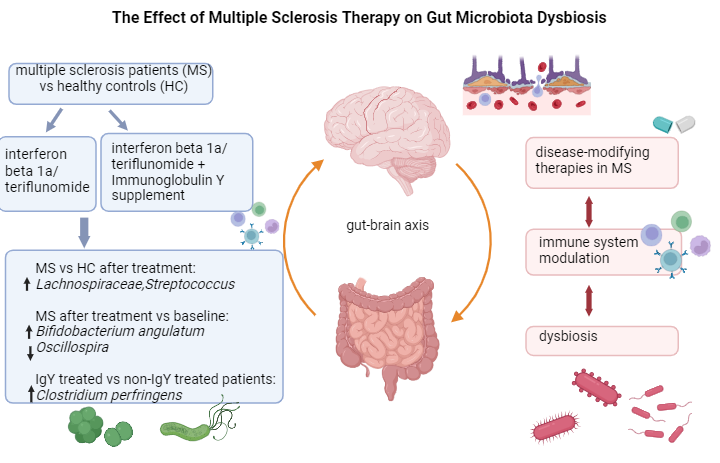
The effect of multiple sclerosis therapy on gut microbiota dysbiosis: a longitudinal prospective study
Andreea-Cristina Paraschiv1,a, Vitalie Vacaras1,2,a, Cristina Nistor1,2, Cristiana Vacaras3, Stefan Strilciuc1 and Dafin F Muresanu1,2
The gut microbiota, a complex ecosystem with various immune functions, plays a significant role in MS, and its response to different treatments is highlighted in this study. In clinical practice, maintaining a healthy microbiota is crucial for individuals with MS.
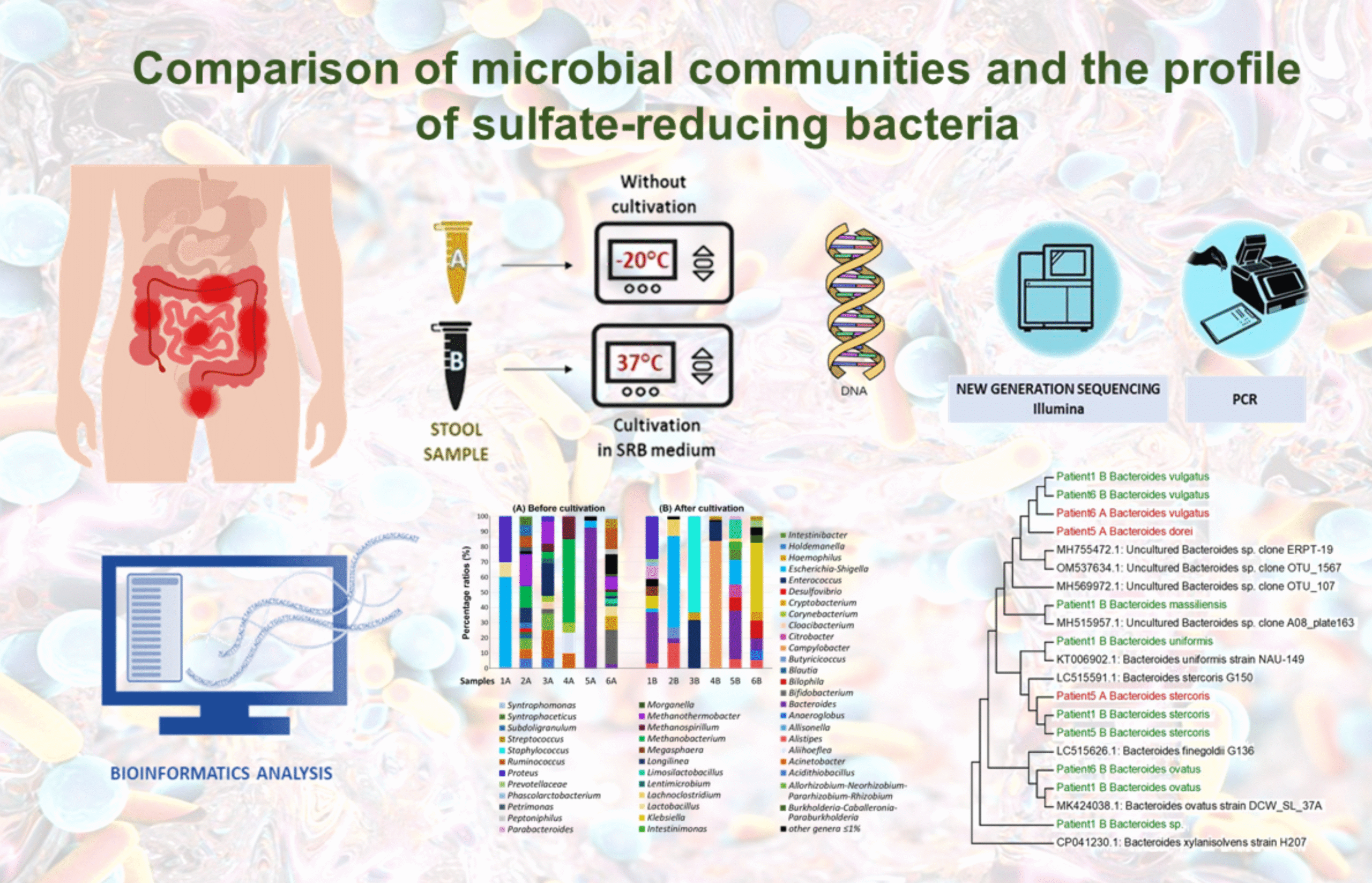
Comparison of microbial communities and the profile of sulfate-reducing bacteria in patients with ulcerative colitis and their association with bowel diseases: a pilot study
Ivan Kushkevych1, Kristýna Martínková1, Lenka Mráková1, Francesco Giudici2, Simone Baldi2, David Novak3, Márió Gajdács4, Monika Vítězová1, Dani Dordevic5, Amedeo Amedei2 and Simon K.-M. R. Rittmann6
Considerable evidence has accumulated regarding the molecular relationship between gut microbiota (GM) composition and the onset (clinical presentation and prognosis) of ulcerative colitis UC. Our findings highlight, among other observations, significant variations in the gut microbial composition among patients with varying disease severity and activity.

Replicative aging in yeast involves dynamic intron retention patterns associated with mRNA processing/export and protein ubiquitination
Jesús Gómez-Montalvo1, Alvaro de Obeso Fernández del Valle1, Luis Fernando De la Cruz Gutiérrez1, Jose Mario Gonzalez-Meljem1 and Christian Quintus Scheckhuber1
Saccharomyces cerevisiae has yielded relevant insights into some of the basic mechanisms of organismal aging. Among these are genomic instability, oxidative stress, caloric restriction and mitochondrial dysfunction. Our work uncovers a previously unexplored layer of the transcriptional program of yeast aging and, more generally, expands the knowledge on the occurrence of alternative splicing in baker´s yeast.
Peering into the ‘black box’ of pathogen recognition by cellular autophagy systems
Shu-chin Lai# and Rodney J Devenish
Autophagy is an intracellular process that plays an important role in protecting eukaryotic cells and maintaining intracellular homeostasis. This review summarises the available evidence regarding the specific recognition of invading pathogens by which they are targeted into host autophagy pathways.
Per aspera ad astra: When harmful chromosomal translocations become a plus value in genetic evolution. Lessons from Saccharomyces cerevisiae
Valentina Tosato and Carlo V. Bruschi
This review will focus on chromosomal translocations (either spontaneous or induced) in budding yeast. Indeed, very few organisms tolerate so well aneuploidy like Saccharomyces, allowing in depth studies on chromosomal numerical aberrations. The phenomenon of post-translocational adaptation (PTA) is discussed, providing some new unpublished data and proposing the hypothesis that translocations may drive evolution through adaptive genetic selection.
Intracellular phase for an extracellular bacterial pathogen: MgtC shows the way
Audrey Bernut1,#, Claudine Belon1, Chantal Soscia2, Sophie Bleves2, Anne-Béatrice Blanc-Potard1
This article discusses the article “A macrophage subversion factor is shared by intracellular and extracellular pathogens” by Belon et al. (PLoS Pathogens 11(6): e1004969, 2015).
The role of transcriptional ‘futile cycles’ in autophagy and microbial pathogenesis
Guowu Hu1, Travis McQuiston1, Amélie Bernard2, Yoon-Dong Park1, Jin Qiu1, Ali Vural3, Nannan Zhang1, Scott R. Waterman1, Nathan H. Blewett4, Timothy G. Myers5, John H. Kehrl3, Gulbu Uzel1, Daniel J. Klionsky2 and Peter R. Williamson1
Eukaryotic cells utilize macroautophagy (hereafter autophagy) to recycle cellular materials during nutrient stress. Target of rapamycin (Tor) is a central regulator of this process, acting by post-translational mechanisms, phosphorylating preformed autophagy-related (Atg) proteins to repress autophagy during log-phase growth. A role for this regulatory process in fungal virulence was further demonstrated by showing that overexpression of the Dcp2-associated mRNA-binding protein Vad1 in the AIDS-associated pathogen Cryptococcus neoformans results in constitutive repression of autophagy even under starvation conditions as well as attenuated virulence in a mouse model. In summary, Tor-dependent post-transcriptional regulation of autophagy plays a key role in the facilitation of microbial pathogenesis.
The many facets of homologous recombination at telomeres
Clémence Claussin and Michael Chang
The ends of linear chromosomes are capped by nucleoprotein structures called telomeres. A dysfunctional telomere may resemble a DNA double-strand break (DSB), which is a severe form of DNA damage. The presence of one DSB is sufficient to drive cell cycle arrest and cell death. Therefore cells have evolved mechanisms to repair DSBs such as homologous recombination (HR). HR-mediated repair of telomeres can lead to genome instability, a hallmark of cancer cells, which is why such repair is normally inhibited. However, some HR-mediated processes are required for proper telomere function. The need for some recombination activities at telomeres but not others necessitates careful and complex regulation, defects in which can lead to catastrophic consequences. Furthermore, some cell types can maintain telomeres via telomerase-independent, recombination-mediated mechanisms. In humans, these mechanisms…
From the baker to the bedside: yeast models of Parkinson’s disease
Regina Menezes1,2, Sandra Tenreiro3,5, Diana Macedo2, Cláudia N. Santos1,2, Tiago Fleming Outeiro4,5,6
The baker’s yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae has been extensively explored for our understanding of fundamental cell biology processes highly conserved in the eukaryotic kingdom. This review provides a brief historical perspective on the emergence of yeast as an experimental model and on how the field evolved to exploit the potential of the model for tackling the intricacies of various human diseases. In particular, the authors focus on existing yeast models of the molecular underpinnings of Parkinson’s disease (PD), focusing primarily on the central role of protein quality control systems.
Why are essential genes essential? – The essentiality of Saccharomyces genes
Zhaojie Zhang and Qun Ren
Essential genes are defined as required for the survival of an organism or a cell. This article reviews and analyzes the levels of essentiality of the Saccharomyces cerevisiae genes and groups the genes into four categories: (1) Conditional essential: essential only under certain circumstances or growth conditions; (2) Essential: required for survival under optimal growth conditions; (3) Redundant essential: synthetic lethal due to redundant pathways or gene duplication; and (4) Absolute essential: the minimal genes required for maintaining a cellular life under a stress-free environment. The essential and non-essential functions of the essential genes are further analyzed.
Membrane depolarization-triggered responsive diversification leads to antibiotic tolerance
Natalie Verstraeten, Wouter Joris Knapen, Maarten Fauvart, Jan Michiels
In this article, the authors discuss the article “Obg and membrane depolarization are part of a microbial bet-hedging strategy that leads to antibiotic tolerance”, Verstraeten et al., Mol. Cell 2015 Jul 2; 59 (1): 9-21.
Evolutionary rewiring of bacterial regulatory networks
Tiffany B. Taylor1,*, Geraldine Mulley1, Liam J. McGuffin1, Louise J. Johnson1, Michael A. Brockhurst2, Tanya Arseneault1,3, Mark W. Silby4 and Robert W. Jackson1,5
Bacteria have evolved complex regulatory networks that enable integration of multiple intracellular and extracellular signals to coordinate responses to environmental changes. However, our knowledge of how regulatory systems function and evolve is still relatively limited. There is often extensive homology between components of different networks, due to past cycles of gene duplication, divergence, and horizontal gene transfer, raising the possibility of cross-talk or redundancy. Consequently, evolutionary resilience is built into gene networks – homology between regulators can potentially allow rapid rescue of lost regulatory function across distant regions of the genome. This article discusses Taylor, et al. Science (2015), 347(6225), reporting mutations that facilitate cross-talk between pathways can contribute to gene network evolution, but which come with severe pleiotropic costs. Arising from this work are a number of questions surrounding how this phenomenon occurs.
Starting with a degron: N-terminal formyl-methionine of nascent bacterial proteins contributes to their proteolytic control
R. Jürgen Dohmen
In this article, the author comments on the study “Formyl-methionine as a degradation signal at the N-termini of bacterial proteins.” by Piatkov et al. (Microbial Cell, 2015), discussing a novel N-terminal degradation signal (N-degron) that targets nascent proteins for degradation in Escherichia coli by a new branch of the bacterial N-end rule pathway, termed the fMet/N-end rule pathway
Elongation factor-P at the crossroads of the host-endosymbiont interface
Andrei Rajkovic1, Anne Witzky2, William Navarre3, Andrew J. Darwin4 and Michael Ibba5
Elongation factor P (EF-P) is an ancient bacterial translational factor that aids the ribosome in polymerizing oligo-prolines. EF-P structurally resembles tRNA and binds in-between the exit and peptidyl sites of the ribosome to accelerate the intrinsically slow reaction of peptidyl-prolyl bond formation. Recent studies have identified in separate organisms, two evolutionarily convergent EF-P post-translational modification systems (EPMS), split predominantly between gammaproteobacteria, and betaproteobacteria. Here, the authors highlight the recent discoveries made regarding EPMSs, with a focus on how these incomplete modification pathways shape or have been shaped by the endosymbiont-host relationship.
Feelin’ it: Differential oxidative stress sensing mediated by Cyclin C
W. Scott Moye-Rowley
Microbial cells that live exposed directly to their environmental milieu are faced with the challenge of adapting to the dynamic stress conditions that will inevitably be encountered. These stress conditions may vary over wide ranges and the most efficient responses would be tuned to produce a proportional buffering change. A mild stress would most efficiently be dealt with by a mild metabolic reprogramming that would prevent serious damage. A more severe environmental challenge would demand a more dramatic cellular compensatory response.
Subverting lysosomal function in Trypanosoma brucei
Sam Alsford
This article discusses Koh et al. (2015) “The lysosomotropic drug LeuLeu-OMe induces lysosome disruption and autophagy-independent cell death in Trypanosoma brucei (Microbial Cell 2(8): 288-298).
Entamoeba histolytica – tumor necrosis factor: a fatal attraction
Serge Ankri
This article comments on the study “In Entamoeba histolytica, a BspA family protein is required for chemotaxis toward tumour necrosis factor” by Silvestre et al. (Microbial Cell, 2015).
Toxoplasma control of host apoptosis: the art of not biting too hard the hand that feeds you
Sébastien Besteiro
Toxoplasma gondii is an obligate intracellular parasite that is able to infect a multitude of different vertebrate hosts and can survive in virtually any nucleated cell. Here, the authors discuss the article “Toxoplasma gondii inhibits cytochrome c-induced caspase activation in its host cell by interference with holo-apoptosome assembly” by Graumann et al. (2015, Microbial Cell).
A safety catch for ornithine decarboxylase degradation
Christof Taxis
Feedback inhibition is a common mechanism to adjust the activity of an enzyme in accordance with the abundance of a product. This article comments on the study “Polyamines directly promote antizyme-mediated degradation of ornithine decarboxylase by the proteasome” by Beenukumar et al. (2015), Microbial Cell.
Fancy a gene? A surprisingly complex evolutionary history of peroxiredoxins.
Alena Zíková1,2, Miroslav Oborník1,2,3 and Julius Lukeš1,2,4
In this comment, the authors discuss the article “Prokaryotic ancestry and gene fusion of a dual localized peroxiredoxin in malaria parasites” (Djuika et al., Microbial Cell 2015).
Quorum protection, growth and survival
Ian G . Macreadie
For the growth of a cell culture, one inoculates not with one cell but with a quorum of cells. This most often a requirement, not just a convenience, and most of us take this for granted without question. Here this observation is re-examined to understand why a quorum may be required to grow cells. The importance of quorums may be widespread in the aspects of microbiology they affect. It is very likely that quorums are connected with and have a large impact on the determination of Minimal Inhibitory Concentrations. It is also possible that low cell density may adversely affect cell survival, however, this is an area where even less is known. The need for a quorum might affect other aspects of microbial cell culture, cell isolation and cell preservation. Effects also extend to mammalian cell culture. Here I seek to review studies that have been documented and speculate on how the information might be utilized in the future.
Microbial Cell
is an open-access, peer-reviewed journal that publishes exceptionally relevant research works that implement the use of unicellular organisms (and multicellular microorganisms) to understand cellular responses to internal and external stimuli and/or human diseases.
you can trust
Can’t find what you’re looking for?
You can browse all our issues and published articles here.
FAQs
Peer-reviewed, open-access research using unicellular organisms (and multicellular microorganisms) to understand cellular responses and human disease.
The journal (founded in 2014) is led by its Editors-in-Chief Frank Madeo, Didac Carmona-Gutierrez, and Guido Kroemer
Microbial Cell has been publishing original scientific literature since 2014, and from the very beginning has been managed by active scientists through an independent Publishing House (Shared science Publishers). The journal was conceived as a platform to acknowledge the importance of unicellular organisms, both as model systems as well as in the biological context of human health and disease.
Ever since, Microbial Cell has very positively developed and strongly grown into a respected journal in the unicellular research community and even beyond. This scientific impact is reflected in the yearly number of citations obtained by articles published in Microbial Cell, as recorded by the Web of Science (Clarivate, formerly Thomson/Reuters):

The scientific impact of Microbial Cell is also mirrored in a series of milestones:
2015: Microbial Cell is included in the Emerging Sources Citation Index (ESCI), a selection of developing journals drafted by Clarivate Analytics based on the candidate’s publishing standards, quality, editorial content, and citation data. Note: As an ESCI-selected journal, Microbial Cell is currently being evaluated in a rigorous and long process to determine an inclusion in the Science Citation Index Expanded (SCIE), which allows the official calculation of Clarivate Analytics’ impact factor.
2016: Microbial Cell is awarded the so-called DOAJ Seal by the selective Directory of Open Access Journals (DOAJ). The DOAJ Seal is an exclusive mark of certification for open access journals granted by DOAJ to journals that adhere to outstanding best practice and achieve an extra high and clear commitment to open access and high publishing standards.
2017: Microbial Cell is included in Pubmed Central (PMC), allowing the archiving of all the journal’s articles in PMC and PubMed.
2019: Microbial Cell is indexed in the prestigious abstract and citation database Scopus after a thorough selection process. This also means that Microbial Cell obtains, for the first time, an official Scopus CiteScore as well as an official journal ranking in the Scimago Journal and Country Ranking.
2022: Microbial Cell’s CiteScore reaches a value of 7.2 for the year 2021, positioning Microbial Cell among the top microbiology journals (previously available CiteScores: 2019: 5.4; 2020: 5.1).
2022: Microbial Cell is indexed in the highly selective Science Citation Index Expanded™, which covers approx. 9,500 of the world’s most impactful journals across 178 scientific disciplines. In their journal selection and curation process, Clarivate´s editors apply 24 ‘quality’ criteria and four ‘impact’ criteria to select the most influential journals in their respective fields. This selection is also a pre-requisite for inclusion in the JCR, which features the impact factor.
2022: Microbial Cell is listed in the Journal Citation Reports™ (JCR), and obtains its first official Journal Impact Factor™ (JIF) for the year 2021: 5.316.Check Article Types and Manuscript Preparation guidelines. Submit online via Scholastica.


