
Regulation of extracellular vesicles for protein secretion in Aspergillus nidulans
This study reveals that Aspergillus nidulans boosts extracellular vesicle production when ER-trafficked enzymes are induced, uncovering how fungi remodel their secretome through vesicle-mediated secretion to adapt to changing environments and biofilm formation.

Transcriptomic response to different heme sources in Trypanosoma cruzi epimastigotes
This study uncovers how the Chagas disease parasite adapts to changes in heme, an essential molecule for its survival, providing transcriptional clues to heme metabolism and identifying a previously unreported heme-binding protein in T. cruzi.

Luminal acetylation of microtubules is not essential for Plasmodium berghei and Toxoplasma gondii survival
Acetylation of α-tubulin at lysine 40 is not essential for cytoskeletal stability in Plasmodium berghei or Toxoplasma gondii, suggesting redundancy and plasticity in microtubule regulation in these parasites.

The dual-site agonist for human M2 muscarinic receptors Iper-8-naphtalimide induces mitochondrial dysfunction in Saccharomyces cerevisiae
S. cerevisiae is a model to study human GPCRs. N-8-Iper, active against glioblastoma via M2 receptor, causes mitochondrial damage in yeast by binding Ste2, highlighting evolutionary conservation of GPCRs.

Integrative Omics reveals changes in the cellular landscape of peroxisome-deficient pex3 yeast cells
To uncover the consequences of peroxisome deficiency, we compared Saccharomyces cerevisiae wild-type with pex3 cells, which lack peroxisomes, employing quantitative proteomics and transcriptomics technologies.

Regulation of extracellular vesicles for protein secretion in Aspergillus nidulans
Rebekkah E. Pope1, Patrick Ballmann2, Lisa Whitworth3 and Rolf A. Prade1,*
This study reveals that Aspergillus nidulans boosts extracellular vesicle production when ER-trafficked enzymes are induced, uncovering how fungi remodel their secretome through vesicle-mediated secretion to adapt to changing environments and biofilm formation.

Transcriptomic response to different heme sources in Trypanosoma cruzi epimastigotes
Evelyn Tevere1,a, María G. Mediavilla1,a, Cecilia B. Di Capua1, Marcelo L. Merli1, Carlos Robello2,3, Luisa Berná2,4 and Julia A. Cricco
This study uncovers how the Chagas disease parasite adapts to changes in heme, an essential molecule for its survival, providing transcriptional clues to heme metabolism and identifying a previously unreported heme-binding protein in T. cruzi.
Sir2 regulates selective autophagy in stationary-phase yeast cells
Ji-In Ryua, Juhye Junga, and Jeong-Yoon Kim
This study establishes Sir2 as a previously unrecognized regulator of selective autophagy during the stationary phase and highlight how cells dynamically control organelle degradation.
Filamentation protects Candida albicans from amphotericin B-induced programmed cell death via a mechanism involving the yeast metacaspase, MCA1
David J. Laprade, Melissa S. Brown#, Morgan L. McCarthy#, James J. Ritch, and Nicanor Austriaco
Candida albicans proliferates in two distinct cell types: blastopores and filaments. Programmed cell death is a controlled form of cell suicide that occurs when C. albicans cells are exposed to fungicidal drugs like amphotericin B and caspofungin, and to other stressful conditions. We provide evidence that programmed cell death is cell-type specific in yeast: Filamentous C. albicans cells are more resistant to amphotericin B- and caspofungin-induced programmed cell death than their blastospore counterparts. Our genetic data suggest that this phenomenon is mediated by a protective mechanism involving the yeast metacaspase, MCA1.
Formaldehyde fixation is detrimental to actin cables in glucose-depleted S. cerevisiae cells
Pavla Vasicova1,#, Mark Rinnerthaler2, Danusa Haskova1, Lenka Novakova1, Ivana Malcova1, Michael Breitenbach2, Jiri Hasek1
Actin filaments form cortical patches and emanating cables in fermenting cells of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. We assume that stability of actin cables reflects the metabolic status of the cell. Based on comparison of live and formaldehyde-fixed cells, our data suggest that formaldehyde affects respiration before fixation and this uneven signaling results in destabilization of actin cables in glucose-deprived cells.
Insights into dynamin-associated disorders through analysis of equivalent mutations in the yeast dynamin Vps1
Laila Moustaq, Iwona I. Smaczynska-de Rooij, Sarah E. Palmer, Christopher J. Marklew, Kathryn R. Ayscough
The dynamins represent a superfamily of proteins that have been shown to function in a wide range of membrane fusion and fission events. An increasing number of mutations in the human classical dynamins, Dyn-1 and Dyn-2 has been reported, with diseases caused by these changes ranging from Charcot-Marie-Tooth disorder to epileptic encephalopathies. This study aimed to use the dynamin-like protein Vps1 of Saccharomyces cerevisiae as a model to gain insights into the mechanistic defects caused by specific dynamin mutations considered to underlie a number of diseases.
Genomic saturation mutagenesis and polygenic analysis identify novel yeast genes affecting ethyl acetate production, a non-selectable polygenic trait
Tom Den Abt1,2, Ben Souffriau1,2, Maria R. Foulquié-Moreno1,2, Jorge Duitama3, and Johan M. Thevelein1,2
Isolation of mutants in populations of microorganisms has been a valuable tool in experimental genetics for decades. The main disadvantage, however, is the inability of isolating mutants in non-selectable polygenic traits. Our study shows that genomic saturation mutagenesis combined with complex trait polygenic analysis could be used successfully to identify causative alleles underlying many non-selectable, polygenic traits in small collections of haploid strains with multiple induced mutations.
Differentiated cytoplasmic granule formation in quiescent and non-quiescent cells upon chronological aging
Hsin-Yi Lee1,3,†, Kuo-Yu Cheng2,3,†, Jung-Chi Chao3 and Jun-Yi Leu3
Stationary phase cultures represent a complicated cell population comprising at least two different cell types, quiescent (Q) and non-quiescent (NQ) cells. The authors show that the cell fate of NQ cells is largely irreversible even if they are allowed to reenter mitosis. Their results reveal that the formation of different granule structures may represent the early stage of cell type differentiation in yeast stationary phase cultures.
Towards understanding the gliotoxin detoxification mechanism: in vivo thiomethylation protects yeast from gliotoxin cytotoxicity
Elizabeth B. Smith, Stephen K. Dolan, David A. Fitzpatrick, Sean Doyle and Gary W. Jones
Gliotoxin is a mycotoxin produced by some species of ascomycete fungi including the opportunistic human pathogen Aspergillus fumigatus. In order to produce gliotoxin the host organism needs to have evolved a self-protection mechanism. The authors demonstrate that the activity of a novel thiomethyltransferase is requiered for protection against exogenous gliotoxin and provide implications for understanding the evolution of gliotoxin self-protection mechanisms.
Mitochondrial proteomics of the acetic acid – induced programmed cell death response in a highly tolerant Zygosaccharomyces bailii – derived hybrid strain
Joana F Guerreiro1, Belém Sampaio-Marques2,3, Renata Soares4, Ana Varela Coelho4, Cecília Leão2,3, Paula Ludovico2,3, Isabel Sá-Correia1
Very high concentrations of acetic acid at low pH induce programmed cell death (PCD) in both the experimental model Saccharomyces cerevisiae and in Zygosaccharomyces bailii, the latter being considered the most problematic acidic food spoilage yeast due to its remarkable intrinsic resistance to this food preservative. This study offers insights into the mechanisms involved in acetic acid – induced PCD in the Z. bailii-derived hybrid strain ISA1307 by analyzing the yeast mitochondrial protein expression profile of cells challenged by acetic acid.
The transcriptional repressor Sum1p counteracts Sir2p in regulation of the actin cytoskeleton, mitochondrial quality control and replicative lifespan in Saccharomyces cerevisiae
Ryo Higuchi-Sanabria1, Jason D. Vevea1,3, Joseph K. Charalel1,4, Maria L. Sapar5, Liza A. Pon1,2
Increasing the stability or dynamics of the actin cytoskeleton can extend lifespan in C. elegans and S. cerevisiae. Actin cables of budding yeast, bundles of actin filaments that mediate cargo transport, affect lifespan control through effects on mitochondrial quality control. Here, we report that Sum1p and Sir2p inversely regulate actin and mitochondrial maintenance, as well as lifespan.
Inhibition of Aβ42 oligomerization in yeast by a PICALM ortholog and certain FDA approved drugs
Sei-Kyoung Park1, Kiira Ratia2, Mariam Ba1, Maria Valencik1 and Susan W. Liebman1,3
The formation of small Aβ42 oligomers has been implicated as a toxic species in Alzheimer disease (AD). Here, we show that the mechanism of the PICALM, human AD risk factor, is likely to reduce the level of Aβ42 oligomers in cells. We screened FDA-approved drugs to identify candidates that prevent the formation of Aβ42 small oligomers using the yeast Aβ42-RF reporter system. We also showed that each of the drug hits counteract yeast and mammalian cell toxicity associated with Aβ42 small aggregates.
A roadmap for designing narrow-spectrum antibiotics targeting bacterial pathogens
Xinyun Cao1,*, Robert Landick1,2, Elizabeth A. Campbell3
This comment discusses the article “Basis of narrow-spectrum activity of fidaxomicin on Clostridioides difficile” by Cao et al. (2022, Nature).
Breaking the clip for cargo unloading from motor proteins: mechanism and significance
Keisuke Obara1, and Takumi Kamura1
The mitochondrion is an essential organelle involved in ATP generation, lipid metabolism, regulation of calcium ions, etc. Therefore, it should be inherited properly by newly generated cells. In the budding yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae, mitochondria are passed on to daughter cells by the motor protein, Myo2, on the actin cable. The mitochondria and Myo2 are connected via the adaptor protein Mmr1. After reaching daughter cells, mitochondria are released from the actin-myosin machinery and move dynamically. In our recent paper (Obara K et al. (2022), Nat Commun, doi:10.1038/s41467-022-29704-8), we demonstrated that the regulated proteolysis of Mmr1 is required for the unloading of mitochondria from Myo2 in daughter cells. Sequential post-translational modifications of Mmr1, i.e., phosphorylation followed by ubiquitination, are essential for Mmr1 degradation and mitochondrial release from Myo2. Defects in Mmr1 degradation cause stacking and deformation of mitochondria at the bud-tip and bud-neck, where Myo2 accumulates. Compared to wild-type cells, mutant cells with defects in Mmr1 degradation possess an elevated mitochondrial membrane potential and produce higher levels of reactive oxygen species (ROS), along with hypersensitivity to oxidative stress.
Pirates of the haemoglobin
Daniel Akinbosede1, Robert Chizea1 and Stephen A. Hare1,†
Not all treasure is silver and gold; for pathogenic bacteria, iron is the most precious and the most pillaged of metallic elements. Iron is essential for the survival and growth of all life; however free iron is scarce for bacteria inside human hosts. As a mechanism of defence, humans have evolved ways to store iron so as to render it inaccessible for invading pathogens, such as keeping the metal bound to iron-carrying proteins. For bacteria to survive within humans, they must therefore evolve counters to this defence to compete with these proteins for iron binding, or directly steal iron from them. (…)
An ionophore breaks the multi-drug-resistance of Acinetobacter baumannii
David M.P. De Oliveira1 and Mark J. Walker1
Within intensive care units, multi-drug resistant Acinetobacter baumannii outbreaks are a frequent cause of ventilator-associated pneumonia. During the on-going COVID-19 pandemic, patients who receive ventilator support experience a 2-fold increased risk of mortality when they contract a secondary A. baumannii pulmonary infection. In our recent paper (De Oliveira et al. (2022), Mbio, doi: 10.1128/mbio.03517-21), we demonstrate that the 8-hydroxquinoline ionophore, PBT2 breaks the resistance of A. baumannii to tetracycline class antibiotics. In vitro, the combination of PBT2 and zinc with either tetracycline, doxycycline, or tigecycline was shown to be bactericidal against multi-drug-resistant A. baumannii, (…)
Endomembrane remodeling and dynamics in Salmonella infection
Ziyan Fang1 and Stéphane Méresse1
Salmonellae are bacteria that cause moderate to severe infections in humans, depending on the strain and the immune status of the infected host. These pathogens have the particularity of residing in the cells of the infected host. They are usually found in a vacuolar compartment that the bacteria shape with the help of effector proteins. Following invasion of a eukaryotic cell, the bacterial vacuole undergoes maturation characterized by changes in localization, composition and morphology. In particular, membrane tubules stretching over the microtubule cytoskeleton are formed from the bacterial vacuole. Although these tubules do not occur in all infected cells, they are functionally important and promote intracellular replication. This review focuses on the role and significance of membrane compartment remodeling observed in infected cells and the bacterial and host cell pathways involved.
The small bowel microbiome changes significantly with age and aspects of the ageing process
Gabriela Leite1, Mark Pimentel1,2, Gillian M. Barlow1 and Ruchi Mathur1,3
Gut microbiome changes have been associated with human ageing and implicated in age-related diseases including Alzheimer’s disease and Parkinson’s disease. However, studies to date have used stool samples, which do not represent the entire gut. Although more challenging to access, the small intestine plays critical roles in host metabolism and immune function. In this paper (Leite et al. (2021), Cell Reports, doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2021.109765), we demonstrate significant differences in the small intestinal microbiome in older subjects, (…)
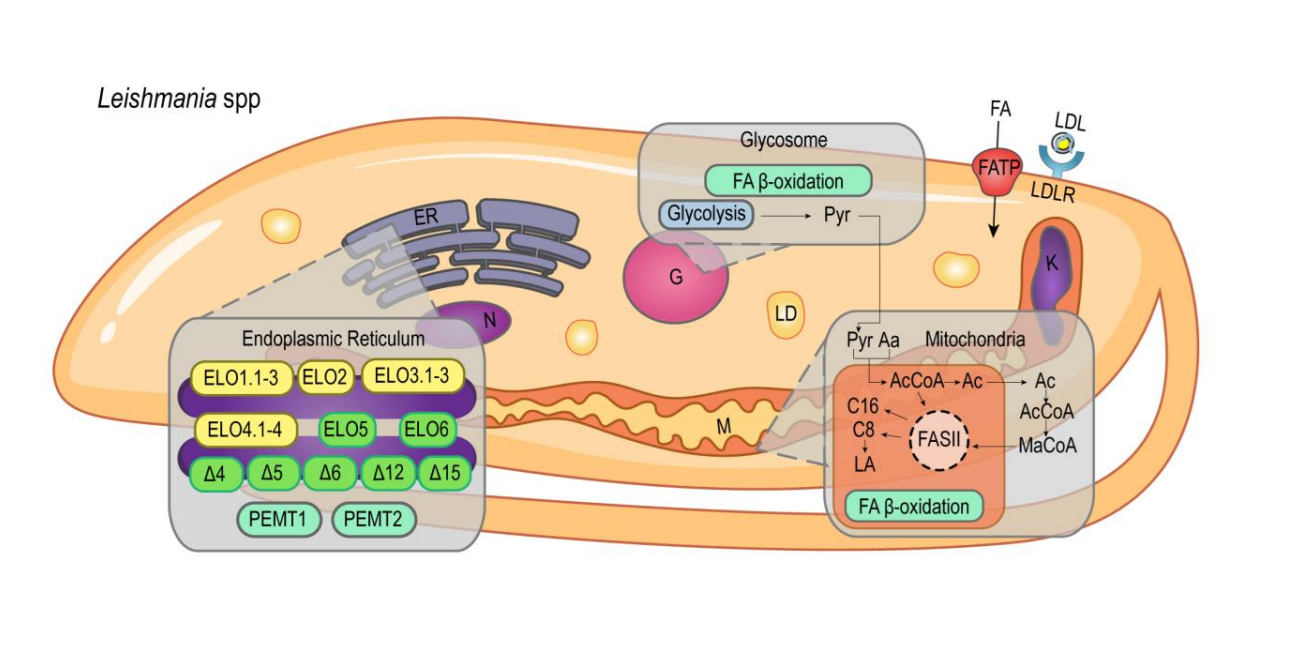
Lipid and fatty acid metabolism in trypanosomatids
Giovana Parreira de Aquino1,#, Marco Antonio Mendes Gomes1,#, Roberto Köpke Salinas2 and Maria Fernanda Laranjeira-Silva1
This work reviews specific aspects of lipid and fatty acid metabolism in the protozoan parasites T. brucei, T. cruzi, and Leishmania spp., as well as the pathways that have been explored for the development of new chemotherapies.
The emerging role of complex modifications of tRNALysUUU in signaling pathways
Patrick C. Thiaville1,2,3,4 and Valérie de Crécy-Lagard2,4
This comment discusses the article “Loss of wobble uridine modification in tRNA anticodons interferes with TOR pathway signaling” by Scheidt et al (Microbial Cell, 2014).
Only functional localization is faithful localization
Roland Lill1,2,3
This article comments on work published by Peleh et al. (Microbial Cell 2014), which analyzes the localization of Dre2 in Saccharomyces cerevisiae.
One cell, one love: a journal for microbial research
Didac Carmona-Gutierrez1, Guido Kroemer2-6 and Frank Madeo1
In this inaugural article of Microbial Cell, we highlight the importance of microbial research in general and the journal’s intention to serve as a publishing forum that supports and enfolds the scientific diversity in this area as it provides a unique, high-quality and universally accessible source of information and inspiration.
What’s the role of autophagy in trypanosomes?
Katherine Figarella1 and Néstor L. Uzcátegui1,2
This article comments on Proto et al. (Microbial Cell, 2014), who report first insights into the molecular mechanism of autophagy in African trypanosomes by generating reporter bloodstream form cell lines.
Microbial Cell
is an open-access, peer-reviewed journal that publishes exceptionally relevant research works that implement the use of unicellular organisms (and multicellular microorganisms) to understand cellular responses to internal and external stimuli and/or human diseases.
you can trust
Can’t find what you’re looking for?
You can browse all our issues and published articles here.
FAQs
Peer-reviewed, open-access research using unicellular organisms (and multicellular microorganisms) to understand cellular responses and human disease.
The journal (founded in 2014) is led by its Editors-in-Chief Frank Madeo, Didac Carmona-Gutierrez, and Guido Kroemer
Microbial Cell has been publishing original scientific literature since 2014, and from the very beginning has been managed by active scientists through an independent Publishing House (Shared science Publishers). The journal was conceived as a platform to acknowledge the importance of unicellular organisms, both as model systems as well as in the biological context of human health and disease.
Ever since, Microbial Cell has very positively developed and strongly grown into a respected journal in the unicellular research community and even beyond. This scientific impact is reflected in the yearly number of citations obtained by articles published in Microbial Cell, as recorded by the Web of Science (Clarivate, formerly Thomson/Reuters):

The scientific impact of Microbial Cell is also mirrored in a series of milestones:
2015: Microbial Cell is included in the Emerging Sources Citation Index (ESCI), a selection of developing journals drafted by Clarivate Analytics based on the candidate’s publishing standards, quality, editorial content, and citation data. Note: As an ESCI-selected journal, Microbial Cell is currently being evaluated in a rigorous and long process to determine an inclusion in the Science Citation Index Expanded (SCIE), which allows the official calculation of Clarivate Analytics’ impact factor.
2016: Microbial Cell is awarded the so-called DOAJ Seal by the selective Directory of Open Access Journals (DOAJ). The DOAJ Seal is an exclusive mark of certification for open access journals granted by DOAJ to journals that adhere to outstanding best practice and achieve an extra high and clear commitment to open access and high publishing standards.
2017: Microbial Cell is included in Pubmed Central (PMC), allowing the archiving of all the journal’s articles in PMC and PubMed.
2019: Microbial Cell is indexed in the prestigious abstract and citation database Scopus after a thorough selection process. This also means that Microbial Cell obtains, for the first time, an official Scopus CiteScore as well as an official journal ranking in the Scimago Journal and Country Ranking.
2022: Microbial Cell’s CiteScore reaches a value of 7.2 for the year 2021, positioning Microbial Cell among the top microbiology journals (previously available CiteScores: 2019: 5.4; 2020: 5.1).
2022: Microbial Cell is indexed in the highly selective Science Citation Index Expanded™, which covers approx. 9,500 of the world’s most impactful journals across 178 scientific disciplines. In their journal selection and curation process, Clarivate´s editors apply 24 ‘quality’ criteria and four ‘impact’ criteria to select the most influential journals in their respective fields. This selection is also a pre-requisite for inclusion in the JCR, which features the impact factor.
2022: Microbial Cell is listed in the Journal Citation Reports™ (JCR), and obtains its first official Journal Impact Factor™ (JIF) for the year 2021: 5.316.Check Article Types and Manuscript Preparation guidelines. Submit online via Scholastica.


Metabolic pathways further increase the complexity of cell size control in budding yeast
Jorrit M. Enserink
This article comments on work published by Soma et al. (Microbial Cell, 2014), which teased apart the effect of metabolism and growth rate on setting of critical cell size in Saccharomyces cerevisiae.