
Regulation of extracellular vesicles for protein secretion in Aspergillus nidulans
This study reveals that Aspergillus nidulans boosts extracellular vesicle production when ER-trafficked enzymes are induced, uncovering how fungi remodel their secretome through vesicle-mediated secretion to adapt to changing environments and biofilm formation.

Transcriptomic response to different heme sources in Trypanosoma cruzi epimastigotes
This study uncovers how the Chagas disease parasite adapts to changes in heme, an essential molecule for its survival, providing transcriptional clues to heme metabolism and identifying a previously unreported heme-binding protein in T. cruzi.

Luminal acetylation of microtubules is not essential for Plasmodium berghei and Toxoplasma gondii survival
Acetylation of α-tubulin at lysine 40 is not essential for cytoskeletal stability in Plasmodium berghei or Toxoplasma gondii, suggesting redundancy and plasticity in microtubule regulation in these parasites.

The dual-site agonist for human M2 muscarinic receptors Iper-8-naphtalimide induces mitochondrial dysfunction in Saccharomyces cerevisiae
S. cerevisiae is a model to study human GPCRs. N-8-Iper, active against glioblastoma via M2 receptor, causes mitochondrial damage in yeast by binding Ste2, highlighting evolutionary conservation of GPCRs.

Integrative Omics reveals changes in the cellular landscape of peroxisome-deficient pex3 yeast cells
To uncover the consequences of peroxisome deficiency, we compared Saccharomyces cerevisiae wild-type with pex3 cells, which lack peroxisomes, employing quantitative proteomics and transcriptomics technologies.

Regulation of extracellular vesicles for protein secretion in Aspergillus nidulans
Rebekkah E. Pope1, Patrick Ballmann2, Lisa Whitworth3 and Rolf A. Prade1,*
This study reveals that Aspergillus nidulans boosts extracellular vesicle production when ER-trafficked enzymes are induced, uncovering how fungi remodel their secretome through vesicle-mediated secretion to adapt to changing environments and biofilm formation.

Transcriptomic response to different heme sources in Trypanosoma cruzi epimastigotes
Evelyn Tevere1,a, María G. Mediavilla1,a, Cecilia B. Di Capua1, Marcelo L. Merli1, Carlos Robello2,3, Luisa Berná2,4 and Julia A. Cricco
This study uncovers how the Chagas disease parasite adapts to changes in heme, an essential molecule for its survival, providing transcriptional clues to heme metabolism and identifying a previously unreported heme-binding protein in T. cruzi.
Sir2 regulates selective autophagy in stationary-phase yeast cells
Ji-In Ryua, Juhye Junga, and Jeong-Yoon Kim
This study establishes Sir2 as a previously unrecognized regulator of selective autophagy during the stationary phase and highlight how cells dynamically control organelle degradation.

Unresolved mystery of cyclic nucleotide second messengers, periplasmic acid phosphatases and bacterial natural competence
Kristina Kronborg and Yong Everett Zhang
In this study we aimed to identify the promotors responsible for the expression of the non-specific acid phosphatase AphA during different starvation conditions, to confirm the requirement of the cAMP-dependent CRP regulon for aphA expression, and to finally identify regulators of its expression.

Polyadenylated versions of small non-coding RNAs in Saccharomyces cerevisiae are degraded by Rrp6p/Rrp47p independent of the core nuclear exosome
Anusha Chaudhuri1,#, Soumita Paul2,#, Mayukh Banerjea2 and Biswadip Das2
In this investigation, we unveiled a novel functional role of the major nuclear 3′→5′ exoribonuclease, Rrp6p, and its cofactor Rrp47p in the degradation of polyadenylated versions of several mature sncRNAs, including 5S, 5.8S rRNAs, all sn- and some select snoRNAs in the baker’s yeast S. cerevisiae.
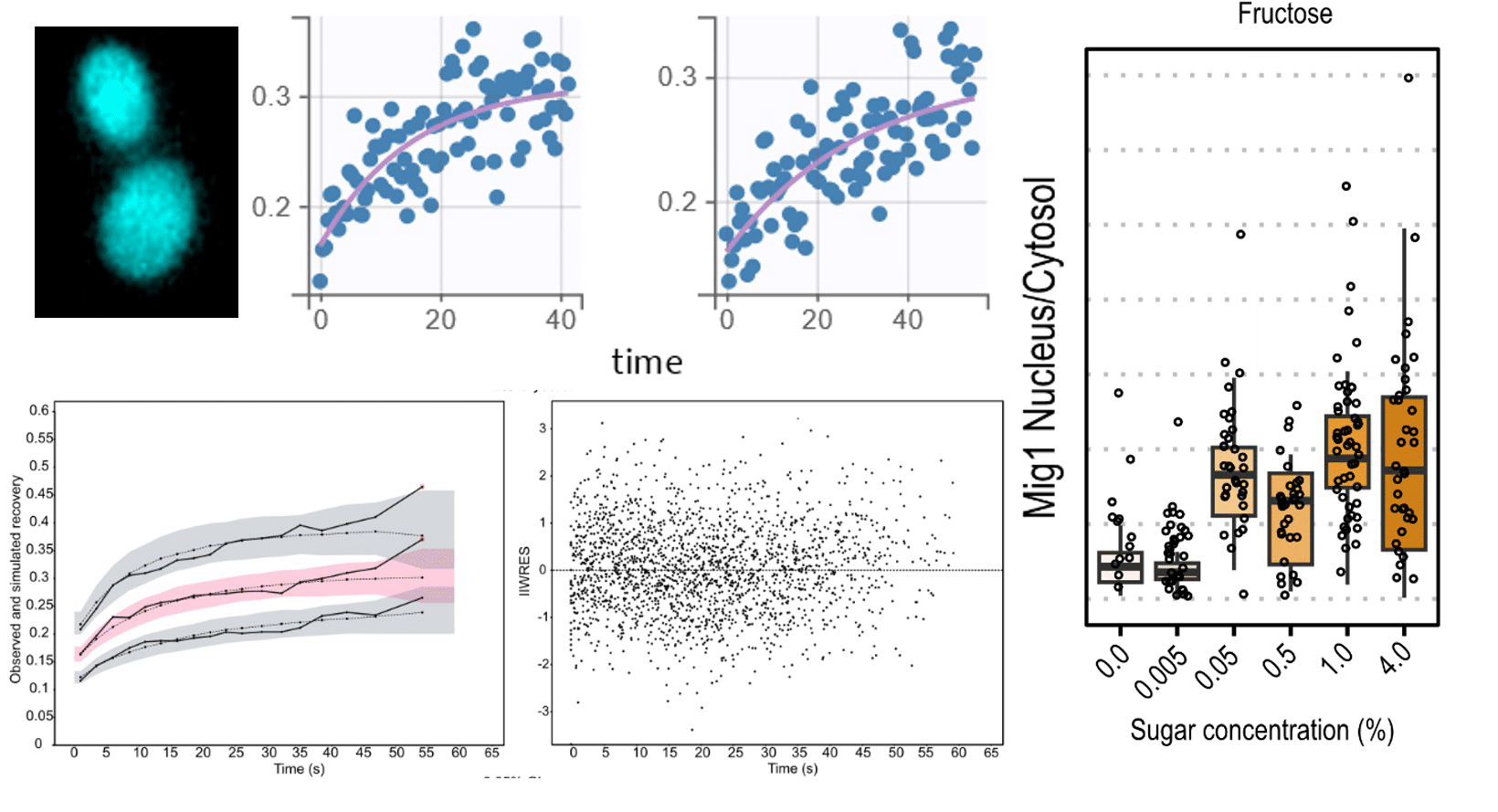
Exploring carbon source related localization and phosphorylation in the Snf1/Mig1 network using population and single cell-based approaches
Svenja Braam1, Farida Tripodi2, Linnea Österberg1,3, Sebastian Persson1, Niek Welkenhuysen1, Paola Coccetti2 and Marija Cvijovic1
In this work we set out to explore the relationship between the subcellular localization and regulation of kinases in the context of carbon source signaling. The data presented in this paper reinforce the notion that not only the activation/inactivation of kinases but also their subcellular localization and that of their targets influence fate decisions in response to environmental changes.

A Modular Cloning Toolkit for the production of recombinant proteins in Leishmania tarentolae
Katrin Hieronimus1,2,#, Tabea Donauer1,2,#, Jonas Klein1,#, Bastian Hinkel1,#, Julia Vanessa Spänle1,#, Anna Probst1,#, Justus Niemeyer1,#, Salina Kibrom1, Anna Maria Kiefer1, Luzia Schneider2, Britta Husemann2, Eileen Bischoff2, Sophie Möhring2, Nicolas Bayer1, Dorothée Klein1, Adrian Engels1, Benjamin Gustav Ziehmer2, Julian Stieß3, Pavlo Moroka1, Michael Schroda1, and Marcel Deponte2
Modular Cloning (MoClo) is based on libraries of standardized genetic parts that can be directionally assembled via Golden Gate cloning in one-pot reactions into transcription units and multigene constructs. We established a MoClo toolkit and exemplified its application for the production of recombinant proteins in L. tarentolae.
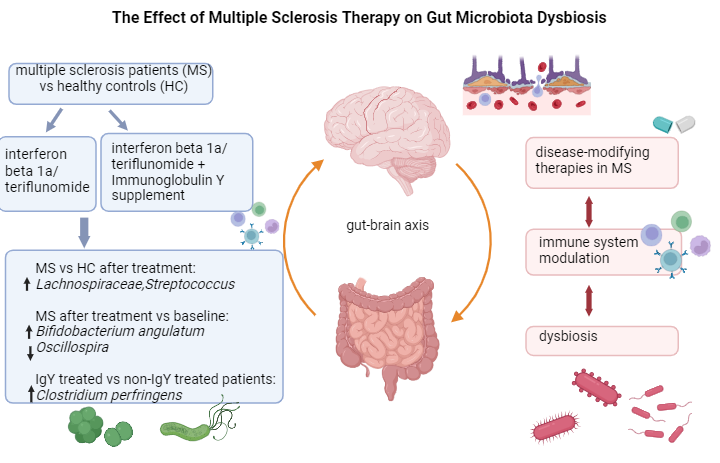
The effect of multiple sclerosis therapy on gut microbiota dysbiosis: a longitudinal prospective study
Andreea-Cristina Paraschiv1,a, Vitalie Vacaras1,2,a, Cristina Nistor1,2, Cristiana Vacaras3, Stefan Strilciuc1 and Dafin F Muresanu1,2
The gut microbiota, a complex ecosystem with various immune functions, plays a significant role in MS, and its response to different treatments is highlighted in this study. In clinical practice, maintaining a healthy microbiota is crucial for individuals with MS.
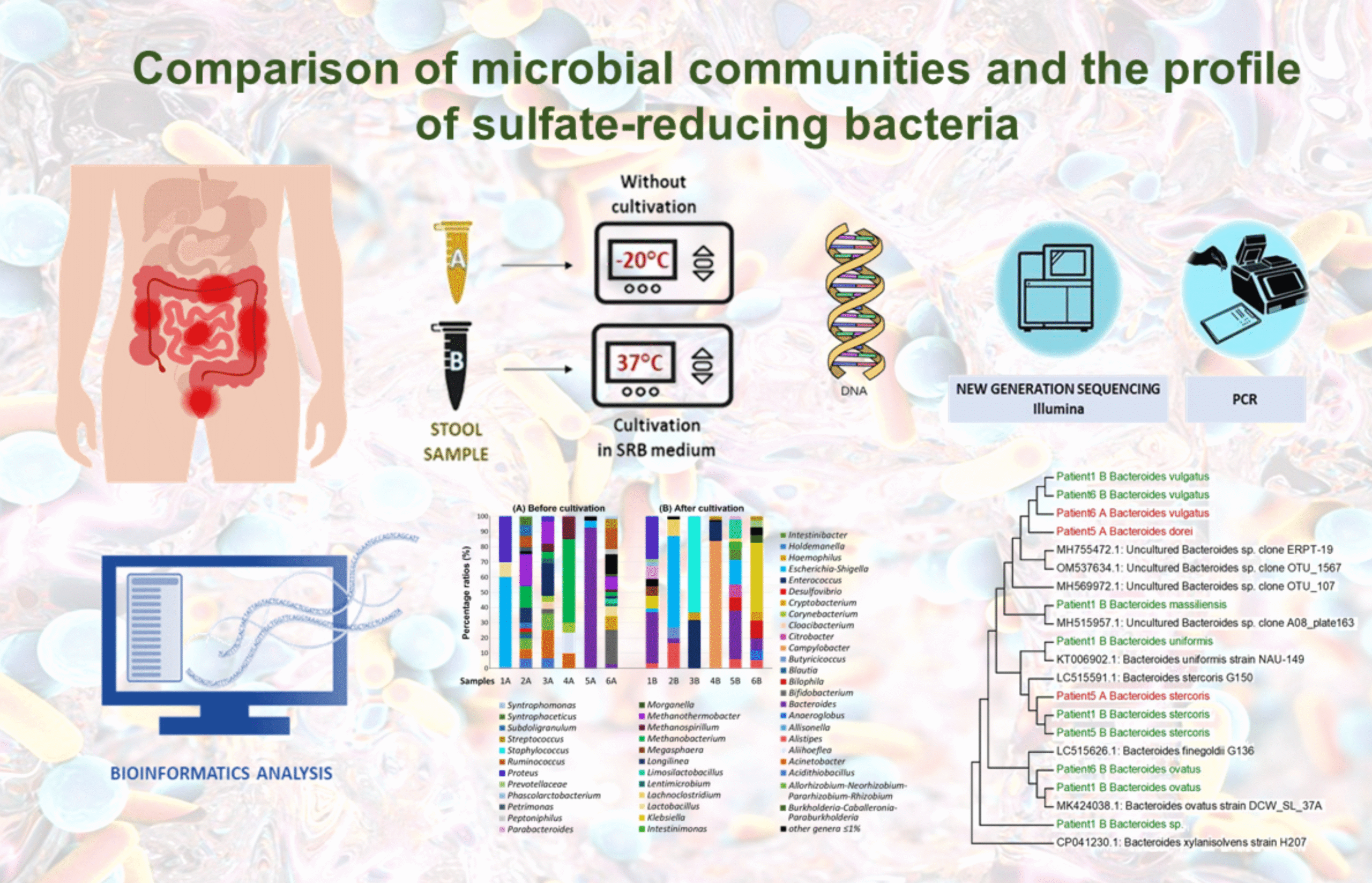
Comparison of microbial communities and the profile of sulfate-reducing bacteria in patients with ulcerative colitis and their association with bowel diseases: a pilot study
Ivan Kushkevych1, Kristýna Martínková1, Lenka Mráková1, Francesco Giudici2, Simone Baldi2, David Novak3, Márió Gajdács4, Monika Vítězová1, Dani Dordevic5, Amedeo Amedei2 and Simon K.-M. R. Rittmann6
Considerable evidence has accumulated regarding the molecular relationship between gut microbiota (GM) composition and the onset (clinical presentation and prognosis) of ulcerative colitis UC. Our findings highlight, among other observations, significant variations in the gut microbial composition among patients with varying disease severity and activity.

Replicative aging in yeast involves dynamic intron retention patterns associated with mRNA processing/export and protein ubiquitination
Jesús Gómez-Montalvo1, Alvaro de Obeso Fernández del Valle1, Luis Fernando De la Cruz Gutiérrez1, Jose Mario Gonzalez-Meljem1 and Christian Quintus Scheckhuber1
Saccharomyces cerevisiae has yielded relevant insights into some of the basic mechanisms of organismal aging. Among these are genomic instability, oxidative stress, caloric restriction and mitochondrial dysfunction. Our work uncovers a previously unexplored layer of the transcriptional program of yeast aging and, more generally, expands the knowledge on the occurrence of alternative splicing in baker´s yeast.
A Cinderella story: how the vacuolar proteases Pep4 and Prb1 do more than cleaning up the cell’s mass degradation processes
Winnie Kerstens1,2 and Patrick Van Dijck1,2
This review summarizes the expanded roles of the Saccharomyces cerevisiae vacuolar proteases Pep4 and Prb1 in non-vacuolar activities outside of autophagy, such as programmed cell death, protection from harmful protein forms, and gene expression regulation. The potential implications of these findings for fungal biology and drug target discovery, including insights for mammalian cell studies, are highlighted, emphasizing the need for a deeper understanding of these molecular processes.
The biosynthesis of pyoverdines
Michael T. Ringel1 and Thomas Brüser1
This review provides an overview of pyoverdine biosynthesis, emphasizing the distinctive fluorophore shared by various pyoverdines derived from ferribactins and the role of periplasmic processes in the maturation and modification of these siderophores, critical for the growth and colonization of hosts by fluorescent pseudomonads.
Toxin release mediated by the novel autolysin Cwp19 in Clostridium difficile
Imane El Meouche1 and Johann Peltier2,3
In this article, the authors comment on the study “Cwp19 is a novel lytic transglycosylase involved in stationary-phase autolysis resulting in toxin release in Clostridium difficile” by Wydau-Dematteis (MBio, 2018) that characterizes a novel peptidoglycan hydrolase, Cwp19, in Clostridioides difficile, highlighting its glucose-dependent mediation of toxins secretion and suggesting a potential role in the pathogenesis of this bacterium, contributing to the understanding of these enzymes in C. difficile and their implication in pathogenicity.
A global view of substrate phosphorylation and dephosphorylation during budding yeast mitotic exit
Sandra A. Touati1 and Frank Uhlmann1
In this article, the authors comment on the study “Phosphoproteome dynamics during mitotic exit in budding yeast” by Touati (EMBO J, 2018) that described a time-resolved global phosphoproteome analysis during a cell cycle phase known as mitotic exit in budding yeast revealed the principles of phosphoregulation governing the ordered sequence of events such as spindle elongation, chromosome decondensation, and completion of cell division.
Gammaretroviruses tether to mitotic chromatin by directly binding nucleosomal histone proteins
Madushi Wanaguru1 and Kate N. Bishop1
In this article, the authors comment on the study “Murine leukemia virus p12 tethers the capsid-containing pre-integration complex to chromatin by binding directly to host nucleosomes in mitosis” by Wanaguruet al. (PLoS Pathog, 2018) that highlights the essential role of the gammaretroviral gag cleavage product, p12, at both early and late stages of the virus life cycle, particularly in the integration of the viral DNA into the host cell chromatin to form a provirus. It also emphasizes the recent findings regarding the N- and C-terminal domains of p12, revealing their direct binding to the viral capsid lattice and nucleosomal histone proteins, respectively, thus elucidating the mechanism by which p12 links the viral pre-integration complex to mitotic chromatin.
Methodologies for in vitro and in vivo evaluation of efficacy of antifungal and antibiofilm agents and surface coatings against fungal biofilms
Patrick Van Dijck1,2,‡, Jelmer Sjollema3,‡, Bruno P.A. Cammue4,5, Katrien Lagrou6,7, Judith Berman8, Christophe d’Enfert9, David R. Andes10,11, Maiken C. Arendrup12-14, Axel A. Brakhage15, Richard Calderone16, Emilia Cantón17, Tom Coenye18,19, Paul Cos20, Leah E. Cowen21, Mira Edgerton22, Ana Espinel-Ingroff23, Scott G. Filler24, Mahmoud Ghannoum25, Neil A.R. Gow26, Hubertus Haas27, Mary Ann Jabra-Rizk28, Elizabeth M. Johnson29, Shawn R. Lockhart30, Jose L. Lopez-Ribot31, Johan Maertens32, Carol A. Munro26, Jeniel E. Nett33, Clarissa J. Nobile34, Michael A. Pfaller35,36, Gordon Ramage19,37, Dominique Sanglard38, Maurizio Sanguinetti39, Isabel Spriet40, Paul E. Verweij41, Adilia Warris42, Joost Wauters43, Michael R. Yeaman44, Sebastian A.J. Zaat45, Karin Thevissen4,*
This article highlights the critical importance of accurate susceptibility testing methods and the discovery of novel antifungal and antibiofilm agents in combating invasive fungal infections associated with biofilm formation on medical devices, thereby emphasizing the need for advancements in medical mycology research to address these complex diseases.
Shepherding DNA ends: Rif1 protects telomeres and chromosome breaks
Gabriele A. Fontana1, Julia K. Reinert1,2, Nicolas H. Thomä1, Ulrich Rass1
This review discusses the conserved mechanisms cells have evolved to protect DNA ends at chromosomal termini and DNA double-strand breaks (DSBs), focusing on the protein Rif1’s roles in telomere homeostasis and DSB repair in eukaryotes. It highlights the intriguing connection between Rif1’s involvement in both telomere maintenance and DSB repair, and suggests that excluding end-processing factors may underlie Rif1’s diverse biological functions at telomeres and chromosome breaks.
The CRISPR conundrum: evolve and maybe die, or survive and risk stagnation
Jesús García-Martínez1, Rafael D. Maldonado1, Noemí M. Guzmán1 and Francisco J. M. Mojica1,2
In this article García-Martínez et al. cover how the model bacterium Escherichia coli deals with CRISPR-Cas to tackle the major dilemma of evolution versus survival.
Non-genetic impact factors on chronological lifespan and stress resistance of baker’s yeast
Michael Sauer and Diethard Mattanovich
This article comments on work published by Bisschops et al. (Microbial Cell, 2015), which illustrates how important the choice of the experimental setup is and how culture conditions influcence cellular aging and survival in biotechnological processes.
What’s old is new again: yeast mutant screens in the era of pooled segregant analysis by genome sequencing
Chris Curtin and Toni Cordente
This article comments on work published by Den Abt et al. (Microbial Cell, 2016), which identified genes involved in ethyl acetate formation in a yeast mutant screen based on a new approach combining repeated rounds of chemical mutagenesis and pooled segregant analysis by whole genome sequencing.
The complexities of bacterial-fungal interactions in the mammalian gastrointestinal tract
Eduardo Lopez-Medina1 and Andrew Y. Koh2
This article comments on work published by Lopez-Medina et al. (PLoS Pathog, 2015) and Fan et al. (Nat Med, 2015), which utilize an “artificial” niche, the antibiotic-treated gut with concomitant pathogenic microbe expansion, to gain insight in bacterial-fungal interactions in clinically common scenarios.
Gearing up for survival – HSP-containing granules accumulate in quiescent cells and promote survival
Ruofan Yu and Weiwei Dang
This article comments on work published by Lee et al. (Microbial Cell, 2016), which reports that distinct granules are formed in quiescent and non-quiescent cells, which determines their respective cell fates.
Yeast screening platform identifies FDA-approved drugs that reduce Aβ oligomerization
Triana Amen1,2 and Daniel Kaganovich1
This article comments on work published by Park et al. (Microbial Cell, 2016), which discovered a number of small molecules capable of modulating Aβ aggregation in a yeast model.
Groupthink: chromosomal clustering during transcriptional memory
Kevin A. Morano
In this article, the authors comment on the study “NO1 transcriptional memory leads to DNA zip code-dependent interchromosomal clustering.” by Brickner et al. (Microbial Cell, 2015), discussing the importance and molecular mechanisms of chromosomal clustering during transcriptional memory.
Yeast proteinopathy models: a robust tool for deciphering the basis of neurodegeneration
Amit Shrestha1, 2 and Lynn A. Megeney1, 2, 3
Protein quality control or proteostasis is an essential determinant of basic cell health and aging. Eukaryotic cells have evolved a number of proteostatic mechanisms to ensure that proteins retain functional conformation, or are rapidly degraded when proteins misfold or self-aggregate. This article discusses the use of budding yeast as a robust proxy to study the intersection between proteostasis and neurodegenerative disease.
Microbial Cell
is an open-access, peer-reviewed journal that publishes exceptionally relevant research works that implement the use of unicellular organisms (and multicellular microorganisms) to understand cellular responses to internal and external stimuli and/or human diseases.
you can trust
Can’t find what you’re looking for?
You can browse all our issues and published articles here.
FAQs
Peer-reviewed, open-access research using unicellular organisms (and multicellular microorganisms) to understand cellular responses and human disease.
The journal (founded in 2014) is led by its Editors-in-Chief Frank Madeo, Didac Carmona-Gutierrez, and Guido Kroemer
Microbial Cell has been publishing original scientific literature since 2014, and from the very beginning has been managed by active scientists through an independent Publishing House (Shared science Publishers). The journal was conceived as a platform to acknowledge the importance of unicellular organisms, both as model systems as well as in the biological context of human health and disease.
Ever since, Microbial Cell has very positively developed and strongly grown into a respected journal in the unicellular research community and even beyond. This scientific impact is reflected in the yearly number of citations obtained by articles published in Microbial Cell, as recorded by the Web of Science (Clarivate, formerly Thomson/Reuters):

The scientific impact of Microbial Cell is also mirrored in a series of milestones:
2015: Microbial Cell is included in the Emerging Sources Citation Index (ESCI), a selection of developing journals drafted by Clarivate Analytics based on the candidate’s publishing standards, quality, editorial content, and citation data. Note: As an ESCI-selected journal, Microbial Cell is currently being evaluated in a rigorous and long process to determine an inclusion in the Science Citation Index Expanded (SCIE), which allows the official calculation of Clarivate Analytics’ impact factor.
2016: Microbial Cell is awarded the so-called DOAJ Seal by the selective Directory of Open Access Journals (DOAJ). The DOAJ Seal is an exclusive mark of certification for open access journals granted by DOAJ to journals that adhere to outstanding best practice and achieve an extra high and clear commitment to open access and high publishing standards.
2017: Microbial Cell is included in Pubmed Central (PMC), allowing the archiving of all the journal’s articles in PMC and PubMed.
2019: Microbial Cell is indexed in the prestigious abstract and citation database Scopus after a thorough selection process. This also means that Microbial Cell obtains, for the first time, an official Scopus CiteScore as well as an official journal ranking in the Scimago Journal and Country Ranking.
2022: Microbial Cell’s CiteScore reaches a value of 7.2 for the year 2021, positioning Microbial Cell among the top microbiology journals (previously available CiteScores: 2019: 5.4; 2020: 5.1).
2022: Microbial Cell is indexed in the highly selective Science Citation Index Expanded™, which covers approx. 9,500 of the world’s most impactful journals across 178 scientific disciplines. In their journal selection and curation process, Clarivate´s editors apply 24 ‘quality’ criteria and four ‘impact’ criteria to select the most influential journals in their respective fields. This selection is also a pre-requisite for inclusion in the JCR, which features the impact factor.
2022: Microbial Cell is listed in the Journal Citation Reports™ (JCR), and obtains its first official Journal Impact Factor™ (JIF) for the year 2021: 5.316.Check Article Types and Manuscript Preparation guidelines. Submit online via Scholastica.



Similar environments but diverse fates: Responses of budding yeast to nutrient deprivation.
Saul M. Honigberg
Diploid budding yeast (Saccharomyces cerevisiae) can adopt one of several alternative differentiation fates in response to nutrient limitation, and each of these fates provides distinct biological functions. When different strain backgrounds are taken into account, these various fates occur in response to similar environmental cues, are regulated by the same signal transduction pathways, and share many of the same master regulators. I propose that the relationships between fate choice, environmental cues and signaling pathways are not Boolean, but involve graded levels of signals, pathway activation and master-regulator activity.