
Regulation of extracellular vesicles for protein secretion in Aspergillus nidulans
This study reveals that Aspergillus nidulans boosts extracellular vesicle production when ER-trafficked enzymes are induced, uncovering how fungi remodel their secretome through vesicle-mediated secretion to adapt to changing environments and biofilm formation.

Transcriptomic response to different heme sources in Trypanosoma cruzi epimastigotes
This study uncovers how the Chagas disease parasite adapts to changes in heme, an essential molecule for its survival, providing transcriptional clues to heme metabolism and identifying a previously unreported heme-binding protein in T. cruzi.

Luminal acetylation of microtubules is not essential for Plasmodium berghei and Toxoplasma gondii survival
Acetylation of α-tubulin at lysine 40 is not essential for cytoskeletal stability in Plasmodium berghei or Toxoplasma gondii, suggesting redundancy and plasticity in microtubule regulation in these parasites.

The dual-site agonist for human M2 muscarinic receptors Iper-8-naphtalimide induces mitochondrial dysfunction in Saccharomyces cerevisiae
S. cerevisiae is a model to study human GPCRs. N-8-Iper, active against glioblastoma via M2 receptor, causes mitochondrial damage in yeast by binding Ste2, highlighting evolutionary conservation of GPCRs.

Integrative Omics reveals changes in the cellular landscape of peroxisome-deficient pex3 yeast cells
To uncover the consequences of peroxisome deficiency, we compared Saccharomyces cerevisiae wild-type with pex3 cells, which lack peroxisomes, employing quantitative proteomics and transcriptomics technologies.

Regulation of extracellular vesicles for protein secretion in Aspergillus nidulans
Rebekkah E. Pope1, Patrick Ballmann2, Lisa Whitworth3 and Rolf A. Prade1,*
This study reveals that Aspergillus nidulans boosts extracellular vesicle production when ER-trafficked enzymes are induced, uncovering how fungi remodel their secretome through vesicle-mediated secretion to adapt to changing environments and biofilm formation.

Transcriptomic response to different heme sources in Trypanosoma cruzi epimastigotes
Evelyn Tevere1,a, María G. Mediavilla1,a, Cecilia B. Di Capua1, Marcelo L. Merli1, Carlos Robello2,3, Luisa Berná2,4 and Julia A. Cricco
This study uncovers how the Chagas disease parasite adapts to changes in heme, an essential molecule for its survival, providing transcriptional clues to heme metabolism and identifying a previously unreported heme-binding protein in T. cruzi.
Sir2 regulates selective autophagy in stationary-phase yeast cells
Ji-In Ryua, Juhye Junga, and Jeong-Yoon Kim
This study establishes Sir2 as a previously unrecognized regulator of selective autophagy during the stationary phase and highlight how cells dynamically control organelle degradation.
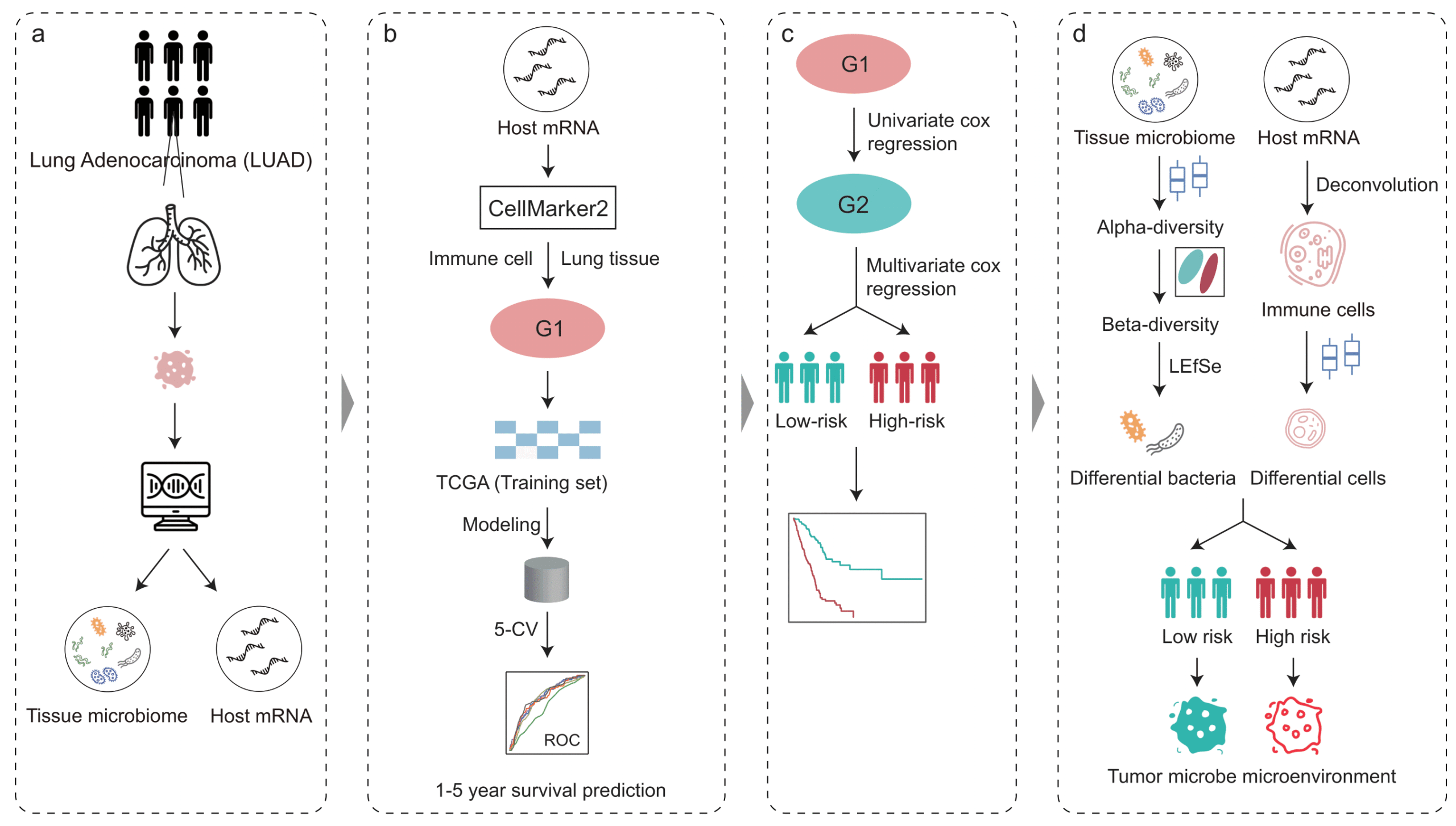
Predictable regulation of survival by intratumoral microbe-immune crosstalk in patients with lung adenocarcinoma
Shuo Shi1, Yuwen Chu2,3, Haiyan Liu4,5, Lan Yu6,7,8, Dejun Sun8,9, Jialiang Yang2,3,5, Geng Tian2,3, Lei Ji2,3, Cong Zhang10 and Xinxin Lu11
Intratumoral microbiota can regulate the tumor immune microenvironment (TIME) and mediate tumor prognosis by promoting inflammatory response or inhibiting anti-tumor effects. Our study demonstrated that intratumoral microbiota-immune crosstalk was strongly associated with prognosis in LUAD patients, which would provide new targets for the development of precise therapeutic strategies.

The last two transmembrane helices in the APC-type FurE transporter act as an intramolecular chaperone essential for concentrative ER-exit
Yiannis Pyrris1, Georgia F. Papadaki1, Emmanuel Mikros2 and George Diallinas1,3
FurE is a H+ symporter specific for the cellular uptake of uric acid, allantoin, uracil, and toxic nucleobase analogues in the fungus Aspergillus nidulans. Being member of the NCS1 protein family, FurE is structurally related to the APC-superfamily of transporters.

Basal level of ppGpp coordinates Escherichia coli cell heterogeneity and ampicillin resistance and persistence
Paulina Katarzyna Grucela1 and Yong Everett Zhang1
The universal stringent response alarmone ppGpp (guanosine penta and tetra phosphates) plays a crucial role in various aspects of fundamental cell physiology (e.g., cell growth rate, cell size) and thus bacterial tolerance to and survival of external stresses, including antibiotics. In tihs study, we discuss the fundamental role of basal level of ppGpp in regulating cell homogeneity and ampicillin persistence.
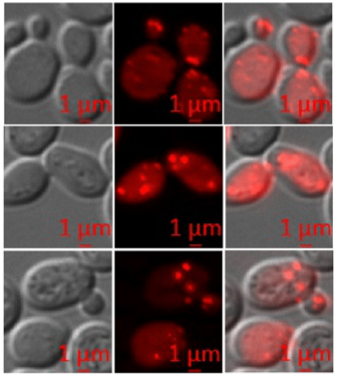
Investigation of the acetic acid stress response in Saccharomyces cerevisiae with mutated H3 residues
Nitu Saha1, Swati Swagatika1 and Raghuvir Singh Tomar1
Yeast cells respond to acetic acid in diverse ways. Here, we have elucidated the deleterious effects of acetic acid on different histone mutants
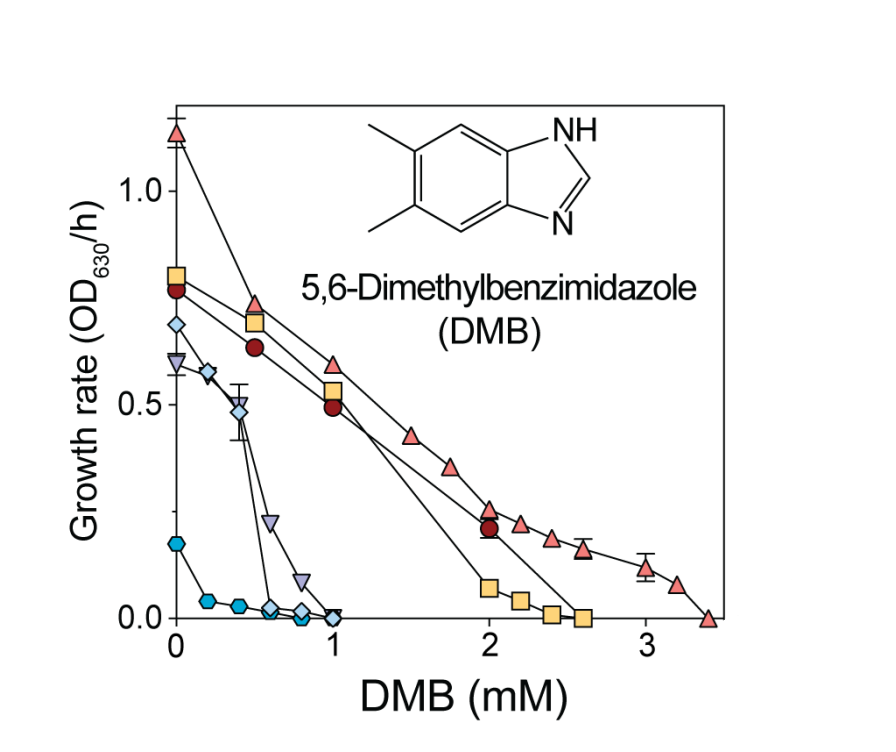
The coenzyme B12 precursor 5,6-dimethylbenzimidazole is a flavin antagonist in Salmonella
Lahiru Malalasekara1 and Jorge C. Escalante-Semerena1,*
Here we investigated why 5,6-dimethylbenzimidazole (DMB) inhibits in S. Typhimurium. Briefly, we determined that the structural similarities of the substituted benzene ring of DMB with the isoalloxazine moiety of flavins is responsible for the deleterious effects of this CoB12 precursor.
Guidelines for DNA recombination and repair studies: Mechanistic assays of DNA repair processes
Hannah L Klein1, Kenny K.H. Ang2, Michelle R. Arkin2, Emily C. Beckwitt3,4, Yi-Hsuan Chang5, Jun Fan6, Youngho Kwon7,8, Michael J. Morten1, Sucheta Mukherjee9, Oliver J. Pambos6, Hafez el Sayyed6, Elizabeth S. Thrall10, João P. Vieira-da-Rocha9, Quan Wang11, Shuang Wang12,13, Hsin-Yi Yeh5, Julie S. Biteen14, Peter Chi5,15, Wolf-Dietrich Heyer9,16, Achillefs N. Kapanidis6, Joseph J. Loparo10, Terence R. Strick12,13,17, Patrick Sung7,8, Bennett Van Houten3,18,19, Hengyao Niu11 and Eli Rothenberg1
Mechanistic assays of DNA repair processes are a powerful tools but each comes with its particular advantages and limitations. Here the most commonly used assays are reviewed, discussed, and presented as the guidelines for future studies.
Imbalance in gut microbes from babies born to obese mothers increases gut permeability and myeloid cell adaptations that provoke obesity and NAFLD
Taylor K. Soderborg1 and Jacob E. Friedman1,2,3
This article comments on work published by Soderborg et al. (Nat Commun, 2018), which demonstrates a causative role of early life microbiome dysbiosis in infants born to mothers with obesity in novel pathways that promote developmental programming of NAFLD.
Retroviral integration site selection: a running Gag?
Paul Lesbats1,2,3 and Vincent Parissi1,2,3
In this article, the authors comment on the study “Structural basis for spumavirus GAG tethering to chromatin” by Lesbats et al. (Proc Natl Acad Sci, 2018) that revealed that the Gag protein of the spumaretrovirus prototype foamy virus (PFV) directly interacts with the nucleosome acidic patch, acting as a chromatin tether, and its disruption leads to delocalization of viral particles and integration sites, shedding light on the importance of retroviral structural proteins in the selection of integration sites.
Insights into the host-pathogen interaction: C. albicans manipulation of macrophage pyroptosis
Teresa R. O’Meara1 and Leah E. Cowen1
In this article, the authors comment on the study “High-Throughput Screening Identifies Genes Required for Candida albicans Induction of Macrophage Pyroptosis” by O’Meara et al. (MBio, 2018) that provides a comprehensive analysis of the genetic circuitry in both Candida albicans and host macrophages that leads to pyroptosis, revealing the impact of altered pyroptosis on infection, the role of pyroptosis in facilitating neutrophil accumulation at the site of C. albicans infection, and the decoupling of inflammasome priming and activation in the response to C. albicans infection, thus shedding new light on the factors governing the outcomes of this interaction.
A comparative approach to decipher intestinal animal-microbe associations
Keisuke Nakashima1
In this article, the authors comment on the study “Chitin-based barrier immunity and its loss predated mucus-colonization by indigenous gut microbiota” by Nakashima et al. (Nat Commun, 2018) that used comparative analyses of chordates to investigate the development of animal-microbe associations, suggesting that microbial colonization of the mucus layer over mammalian gastrointestinal epithelium was established upon the loss of ancestral chitin-based barrier immunity, providing insights into the establishment of these associations in an evolutionary context.
Pathways of host cell exit by intracellular pathogens
Antje Flieger1,#, Freddy Frischknecht2, Georg Häcker3, Mathias W. Hornef4, Gabriele Pradel5
This review provides an overview of the diverse host cell exit strategies employed by intracellular-living bacterial, fungal, and protozoan pathogens, highlighting the commonalities and system-specific variations of these strategies, and discussing potential microbial molecules involved in host cell exit as targets for future intervention approaches.
An unexpected benefit from E. coli: how enterobactin benefits host health
Aileen K. Sewell1,2, Min Han1,2 and Bin Qi1,2
In this article, the authors comment on the study “Microbial Siderophore Enterobactin Promotes Mitochondrial Iron Uptake and Development of the Host via Interaction with ATP Synthase” by Qi et al. (Cell, 2018) that uncovered a surprising role for the Escherichia coli-produced siderophore enterobactin (Ent) in facilitating iron uptake by the host, marking a major shift in the understanding of its function and indicating potential new benefits from commensal bacteria in aiding the host’s iron homeostasis.
Protective roles of ginseng against bacterial infection
Ye-Ram Kim1 and Chul-Su Yang1
This review highlights the antibacterial effects of ginseng against pathogenic bacterial infections, discussing its regulation of pathogenic factors and proposing the therapeutic potential of ginseng as a natural antibacterial drug to address antibiotic resistance and toxicity in the context of global public health challenges.
Means of intracellular communication: touching, kissing, fusing
Anne Spang1
This work highlights different aspects of communication between organelles, including the importance of organellar contact sites.
Neuropathogenesis caused by Trypanosoma brucei, still an enigma to be unveiled
Katherine Figarella1
This Editorial addresses the meningo-encephalitic stage of Trypanosoma brucei infection and the resultig neuropathogenesis as well as the impact that the application of tools developed in the last years in the field of neuroscience will have on the study of neglected tropical diseases.
Lichens – growing greenhouses en miniature
Martin Grube1
This commentary article provides an overview on different aspects of lichen biology and the remarkable symbiotic association between fungi and algae.
Regulation of the mitochondrial permeability transition pore and its effects on aging
Damiano Pellegrino-Coppola1
Aging is linked to mitochondrial function, with the mitochondrial permeability transition pore (mPTP) playing a key role. Yeast is a useful model for studying how mPTP affects cell survival, aging, and related diseases.
Fungal infections in humans: the silent crisis
Katharina Kainz1, Maria A. Bauer1, Frank Madeo1-3 and Didac Carmona-Gutierrez1
This article highlights the growing global threat of fungal infections – exacerbated by rising drug resistance and medical practices – and emphasizes the urgent need for intensified research to develop more effective antifungal strategies.
Digesting the crisis: autophagy and coronaviruses
Didac Carmona-Gutierrez1, Maria A. Bauer1, Andreas Zimmermann1,2, Katharina Kainz1,
Sebastian J. Hofer1, Guido Kroemer3-7 and Frank Madeo1,2,8
This article reviews the multifaceted role of autophagy in antiviral defense and highlights how coronaviruses, including SARS-CoV-2, interact with this pathway, raising the possibility that targeting autophagy could offer novel therapeutic strategies against COVID-19.
Microbial Cell
is an open-access, peer-reviewed journal that publishes exceptionally relevant research works that implement the use of unicellular organisms (and multicellular microorganisms) to understand cellular responses to internal and external stimuli and/or human diseases.
you can trust
Can’t find what you’re looking for?
You can browse all our issues and published articles here.
FAQs
Peer-reviewed, open-access research using unicellular organisms (and multicellular microorganisms) to understand cellular responses and human disease.
The journal (founded in 2014) is led by its Editors-in-Chief Frank Madeo, Didac Carmona-Gutierrez, and Guido Kroemer
Microbial Cell has been publishing original scientific literature since 2014, and from the very beginning has been managed by active scientists through an independent Publishing House (Shared science Publishers). The journal was conceived as a platform to acknowledge the importance of unicellular organisms, both as model systems as well as in the biological context of human health and disease.
Ever since, Microbial Cell has very positively developed and strongly grown into a respected journal in the unicellular research community and even beyond. This scientific impact is reflected in the yearly number of citations obtained by articles published in Microbial Cell, as recorded by the Web of Science (Clarivate, formerly Thomson/Reuters):

The scientific impact of Microbial Cell is also mirrored in a series of milestones:
2015: Microbial Cell is included in the Emerging Sources Citation Index (ESCI), a selection of developing journals drafted by Clarivate Analytics based on the candidate’s publishing standards, quality, editorial content, and citation data. Note: As an ESCI-selected journal, Microbial Cell is currently being evaluated in a rigorous and long process to determine an inclusion in the Science Citation Index Expanded (SCIE), which allows the official calculation of Clarivate Analytics’ impact factor.
2016: Microbial Cell is awarded the so-called DOAJ Seal by the selective Directory of Open Access Journals (DOAJ). The DOAJ Seal is an exclusive mark of certification for open access journals granted by DOAJ to journals that adhere to outstanding best practice and achieve an extra high and clear commitment to open access and high publishing standards.
2017: Microbial Cell is included in Pubmed Central (PMC), allowing the archiving of all the journal’s articles in PMC and PubMed.
2019: Microbial Cell is indexed in the prestigious abstract and citation database Scopus after a thorough selection process. This also means that Microbial Cell obtains, for the first time, an official Scopus CiteScore as well as an official journal ranking in the Scimago Journal and Country Ranking.
2022: Microbial Cell’s CiteScore reaches a value of 7.2 for the year 2021, positioning Microbial Cell among the top microbiology journals (previously available CiteScores: 2019: 5.4; 2020: 5.1).
2022: Microbial Cell is indexed in the highly selective Science Citation Index Expanded™, which covers approx. 9,500 of the world’s most impactful journals across 178 scientific disciplines. In their journal selection and curation process, Clarivate´s editors apply 24 ‘quality’ criteria and four ‘impact’ criteria to select the most influential journals in their respective fields. This selection is also a pre-requisite for inclusion in the JCR, which features the impact factor.
2022: Microbial Cell is listed in the Journal Citation Reports™ (JCR), and obtains its first official Journal Impact Factor™ (JIF) for the year 2021: 5.316.Check Article Types and Manuscript Preparation guidelines. Submit online via Scholastica.




The long and winding road of reverse genetics in Trypanosoma cruzi
Miguel A. Chiurillo1 and Noelia Lander1
This Editorial provides a brief historic overview that highlights the strengths and weaknesses of the molecular strategies that have been developed to genetically modify Trypanosoma cruzi, emphasizing the future directions of the field.