
Regulation of extracellular vesicles for protein secretion in Aspergillus nidulans
This study reveals that Aspergillus nidulans boosts extracellular vesicle production when ER-trafficked enzymes are induced, uncovering how fungi remodel their secretome through vesicle-mediated secretion to adapt to changing environments and biofilm formation.

Transcriptomic response to different heme sources in Trypanosoma cruzi epimastigotes
This study uncovers how the Chagas disease parasite adapts to changes in heme, an essential molecule for its survival, providing transcriptional clues to heme metabolism and identifying a previously unreported heme-binding protein in T. cruzi.

Luminal acetylation of microtubules is not essential for Plasmodium berghei and Toxoplasma gondii survival
Acetylation of α-tubulin at lysine 40 is not essential for cytoskeletal stability in Plasmodium berghei or Toxoplasma gondii, suggesting redundancy and plasticity in microtubule regulation in these parasites.

The dual-site agonist for human M2 muscarinic receptors Iper-8-naphtalimide induces mitochondrial dysfunction in Saccharomyces cerevisiae
S. cerevisiae is a model to study human GPCRs. N-8-Iper, active against glioblastoma via M2 receptor, causes mitochondrial damage in yeast by binding Ste2, highlighting evolutionary conservation of GPCRs.

Integrative Omics reveals changes in the cellular landscape of peroxisome-deficient pex3 yeast cells
To uncover the consequences of peroxisome deficiency, we compared Saccharomyces cerevisiae wild-type with pex3 cells, which lack peroxisomes, employing quantitative proteomics and transcriptomics technologies.

Regulation of extracellular vesicles for protein secretion in Aspergillus nidulans
Rebekkah E. Pope1, Patrick Ballmann2, Lisa Whitworth3 and Rolf A. Prade1,*
This study reveals that Aspergillus nidulans boosts extracellular vesicle production when ER-trafficked enzymes are induced, uncovering how fungi remodel their secretome through vesicle-mediated secretion to adapt to changing environments and biofilm formation.

Transcriptomic response to different heme sources in Trypanosoma cruzi epimastigotes
Evelyn Tevere1,a, María G. Mediavilla1,a, Cecilia B. Di Capua1, Marcelo L. Merli1, Carlos Robello2,3, Luisa Berná2,4 and Julia A. Cricco
This study uncovers how the Chagas disease parasite adapts to changes in heme, an essential molecule for its survival, providing transcriptional clues to heme metabolism and identifying a previously unreported heme-binding protein in T. cruzi.
Sir2 regulates selective autophagy in stationary-phase yeast cells
Ji-In Ryua, Juhye Junga, and Jeong-Yoon Kim
This study establishes Sir2 as a previously unrecognized regulator of selective autophagy during the stationary phase and highlight how cells dynamically control organelle degradation.
The first taxonomic and functional characterization of human CAVD-associated microbiota
Lavinia Curini1,#, Brunilda Alushi2,#, Mary Roxana Christopher3, Simone Baldi1, Leandro Di Gloria4, Pierluigi Stefano5, Anna Laganà5, Luisa Iannone5, Herko Grubitzsch6, Ulf Landmesser7, Matteo Ramazzotti4, Elena Niccolai1,§, Alexander Lauten2,§ and Amedeo Amedei1,8,§
Calcific aortic valve disease (CAVD) is the most common heart valve disorder, defined by a remodeling multistep process. In this study, we aimed to investigate and characterize the presence of valvular microbiota and the associated immune response in human CAV samples originating from two European populations.

Cellular cholesterol licenses Legionella pneumophila intracellular replication in macrophages
Edna Ondari1,#, Ashley Wilkins1,#, Brian Latimer3, Ana-Maria Dragoi2,3 and Stanimir S. Ivanov1
Host membranes are inherently critical for niche homeostasis of vacuolar pathogens such as Legionella. One membrane component that is often subverted by vacuolar bacteria is cholesterol. We provide experimental evidence that cellular cholesterol promotes L. pneumophila replication within a membrane bound organelle in infected macrophages.
DadY (PA5303) is required for fitness of Pseudomonas aeruginosa when growth is dependent on alanine catabolism
Ronnie L. Fulton1 and Diana M. Downs1
Pseudomonas aeruginosa inhabits diverse environmental niches that can have varying nutrient composition. The ubiquity of this organism is facilitated by a metabolic strategy that preferentially utilizes low-energy, non-fermentable organic acids, such as amino acids, rather than the high-energy sugars preferred by many other microbes. The amino acid alanine is among the preferred substrates of P. aeruginosa. The dad locus encodes the constituents of the alanine catabolic pathway of P. aeruginosa. Physiological roles for DadR (AsnC-type transcriptional activator), DadX (alanine racemase), and DadA (D-amino acid dehydrogenase) have been defined in this pathway. An additional protein, PA5303, is encoded in the dad locus in P. aeruginosa. PA5303 is a member of the ubiquitous Rid protein superfamily and is designated DadY based on the data presented herein. (…)
Multiple genome analysis of Candida glabrata clinical isolates renders new insights into genetic diversity and drug resistance determinants
Pedro Pais1,2,3,#, Mónica Galocha1,2,3,#, Azusa Takahashi-Nakaguchi4, Hiroji Chibana4 and Miguel C. Teixeira1,2,3
The emergence of drug resistance significantly hampers the treatment of human infections, including those caused by fungal pathogens such as Candida species. Candida glabrata ranks as the second most common cause of candidiasis worldwide, supported by rapid acquisition of resistance to azole and echinocandin antifungals frequently prompted by single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) in resistance associated genes, such as PDR1 (azole resistance) or FKS1/2 (echinocandin resistance). To determine the frequency of polymorphisms and genome rearrangements as the possible genetic basis of C. glabrata drug resistance, we assessed genomic variation across 94 globally distributed isolates with distinct resistance phenotypes, whose sequence is deposited in GenBank. The(…)
Up-regulation of Osh6 boosts an anti-aging membrane trafficking pathway toward vacuoles
Ilham Kadhim1, Nazneen Begum1, William King1, Licheng Xu1 and Fusheng Tang1
Members of the family of oxysterol-binding proteins mediate non-vesicular lipid transport between membranes and contribute to longevity in different manners. We previously found that a 2-fold up-regulation of Osh6, one of seven yeast oxysterol-binding proteins, remedies vacuolar morphology defects in mid-aged cells, partly down-regulates the target of rapamycin complex 1 (TORC1), and increases the replicative lifespan. At the molecular level, Osh6 transports phosphatidylserine (PS) and phosphatidylinositol-4-phosphate (PI4P) between the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) and the plasma membrane (PM). To decipher how an ER-PM working protein controls vacuolar morphology, we tested genetic interactions between OSH6 and DRS2, whose protein flips PS from the lumen to the cytosolic side of the Golgi, the organelle between ER and vacuoles in many pathways. Up-regulated (…)
Investigating the role of G-quadruplexes at Saccharomyces cerevisiae telomeres
Sonia Stinus1, Fernando R. Rosas Bringas1, Lisa Wanders1, and Michael Chang1
In this study, the authors examine the in vivo relevance of telomeric G-quadruplexes in the budding yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae by expressing a mutant telomerase RNA subunit (tlc1-tm) that introduces mutant telomeric repeats instead to the distal ends of telomeres. (…)
Air- and dustborne fungi in repositories of the National Archive of the Republic of Cuba
Sofia Borrego1, Isbel Vivar1 and Alian Molina1
This study has as objectives to determine the concentration and diversity of the air- and dustborne mycobiota in seven National Archive of the Republic of Cuba repositories, and to assess the potential risk of biodeterioration that iso-lated taxa may have. In the indoor and outdoor environmental microbiological samplings a SAS biocollector was used and the indoor/outdoor (I/O) ratio was determined for each repository. The settled dust was collected during six months. Sørensen’s coefficient of similarity (QS) was calculated to compare the isolated taxa among the three studied niches (indoor air, dust, outdoor air). The biodegradation potential of the isolated taxa was determined by semi-quantitative tests. The concentrations in the air of repositories with natural cross-ventilation ranged from 225.2-750.3 CFU m-3, while in the Map library with air-conditioning (…)
Cleavage-defective Topoisomerase I mutants sharply increase G-quadruplex-associated genomic instability
Alexandra Berroyer1,2, Albino Bacolla3, John A. Tainer2,3,4 and Nayun Kim1,2
Topoisomerase 1 (Top1) removes transcription-associated helical stress to suppress G4-formation and its induced recombination at genomic loci containing guanine-run containing sequences. Interestingly, Top1 binds tightly to G4 structures, and its inhibition or depletion can cause elevated instability at these genomic loci. Top1 is targeted by the widely used anti-cancer chemotherapeutic camptothecin (CPT) and its derivatives, which stabilize Top1 covalently attached on a DNA nick and prevent the re-ligation step. Here we investigated how CPT-resistance conferring Top1 mutants, which emerge in cancer patients and cells treated with CPT, affect G4-induced genomic instability in S. cerevisiae. We found that Top1 mutants form stable complexes with G4 DNA and that expression of Top1 cleavage-defective mutants but not a DNA-binding-defective (…)
Gut microbiota and ankylosing spondylitis: current insights and future challenges
Andrei Lobiuc1, Liliana Groppa2, Lia Chislari2, Eugeniu Russu2,3, Marinela Homitchi2,3, Camelia Ciorescu2,3, Sevag Hamamah4, I. Codruta Bran1 and Mihai Covasa1
This review explores the growing role of gut microbiota in AS and its potential to reshape targeted treatment strategies and facilitate development of adjunct therapies to address disease onset and progression.
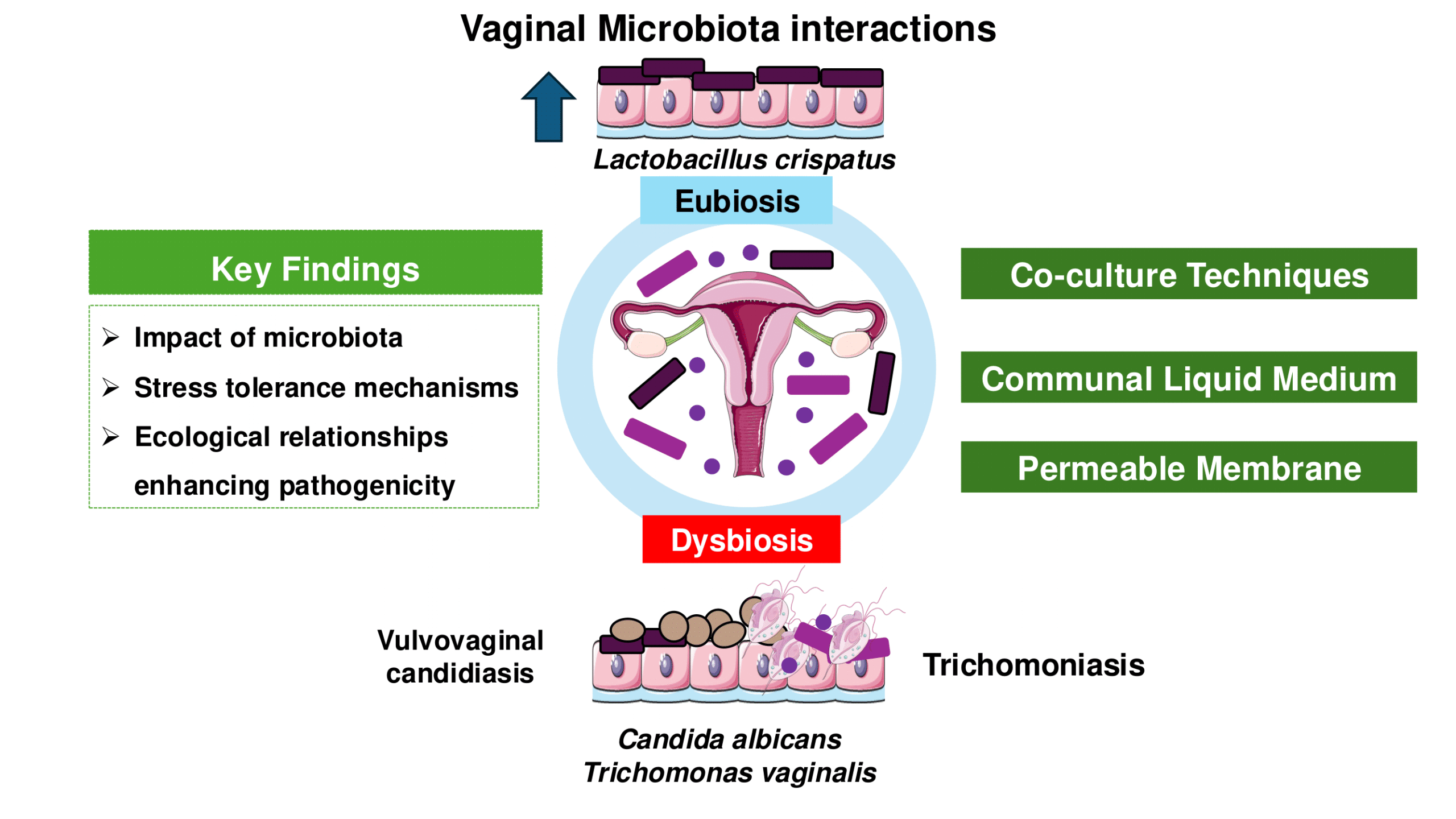
Advancements in vaginal microbiota, Trichomonas vaginalis, and vaginal cell interactions: Insights from co-culture assays
Fernanda Gomes Cardoso and Tiana Tasca
This review updates co-culture and co-incubation techniques for studying interactions of Lactobacillus spp., representing a pre-dominant member of the healthy vaginal microbiota; Candida spp., the most abundant yeast in the vagina, and T. vaginalis, responsible for the most widespread nonviral STI worldwide.
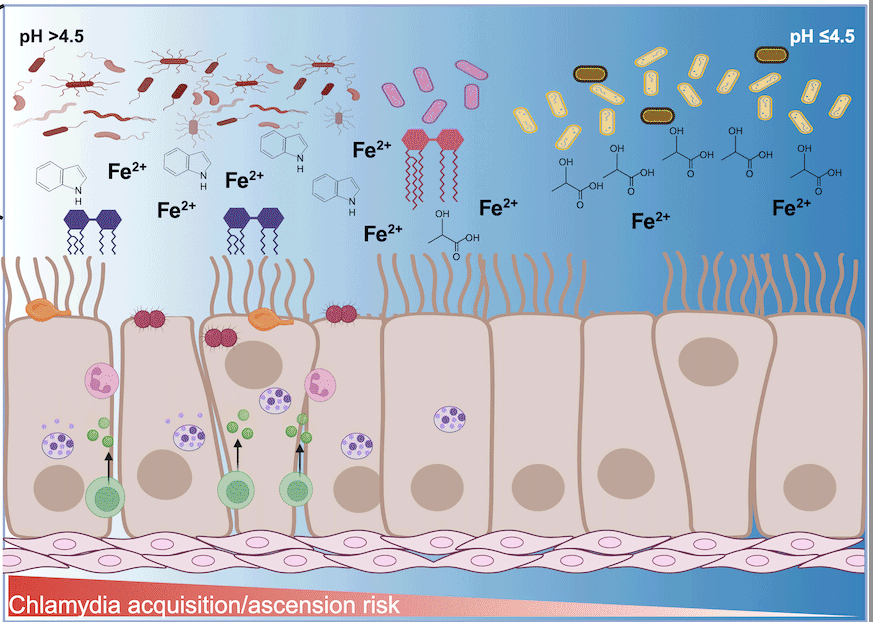
Influence of cervicovaginal microbiota on Chlamydia trachomatis infection dynamics
Emily Hand1, Indriati Hood-Pishchany1,2, Toni Darville1,2 and Catherine M. O’Connell2
This review examines the complex interplay between the cervicovaginal microbiome, C. trachomatis infection, and host immune responses, highlighting the role of metabolites such as short-chain and long-chain fatty acids, indole, and iron in modulating pathogen survival and host defenses.
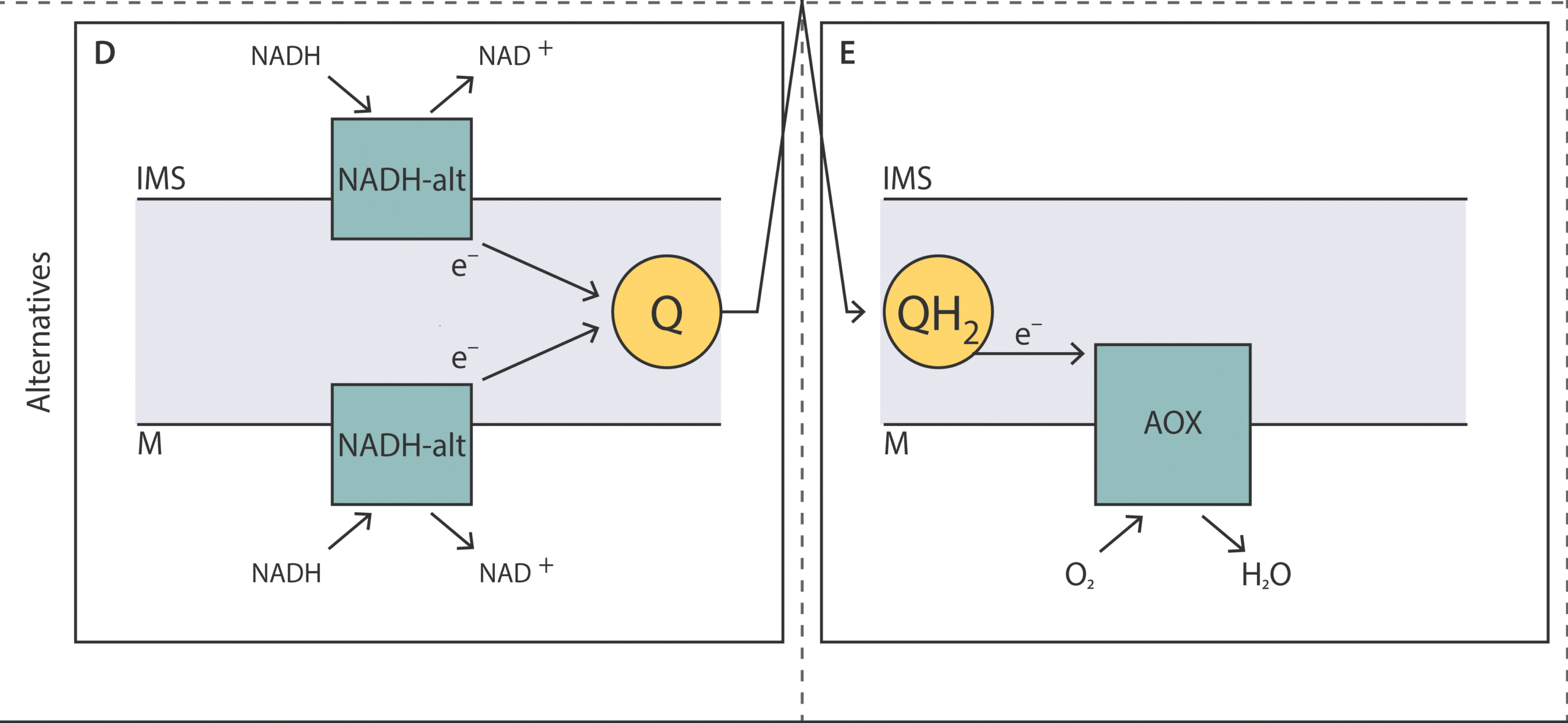
Unveiling the molecular architecture of the mitochondrial respiratory chain of Acanthamoeba castellanii
Christian Q. Scheckhuber1, Sutherland K. Maciver2 and Alvaro de Obeso Fernandez del Valle1
This review provides a comprehensive overview of the mitochondrial res-piratory chain in A. castellanii, focusing on the key alternative components involved in oxidative phosphorylation and their roles in energy metabolism, stress response, and adaptation to various conditions.

Paving the way for new antimicrobial peptides through molecular de-extinction
Karen O. Osiro1, Abel Gil-Ley2, Fabiano C. Fernandes1,3, Kamila B. S. de Oliveira2, Cesar de la Fuente-Nunez4-7, Octavio L. Franco1,2
The advancement of artificial intelligence and molecular de-extinction offers a valuable opportunity not only to discover new antimicrobials but also to provide accurate in silico predictions, thereby shortening the path to addressing the global antibiotic resistance crisis.

Efflux pumps: gatekeepers of antibiotic resistance in Staphylococcus aureus biofilms
Shweta Sinha1, Shifu Aggarwal2,3 and Durg Vijai Singh1
This review aims to elucidate the complex relationship between efflux pumps, antibiotic resistance and biofilm formation in S. aureus with the aim to aid in the development of potential therapeutic targets for combating S. aureus infections, especially those associated with biofilms.

Understanding the molecular mechanisms of human diseases: the benefits of fission yeasts
Lajos Acs-Szabo, Laszlo-Attila Papp and Ida Miklos
Here we collect the latest laboratory protocols and bioinformatics tools for the fission yeasts to highlight the many possibilities available to the research community. In addition, we present several limiting factors that everyone should be aware of when working with yeast models.
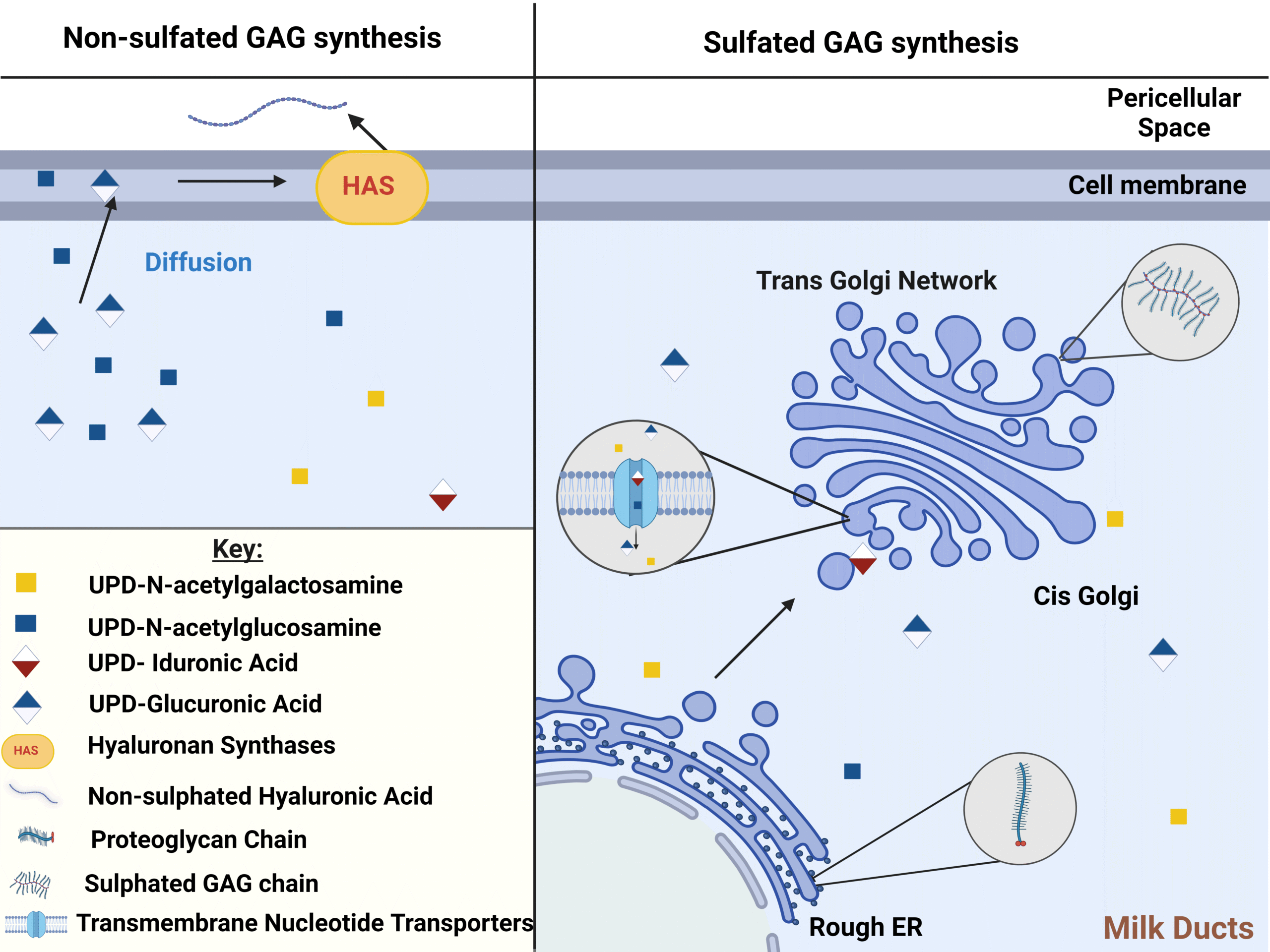
Characterising glycosaminoglycans in human breastmilk and their potential role in infant health
Melissa Greenwood1,2, Patricia Murciano-Martínez3, Janet Berrington4, Sabine L Flitsch5, Sean Austin2 and Christopher Stewart1
Glycosaminoglycans are bioactive components present in breast milk and play a potential key role in determining infant health yet are overlooked by many contemporary studies. This review explores their relevance, use and characterisation techniques.
Ribose 5-phosphate: the key metabolite bridging the metabolisms of nucleotides and amino acids during stringent response in Escherichia coli?
Paulina Katarzyna Grucela1, Tobias Fuhrer2, Uwe Sauer2, Yanjie Chao3 and Yong Everett Zhang1
Here we propose the metabolite ribose 5’-phosphate as the key link between nucleotide and amino acid metabolisms and a working model integrating both the transcriptional and metabolic effects of (p)ppGpp on E. coli physiological adaptation during the stringent response.
Flagellated bacterial porter for in situ tumor vaccine
Haiheng Xu1, Yiqiao Hu1, 2 and Jinhui Wu1, 2, 3
Cancer immunotherapy, which use the own immune system to attack tumors, are increasingly popular treatments. But, due to the tumor immunosuppressive microenvironment, the antigen presentation in the tumor is limited. Recently, a growing number of people use bacteria to stimulate the body’s immunity for tumor treatment due to bacteria themselves have a variety of elements that activate Toll-like receptors. Here, we discuss the use of motility of flagellate bacteria to transport antigens to the tumor periphery to activate peritumoral dendritic cells to enhance the effect of in situ tumor vaccines.
The rise of Candida auris: from unique traits to co-infection potential
Nadine B. Egger1,§, Katharina Kainz1,§, Adina Schulze1, Maria A. Bauer1, Frank Madeo1-3 and Didac Carmona-Gutierrez1
Candida auris is a multidrug resistant (MDR) fungal pathogen with a crude mortality rate of 30-60%. First identified in 2009, C. auris has been rapidly rising to become a global risk in clinical settings and was declared an urgent health threat by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). A concerted global action is thus needed to successfully tackle the challenges created by this emerging fungal pathogen. In this brief article, we underline the importance of unique virulence traits, including its easy transformation, its persistence outside the host and its resilience against multiple cellular stresses, as well as of environmental factors that have mainly contributed to the rise of this superbug.
A hundred spotlights on microbiology: how microorganisms shape our lives
Didac Carmona-Gutierrez1, Katharina Kainz1, Andreas Zimmermann1, Sebastian J. Hofer1, Maria A. Bauer1, Christoph Ruckenstuhl1, Guido Kroemer2-4 and Frank Madeo1,5,6
Viral, bacterial, fungal and protozoal biology is of cardinal importance for the evolutionary history of life, ecology, biotechnology and infectious diseases. Various microbiological model systems have fundamentally contributed to the understanding of molecular and cellular processes, including the cell cycle, cell death, mitochondrial biogenesis, vesicular fusion and autophagy, among many others. Microbial interactions within the environment have profound effects on many fields of biology, from ecological diversity to the highly complex and multifaceted impact of the microbiome on human health. Also, biotechnological innovation and corresponding industrial operations strongly depend on microbial engineering. With this wide range of impact in mind, the peer-reviewed (…)
Yeast goes viral: probing SARS-CoV-2 biology using S. cerevisiae
Brandon Ho1, Raphael Loll-Krippleber1 and Grant W. Brown1
The budding yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae has long been an outstanding platform for understanding the biology of eukaryotic cells. Robust genetics, cell biology, molecular biology, and biochemistry complement deep and detailed genome annotation, a multitude of genome-scale strain collections for functional genomics, and substantial gene conservation with Metazoa to comprise a powerful model for modern biological research. Recently, the yeast model has demonstrated its utility in a perhaps unexpected area, that of eukaryotic virology. Here we discuss three innovative applications of the yeast model system to reveal functions and investigate variants of proteins encoded by the SARS-CoV-2 virus.
Murals meet microbes: at the crossroads of microbiology and cultural heritage
Maria A. Bauer1, Katharina Kainz1, Christoph Ruckenstuhl1, Frank Madeo1-3 and Didac Carmona-Gutierrez1
This article comments on the duality of microorganisms in the conservation and restoration of cultural heritage, which encompasses the negative impact of damaging microorganisms and recent advances in using specific microorganisms and microbial-based technologies for cultural heritage preservation.
Urm1, not quite a ubiquitin-like modifier?
Lars Kaduhr1, Cindy Brachmann1, Keerthiraju Ethiraju Ravichandran2,3, James D. West4, Sebastian Glatt2 and Raffael Schaffrath1
This article comments on work published by Brachmann et al. (Redox Biol, 2020), which studied urmylation of the yeast 2-Cys peroxiredoxin Ahp1, uncovering that promiscuous lysine target sites and specific redox requirements determine the Urm1 acceptor activity of the peroxiredoxin.
Microbial Cell
is an open-access, peer-reviewed journal that publishes exceptionally relevant research works that implement the use of unicellular organisms (and multicellular microorganisms) to understand cellular responses to internal and external stimuli and/or human diseases.
you can trust
Can’t find what you’re looking for?
You can browse all our issues and published articles here.
FAQs
Peer-reviewed, open-access research using unicellular organisms (and multicellular microorganisms) to understand cellular responses and human disease.
The journal (founded in 2014) is led by its Editors-in-Chief Frank Madeo, Didac Carmona-Gutierrez, and Guido Kroemer
Microbial Cell has been publishing original scientific literature since 2014, and from the very beginning has been managed by active scientists through an independent Publishing House (Shared science Publishers). The journal was conceived as a platform to acknowledge the importance of unicellular organisms, both as model systems as well as in the biological context of human health and disease.
Ever since, Microbial Cell has very positively developed and strongly grown into a respected journal in the unicellular research community and even beyond. This scientific impact is reflected in the yearly number of citations obtained by articles published in Microbial Cell, as recorded by the Web of Science (Clarivate, formerly Thomson/Reuters):

The scientific impact of Microbial Cell is also mirrored in a series of milestones:
2015: Microbial Cell is included in the Emerging Sources Citation Index (ESCI), a selection of developing journals drafted by Clarivate Analytics based on the candidate’s publishing standards, quality, editorial content, and citation data. Note: As an ESCI-selected journal, Microbial Cell is currently being evaluated in a rigorous and long process to determine an inclusion in the Science Citation Index Expanded (SCIE), which allows the official calculation of Clarivate Analytics’ impact factor.
2016: Microbial Cell is awarded the so-called DOAJ Seal by the selective Directory of Open Access Journals (DOAJ). The DOAJ Seal is an exclusive mark of certification for open access journals granted by DOAJ to journals that adhere to outstanding best practice and achieve an extra high and clear commitment to open access and high publishing standards.
2017: Microbial Cell is included in Pubmed Central (PMC), allowing the archiving of all the journal’s articles in PMC and PubMed.
2019: Microbial Cell is indexed in the prestigious abstract and citation database Scopus after a thorough selection process. This also means that Microbial Cell obtains, for the first time, an official Scopus CiteScore as well as an official journal ranking in the Scimago Journal and Country Ranking.
2022: Microbial Cell’s CiteScore reaches a value of 7.2 for the year 2021, positioning Microbial Cell among the top microbiology journals (previously available CiteScores: 2019: 5.4; 2020: 5.1).
2022: Microbial Cell is indexed in the highly selective Science Citation Index Expanded™, which covers approx. 9,500 of the world’s most impactful journals across 178 scientific disciplines. In their journal selection and curation process, Clarivate´s editors apply 24 ‘quality’ criteria and four ‘impact’ criteria to select the most influential journals in their respective fields. This selection is also a pre-requisite for inclusion in the JCR, which features the impact factor.
2022: Microbial Cell is listed in the Journal Citation Reports™ (JCR), and obtains its first official Journal Impact Factor™ (JIF) for the year 2021: 5.316.Check Article Types and Manuscript Preparation guidelines. Submit online via Scholastica.



It takes four to tango: the cooperative adventure of scientific publishing
Didac Carmona-Gutierrez1,2, Katharina Kainz1 and Frank Madeo1-3
This Editorial is the 500th article published in Microbial Cell, a journey that started in 2014 and has seen the journal grow steadily and maintain itself as a respected community platform. The foundation that has allowed for and driven this development – as for any responsible journal – is composed of four essential pillars: the readers, the authors, the editors and the referees.