
Regulation of extracellular vesicles for protein secretion in Aspergillus nidulans
This study reveals that Aspergillus nidulans boosts extracellular vesicle production when ER-trafficked enzymes are induced, uncovering how fungi remodel their secretome through vesicle-mediated secretion to adapt to changing environments and biofilm formation.

Transcriptomic response to different heme sources in Trypanosoma cruzi epimastigotes
This study uncovers how the Chagas disease parasite adapts to changes in heme, an essential molecule for its survival, providing transcriptional clues to heme metabolism and identifying a previously unreported heme-binding protein in T. cruzi.

Luminal acetylation of microtubules is not essential for Plasmodium berghei and Toxoplasma gondii survival
Acetylation of α-tubulin at lysine 40 is not essential for cytoskeletal stability in Plasmodium berghei or Toxoplasma gondii, suggesting redundancy and plasticity in microtubule regulation in these parasites.

The dual-site agonist for human M2 muscarinic receptors Iper-8-naphtalimide induces mitochondrial dysfunction in Saccharomyces cerevisiae
S. cerevisiae is a model to study human GPCRs. N-8-Iper, active against glioblastoma via M2 receptor, causes mitochondrial damage in yeast by binding Ste2, highlighting evolutionary conservation of GPCRs.

Integrative Omics reveals changes in the cellular landscape of peroxisome-deficient pex3 yeast cells
To uncover the consequences of peroxisome deficiency, we compared Saccharomyces cerevisiae wild-type with pex3 cells, which lack peroxisomes, employing quantitative proteomics and transcriptomics technologies.

Regulation of extracellular vesicles for protein secretion in Aspergillus nidulans
Rebekkah E. Pope1, Patrick Ballmann2, Lisa Whitworth3 and Rolf A. Prade1,*
This study reveals that Aspergillus nidulans boosts extracellular vesicle production when ER-trafficked enzymes are induced, uncovering how fungi remodel their secretome through vesicle-mediated secretion to adapt to changing environments and biofilm formation.

Transcriptomic response to different heme sources in Trypanosoma cruzi epimastigotes
Evelyn Tevere1,a, María G. Mediavilla1,a, Cecilia B. Di Capua1, Marcelo L. Merli1, Carlos Robello2,3, Luisa Berná2,4 and Julia A. Cricco
This study uncovers how the Chagas disease parasite adapts to changes in heme, an essential molecule for its survival, providing transcriptional clues to heme metabolism and identifying a previously unreported heme-binding protein in T. cruzi.
Sir2 regulates selective autophagy in stationary-phase yeast cells
Ji-In Ryua, Juhye Junga, and Jeong-Yoon Kim
This study establishes Sir2 as a previously unrecognized regulator of selective autophagy during the stationary phase and highlight how cells dynamically control organelle degradation.
Trehalose-6-phosphate promotes fermentation and glucose repression in Saccharomyces cerevisiae
Rebeca L. Vicente1,2, Lucie Spina1, Jose P.L. Gómez1, Sebastien Dejean3, Jean-Luc Parrou1 and Jean Marie François1,4
This study examined the capability of trehalose-6-phosphate synthase (TPS1) homologues from various species to complement the phenotypic defects of a Saccharomyces cerevisiae tps1 mutant, resulting in the classification of complementation into different groups based on metabolic patterns and fermentation capacity, shedding light on the role of TPS1 and trehalose-6-phosphate (T6P) as critical factors in sugar fermentation and glucose repression.
The translationally controlled tumor protein TCTP is involved in cell cycle progression and heat stress response in the bloodstream form of Trypanosoma brucei
Borka Jojic1, Simona Amodeo1,2 and Torsten Ochsenreiter1
This study reveals the involvement of the translationally controlled tumor protein TCTP in cell cycle regulation and heat stress response in the bloodstream form of Trypanosoma brucei, shedding light on its role in these cellular processes.
Single telomere length analysis in Ustilago maydis, a high-resolution tool for examining fungal telomere length distribution and C-strand 5’-end processing
Ganduri Swapna1, Eun Young Yu1 and Neal F. Lue1, 2
This article introduces the development of single telomere length analysis (STELA) for Ustilago maydis, a basidiomycete fungus, enabling the precise measurement of telomere lengths and distributions. The study demonstrates STELA’s utility in revealing the existence of relatively short telomeres in wild-type cells, preferential loss of long telomeres in a mutant defective in telomere replication, and the characterization of telomere C-strand 5’ ends, highlighting U. maydis as a strong model for telomere research.
Temporal analysis of the autophagic and apoptotic phenotypes in Leishmania parasites
Louise Basmaciyan1, Laurence Berry2, Julie Gros3, Nadine Azas3 and Magali Casanova3
This article details a comprehensive analysis of miltefosine-induced cell death and autophagy in Leishmania major, providing criteria for clear identification of apoptotic and autophagic cells, demonstrating the sequential nature of autophagy followed by apoptosis in nutrient-deprived conditions, and cautioning against using the generic kinase inhibitor staurosporine as a Leishmania apoptosis inducer, with the aim of improving the understanding of these processes and their targeting for new anti-leishmanial drugs.
Snf1 cooperates with the CWI MAPK pathway to mediate the degradation of Med13 following oxidative stress
Stephen D. Willis1, David C. Stieg1, Kai Li Ong2, Ravina Shah1,3, Alexandra K. Strich1,4, Julianne H. Grose2 and Katrina F. Cooper1
This article explores the response of eukaryotic cells to environmental stress, highlighting the role of the conserved cyclin C-Cdk8 kinase in determining pro-survival or pro-death programs. Specifically, it discusses how oxidative stress triggers the destruction of Med13 by the SCFGrr1 ubiquitin ligase, releasing cyclin C to promote mitochondrial fission and cell death in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Additionally, it reveals that the AMP kinase Snf1 activates a separate degron in Med13, contributing to the complex regulation of Med13 degradation following H2O2 stress through the coordination of the cell wall integrity and MAPK pathways.
Importance of polyphosphate in the Leishmania life cycle
Kid Kohl1, Haroun Zangger1, Matteo Rossi1, Nathalie Isorce1, Lon-Fye Lye2, Katherine L. Owens2, Stephen M. Beverley2, Andreas Mayer1 and Nicolas Fasel1
This article explores the importance of polyphosphate (polyP) in Leishmania parasites, emphasizing the role of the polyP polymerase VTC4 and its impact on parasite survival at higher temperatures. Additionally, it discusses the effects of VTC4 knockout in mouse infections, noting a delay in lesion formation and strong pathology in L. major VTC4 knockout, without confirmation through complementation and no alteration in L. guyanensis infections in mice with VTC4 knockdown.
Antagonism between salicylate and the cAMP signal controls yeast cell survival and growth recovery from quiescence
Maurizio D. Baroni1, Sonia Colombo2 and Enzo Martegani2
This article describes the effects of salicylate, the main metabolite of aspirin, on S. cerevisiae cells. It outlines how salicylate influences glucose transport, sugar phosphate biosynthesis, and apoptosis, particularly in MnSOD-deficient cells. Furthermore, it emphasizes the significant impact of salicylate on the exit from a quiescent state, inhibiting growth recovery and viability in long-term stationary phase cells. The passage also discusses the potential therapeutic implications of understanding the antagonistic relationship between cAMP and salicylate in targeting quiescent cancer cells with stem-like properties.
Evolution of substrate specificity in the Nucleobase-Ascorbate Transporter (NAT) protein family
Anezia Kourkoulou1,#, Alexandros A. Pittis2,# and George Diallinas1
L-ascorbic acid (vitamin C) is an essential metabolite in animals and plants due to its role as an enzyme co-factor and antioxidant activity. Here, Kourkoulou et al. show further evidence that ascorbate-specific Nucleobase-Ascorbate Transporters (NATs) evolved by optimization of a sub-function of ancestral nucleobase transporters.
Valine biosynthesis in Saccharomyces cerevisiae is regulated by the mitochondrial branched-chain amino acid aminotransferase Bat1
Natthaporn Takpho1, Daisuke Watanabe1 and Hiroshi Takagi1
In Saccharomyces cerevisiae, the yeast, the Bat1 and Bat2 proteins, which are branched-chain amino acid aminotransferases, play distinct roles in valine biosynthesis and cell growth regulation, with Bat1 primarily located in the mitochondria and Bat2 in the cytosol, and the mitochondria being identified as the major site of valine biosynthesis in this yeast.

From microbes to medicine: harnessing the gut microbiota to combat prostate cancer
Anjali Yadav1, Meenakshi Kaushik1, Prabhakar Tiwari1 and Rima Dada1
The gut microbiome (GM) has been identified as a crucial factor in the development and progression of various diseases, including cancer. This review highlights the important role that the GM may play in the development and progression of prostate cancer, through its influence on chronic inflammation, immune modulation, and other pathogenic mechanisms.
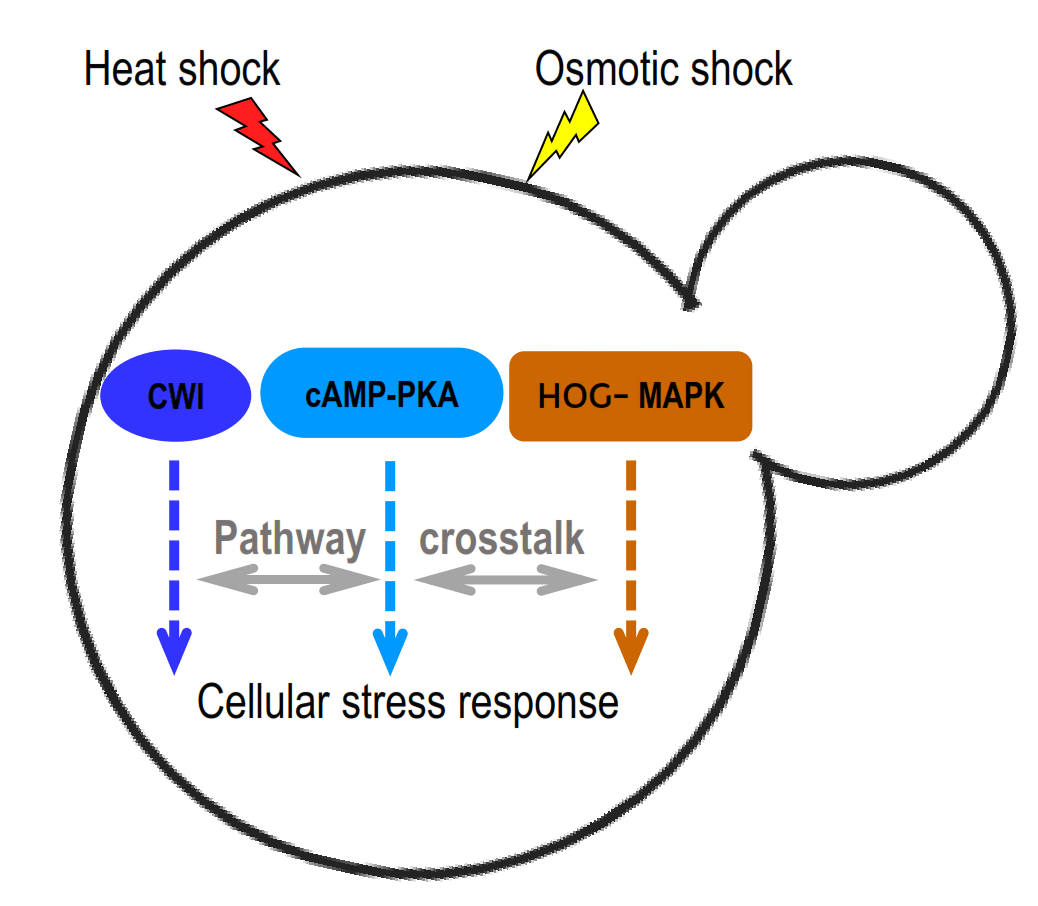
The cAMP-PKA signalling crosstalks with CWI and HOG-MAPK pathways in yeast cell response to osmotic and thermal stress
Fiorella Galello1, Mariana Bermúdez-Moretti1, María Clara Ortolá Martínez1, Silvia Rossi1 and Paula Portela1
During industrial fermentation yeast strains are exposed to fluctuations in oxygen concentration, osmotic pressure, pH, ethanol concentration, nutrient availability and temperature. The scope of this review is to outline the advancement of knowledge about the cAMP-PKA signalling and the crosstalk of this pathway with the CWI and HOG-MAPK cascades in response to the environmental challenges heat and hyperosmotic stress.
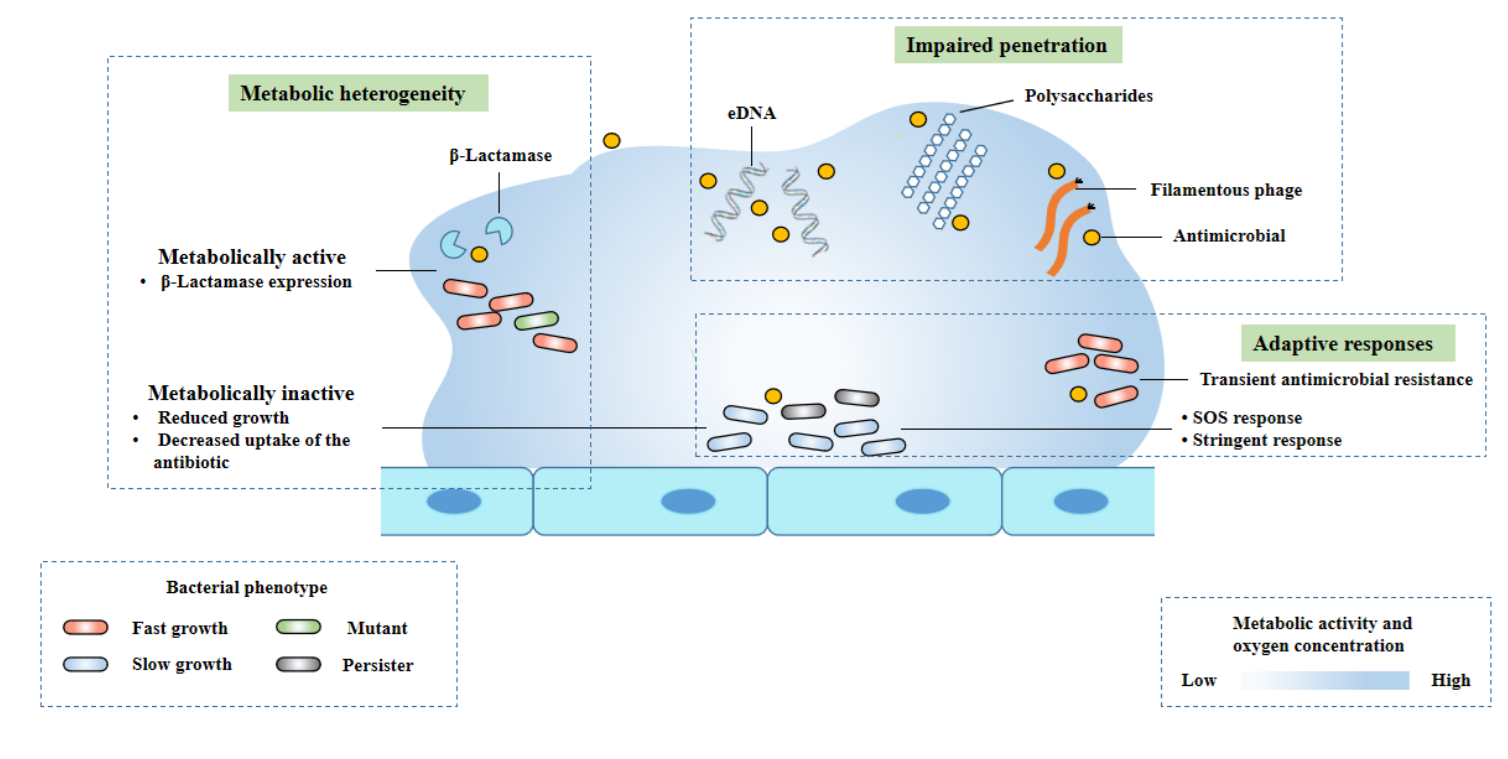
Biofilm tolerance, resistance and infections increasing threat of public health
Shanshan Yang1,3, Xinfei Li1,2, Weihe Cang1,2, Delun Mu1,3, Shuaiqi Ji1,3, Yuejia An1, Rina Wu1,2,3 and Junrui Wu1,2,3
The review explores the role of biofilms in the development of bacterial resistance mechanisms and proposed therapeutic intervention strategies for biofilm related diseases.

Infinity war: Trichomonas vaginalis and interactions with host immune response
Giulia Bongiorni Galego1 and Tiana Tasca1
Trichomonas vaginalis is the pathological agent of human trichomoniasis with an incidence of 156 million cases worldwide. This review highlights parasite strategies to activate and stimulate or evade variated and complex immunological mechanisms related to the symptoms and clinical complications observed here.
Effects of the intestinal microbiota on prostate cancer treatment by androgen deprivation therapy
Safae Terrisse1, Laurence Zitvogel2-5 and Guido Kroemer6-8
Prostate cancer (PC) can be kept in check by androgen deprivation therapy (ADT, usually with the androgen synthesis inhibitor abiraterone acetate or the androgen receptor antagonist such as enzalutamide) until the tumor evolves to castration-resistant prostate cancer (CRPC). The transition of hormone-sensitive PC (HSPC) to CPRC has been explained by cancer cell-intrinsic resistance mechanisms. Recent data indicate that this transition is also marked by cancer cell-extrinsic mechanisms such as the failure of ADT-induced PC immunosurveillance, which depends on the presence of immunostimulatory bacteria in the gut. Moreover, intestinal bacteria that degrade drugs used for ADT, as well as bacteria that produce androgens, can interfere with the efficacy of ADT. Thus, specific bacteria in the gut serve as a source of testosterone, which accelerates prostate cancer progression, and men with CRPC exhibit an increased abundance of such bacteria with androgenic functions. In conclusion, the response of PC to ADT is profoundly influenced by the composition of the microbiota with its immunostimulatory, immunosuppressive and directly ADT-subversive elements.
Occurrence and potential mechanism of holin-mediated non-lytic protein translocation in bacteria
Thomas Brüser1 and Denise Mehner-Breitfeld1
Holins are generally believed to generate large membrane lesions that permit the passage of endolysins across the cytoplasmic membrane of prokaryotes, ultimately resulting in cell wall degradation and cell lysis. However, there are more and more examples known for non-lytic holin-dependent secretion of proteins by bacteria, indicating that holins somehow can transport proteins without causing large membrane lesions. Phage-derived holins can be used for a non-lytic endolysin translocation to permeabilize the cell wall for the passage of secreted proteins. In addition, clostridia, which do not possess the Tat pathway for transport of folded proteins, most likely employ non-lytic holin-mediated transport also for secretion of toxins and bacteriocins that are incompatible with the general Sec pathway. The mechanism for non-lytic holin-mediated transport is (…)
Swimming faster despite obstacles: a universal mechanism behind bacterial speed enhancement in complex fluids
Bacteria constitute about 15% of global biomass and their natural environments often contain polymers and colloids, which show complex flow properties. It is crucial to study their motion in such environments to understand their growth and spreading as well as to design synthetic microswimmers for biomedical applications. Bacterial motion in complex viscous environments, although extensively studied over the past six decades, still remains poorly understood. In our recent study combining experimental data and theoretical analysis, we found a surprising similarity between bacterial motion in dilute colloidal suspensions and polymer solutions, which challenged the established view on the role of polymer dynamics on bacterial speed enhancement. We subsequently developed a physical model that provides a universal mechanism explaining bacterial speed enhancement (…)
Targeting GATA transcription factors – a novel strategy for anti-aging interventions?
Andreas Zimmermann1, Katharina Kainz1,2, Sebastian J. Hofer1,3, Maria A. Bauer1, Sabrina Schroeder1, Jörn Dengjel4, Federico Pietrocola5, Oliver Kepp6-9, Christoph Ruckenstuhl1, Tobias Eisenberg1,3,10,11, Stephan J. Sigrist12, Frank Madeo1,3,10, Guido Kroemer6-9, 13-15 and Didac Carmona-Gutierrez1
This article comments on work published by Carmona-Gutierrez et al. (Nat Commun., 2019), which identified a natural compound, 4,4′-dimethoxychalcone, inducing autophagy and prolonging lifespan in different organisms through a mechanism that involves GATA transcription factors.
In the beginning was the word: How terminology drives our understanding of endosymbiotic organelles
Miroslav Oborník 1,2
This In the Pit article argues that the naming conventions for biological entities influence research perspectives and methodologies, advocating for mitochondria and plastids to be classified and named as bacteria due to their endosymbiotic origins, with potential implications for our understanding of bacterial prevalence, definitions of the microbiome and multicellularity, and the concept of endosymbiotic domestication.
What’s in a name? How organelles of endosymbiotic origin can be distinguished from endosymbionts
Ansgar Gruber1
This In the Pit article suggests redefining the relationship between hosts and endosymbionts, like mitochondria and plastids, as a single species based on “sexual symbiont integration,” the loss of independent speciation, and congruence in genetic recombination and population sizes, rather than solely on historic classifications or structural properties.
Microbial wars: competition in ecological niches and within the microbiome
Maria A. Bauer1, Katharina Kainz1, Didac Carmona-Gutierrez1 and Frank Madeo1,2
In this Editorial Bauer et al. provide a brief overview on microbial competition and discuss some of its roles and consequences that directly affect humans.
Exploring the mechanism of amebic trogocytosis: the role of amebic lysosomes
Allissia A. Gilmartin1 and William A. Petri, Jr1,2,3
In this article, the authors comment on the study “Inhibition of Amebic Lysosomal Acidification Blocks Amebic Trogocytosis and Cell Killing” by Gilmartin et al. (MBio, 2017), discussing the the role of amebic lysosomes in Trogocytosis, the intracellular transfer of fragments of cell material.
Uncovering the hidden: complexity and strategies for diagnosing latent tuberculosis
Mario Alberto Flores-Valdez
This editorial postulates that advanced proteomic and transcriptomic techniques are evolving and may enhance the detection of latent tuberculosis, thereby distinguishing true M. tuberculosis infections from other conditions, which is vital for controlling potential reactivation and transmission.
The Yin & Yang of Mitochondrial Architecture – Interplay of MICOS and F1Fo-ATP synthase in cristae formation
Heike Rampelt1 and Martin van der Laan2
This Editorial posits that mitochondrial cristae architecture is shaped by the interplay of MICOS and ATP synthase, with a recent study illuminating their roles in cristae formation and maintenance.
When a ribosomal protein grows up – the ribosome assembly path of Rps3
Brigitte Pertschy
This article comments on two papers by Mitterer et al., which followed yeast protein Rps3, highlighting the sophisticated mechanisms for protein protection, nuclear transport, and integration into pre-ribosomal particles for final assembly with 40S subunits.
Microbial Cell
is an open-access, peer-reviewed journal that publishes exceptionally relevant research works that implement the use of unicellular organisms (and multicellular microorganisms) to understand cellular responses to internal and external stimuli and/or human diseases.
you can trust
Can’t find what you’re looking for?
You can browse all our issues and published articles here.
FAQs
Peer-reviewed, open-access research using unicellular organisms (and multicellular microorganisms) to understand cellular responses and human disease.
The journal (founded in 2014) is led by its Editors-in-Chief Frank Madeo, Didac Carmona-Gutierrez, and Guido Kroemer
Microbial Cell has been publishing original scientific literature since 2014, and from the very beginning has been managed by active scientists through an independent Publishing House (Shared science Publishers). The journal was conceived as a platform to acknowledge the importance of unicellular organisms, both as model systems as well as in the biological context of human health and disease.
Ever since, Microbial Cell has very positively developed and strongly grown into a respected journal in the unicellular research community and even beyond. This scientific impact is reflected in the yearly number of citations obtained by articles published in Microbial Cell, as recorded by the Web of Science (Clarivate, formerly Thomson/Reuters):

The scientific impact of Microbial Cell is also mirrored in a series of milestones:
2015: Microbial Cell is included in the Emerging Sources Citation Index (ESCI), a selection of developing journals drafted by Clarivate Analytics based on the candidate’s publishing standards, quality, editorial content, and citation data. Note: As an ESCI-selected journal, Microbial Cell is currently being evaluated in a rigorous and long process to determine an inclusion in the Science Citation Index Expanded (SCIE), which allows the official calculation of Clarivate Analytics’ impact factor.
2016: Microbial Cell is awarded the so-called DOAJ Seal by the selective Directory of Open Access Journals (DOAJ). The DOAJ Seal is an exclusive mark of certification for open access journals granted by DOAJ to journals that adhere to outstanding best practice and achieve an extra high and clear commitment to open access and high publishing standards.
2017: Microbial Cell is included in Pubmed Central (PMC), allowing the archiving of all the journal’s articles in PMC and PubMed.
2019: Microbial Cell is indexed in the prestigious abstract and citation database Scopus after a thorough selection process. This also means that Microbial Cell obtains, for the first time, an official Scopus CiteScore as well as an official journal ranking in the Scimago Journal and Country Ranking.
2022: Microbial Cell’s CiteScore reaches a value of 7.2 for the year 2021, positioning Microbial Cell among the top microbiology journals (previously available CiteScores: 2019: 5.4; 2020: 5.1).
2022: Microbial Cell is indexed in the highly selective Science Citation Index Expanded™, which covers approx. 9,500 of the world’s most impactful journals across 178 scientific disciplines. In their journal selection and curation process, Clarivate´s editors apply 24 ‘quality’ criteria and four ‘impact’ criteria to select the most influential journals in their respective fields. This selection is also a pre-requisite for inclusion in the JCR, which features the impact factor.
2022: Microbial Cell is listed in the Journal Citation Reports™ (JCR), and obtains its first official Journal Impact Factor™ (JIF) for the year 2021: 5.316.Check Article Types and Manuscript Preparation guidelines. Submit online via Scholastica.



Sulfur dioxide resistance in Saccharomyces cerevisiae: beyond SSU1
Estéfani García-Ríos1 and José Manuel Guillamón1
This article discusses the importance of understanding sulfite resistance in Saccharomyces cerevisiae due to its use in winemaking and the potential role of the transcription factor Com2. While the SSU1 gene and its activity have been correlated with sulfite tolerance, the work by Lage et al. (2019) indicates that Com2 might control a large percentage of the genes activated by SO2 and contribute to the yeast’s protective response, offering new insights into the molecular factors influencing this oenological trait.