
Regulation of extracellular vesicles for protein secretion in Aspergillus nidulans
This study reveals that Aspergillus nidulans boosts extracellular vesicle production when ER-trafficked enzymes are induced, uncovering how fungi remodel their secretome through vesicle-mediated secretion to adapt to changing environments and biofilm formation.

Transcriptomic response to different heme sources in Trypanosoma cruzi epimastigotes
This study uncovers how the Chagas disease parasite adapts to changes in heme, an essential molecule for its survival, providing transcriptional clues to heme metabolism and identifying a previously unreported heme-binding protein in T. cruzi.

Luminal acetylation of microtubules is not essential for Plasmodium berghei and Toxoplasma gondii survival
Acetylation of α-tubulin at lysine 40 is not essential for cytoskeletal stability in Plasmodium berghei or Toxoplasma gondii, suggesting redundancy and plasticity in microtubule regulation in these parasites.

The dual-site agonist for human M2 muscarinic receptors Iper-8-naphtalimide induces mitochondrial dysfunction in Saccharomyces cerevisiae
S. cerevisiae is a model to study human GPCRs. N-8-Iper, active against glioblastoma via M2 receptor, causes mitochondrial damage in yeast by binding Ste2, highlighting evolutionary conservation of GPCRs.

Integrative Omics reveals changes in the cellular landscape of peroxisome-deficient pex3 yeast cells
To uncover the consequences of peroxisome deficiency, we compared Saccharomyces cerevisiae wild-type with pex3 cells, which lack peroxisomes, employing quantitative proteomics and transcriptomics technologies.

Regulation of extracellular vesicles for protein secretion in Aspergillus nidulans
Rebekkah E. Pope1, Patrick Ballmann2, Lisa Whitworth3 and Rolf A. Prade1,*
This study reveals that Aspergillus nidulans boosts extracellular vesicle production when ER-trafficked enzymes are induced, uncovering how fungi remodel their secretome through vesicle-mediated secretion to adapt to changing environments and biofilm formation.

Transcriptomic response to different heme sources in Trypanosoma cruzi epimastigotes
Evelyn Tevere1,a, María G. Mediavilla1,a, Cecilia B. Di Capua1, Marcelo L. Merli1, Carlos Robello2,3, Luisa Berná2,4 and Julia A. Cricco
This study uncovers how the Chagas disease parasite adapts to changes in heme, an essential molecule for its survival, providing transcriptional clues to heme metabolism and identifying a previously unreported heme-binding protein in T. cruzi.
Sir2 regulates selective autophagy in stationary-phase yeast cells
Ji-In Ryua, Juhye Junga, and Jeong-Yoon Kim
This study establishes Sir2 as a previously unrecognized regulator of selective autophagy during the stationary phase and highlight how cells dynamically control organelle degradation.

Yeast gene KTI13 (alias DPH8) operates in the initiation step of diphthamide synthesis on elongation factor 2
Meike Arend1, Koray Ütkür1, Harmen Hawer1, Klaus Mayer2, Namit Ranjan3, Lorenz Adrian4, Ulrich Brinkmann2 and Raffael Schaffrath1
We show here that apart from its effector role for Elongator-dependent tRNA modification in yeast, Kti13 alias Dph8 also operates in step one of the diphthamide modification pathway.
GFP fusions of Sec-routed extracellular proteins in Staphylococcus aureus reveal surface-associated coagulase in biofilms
Dominique C. S. Evans1,2,#, Amanda B. Khamas1,#, Lisbeth Marcussen1, Kristian S. Rasmussen3, Janne K. Klitgaard3, Birgitte H. Kallipolitis3, Janni Nielsen1, Daniel E. Otzen1, Mark C. Leake2,4 and Rikke L. Meyer1,5
We show that msfGFP can be used to generate extracellular fluorescent fusion proteins in S. aureus, applicable for proteins that are secreted through the Sec pathway. When fused to coagulase, msfGFP did not hinder the biological function, and the fusion protein localised to the fibrin pseudocapsule surrounding clusters of S. aureus cells.
Atg1, a key regulator of autophagy, functions to promote MAPK activation and cell death upon calcium overload in fission yeast
Teruaki Takasaki1, Ryosuke Utsumi1, Erika Shimada1, Asuka Bamba1, Kanako Hagihara2, Ryosuke Satoh1, and Reiko Sugiura1
Here, we provide evidence that the fission yeast Atg1 regulates cell death responses upon intracellular calcium load in addition to its role in promoting Pmk1 MAPK.
TL-532, a novel specific Toll-like receptor 3 agonist rationally designed for targeting cancers: discovery process and biological characterization
Sylvain Thierry1, Sarah Maadadi1, Aurore Berton1, Laura Dimier1, Clémence Perret1, Nelly Vey1, Saïd Ourfali2, Mathilde Saccas1, Solène Caron1, Mathilde Boucard-Jourdin1, Marc Colombel3, Bettina Werle1 and Marc Bonnin1
In the present study, we identified a new family of TLR3 agonists that activates myeloid cells, triggers the secretion of pro-inflammatory cytokines in both myeloid and cancer cells, and induces apoptosis specifically in cancer cells.
Acetate modulates the inhibitory effect of Lactobacillus gasseri against the pathogenic yeasts Candida albicans and Candida glabrata
Nuno A. Pedro1,2, Gabriela Fontebasso1,2, Sandra N. Pinto1,2, Marta Alves3 and Nuno P. Mira1,2
The results herein described advance the design of new anti-Candida therapies based on probiotics, in particular, those based on vaginal lactobacilli species, helping to reduce the significant burden that infections caused by Candida have today in human health.

D-Serine reduces the expression of the cytopathic genotoxin colibactin
Jennifer C. Hallam1,#, Sofia Sandalli1,#, Iris Floria1, Natasha C. A. Turner1, Min Tang-Fichaux2, Eric Oswald2,3, Nicky O’Boyle1,4 and Andrew J. Roe1
Sensing and responding to environmental cues and signalling molecules is crucial for bacterial survival. In this study we have identified a D-amino acid that has a strong regulatory effect on the pks genomic island which encodes for biosynthesis genes for the genotoxic compound colibactin.
A modular cloning (MoClo) toolkit for reliable intracellular protein targeting in the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae
Pavel Simakin1,#, Christian Koch1,# and Johannes M. Herrmann1
In this study, we describe an advanced Molecular cloning toolkit that is designed for the baker’s yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae and optimized for the targeting of proteins of interest to specific cellular compartments.

From microbes to medicine: harnessing the gut microbiota to combat prostate cancer
Anjali Yadav1, Meenakshi Kaushik1, Prabhakar Tiwari1 and Rima Dada1
The gut microbiome (GM) has been identified as a crucial factor in the development and progression of various diseases, including cancer. This review highlights the important role that the GM may play in the development and progression of prostate cancer, through its influence on chronic inflammation, immune modulation, and other pathogenic mechanisms.
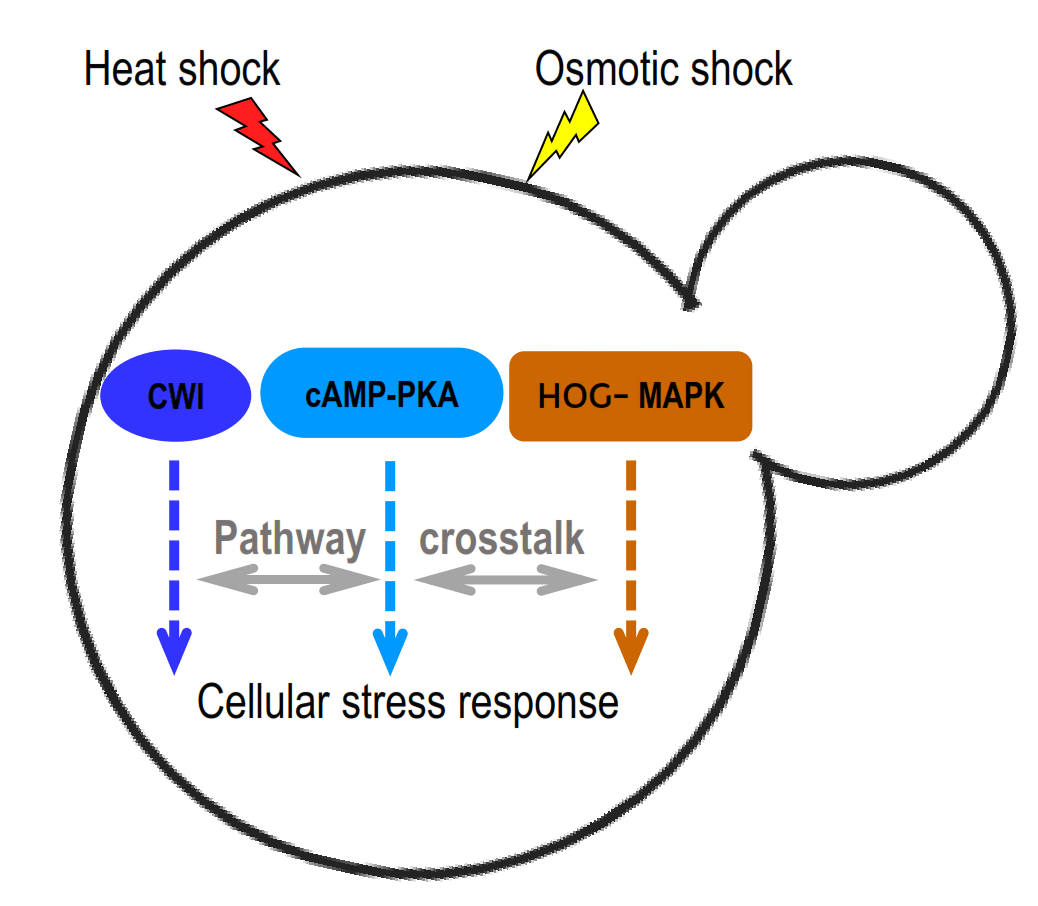
The cAMP-PKA signalling crosstalks with CWI and HOG-MAPK pathways in yeast cell response to osmotic and thermal stress
Fiorella Galello1, Mariana Bermúdez-Moretti1, María Clara Ortolá Martínez1, Silvia Rossi1 and Paula Portela1
During industrial fermentation yeast strains are exposed to fluctuations in oxygen concentration, osmotic pressure, pH, ethanol concentration, nutrient availability and temperature. The scope of this review is to outline the advancement of knowledge about the cAMP-PKA signalling and the crosstalk of this pathway with the CWI and HOG-MAPK cascades in response to the environmental challenges heat and hyperosmotic stress.
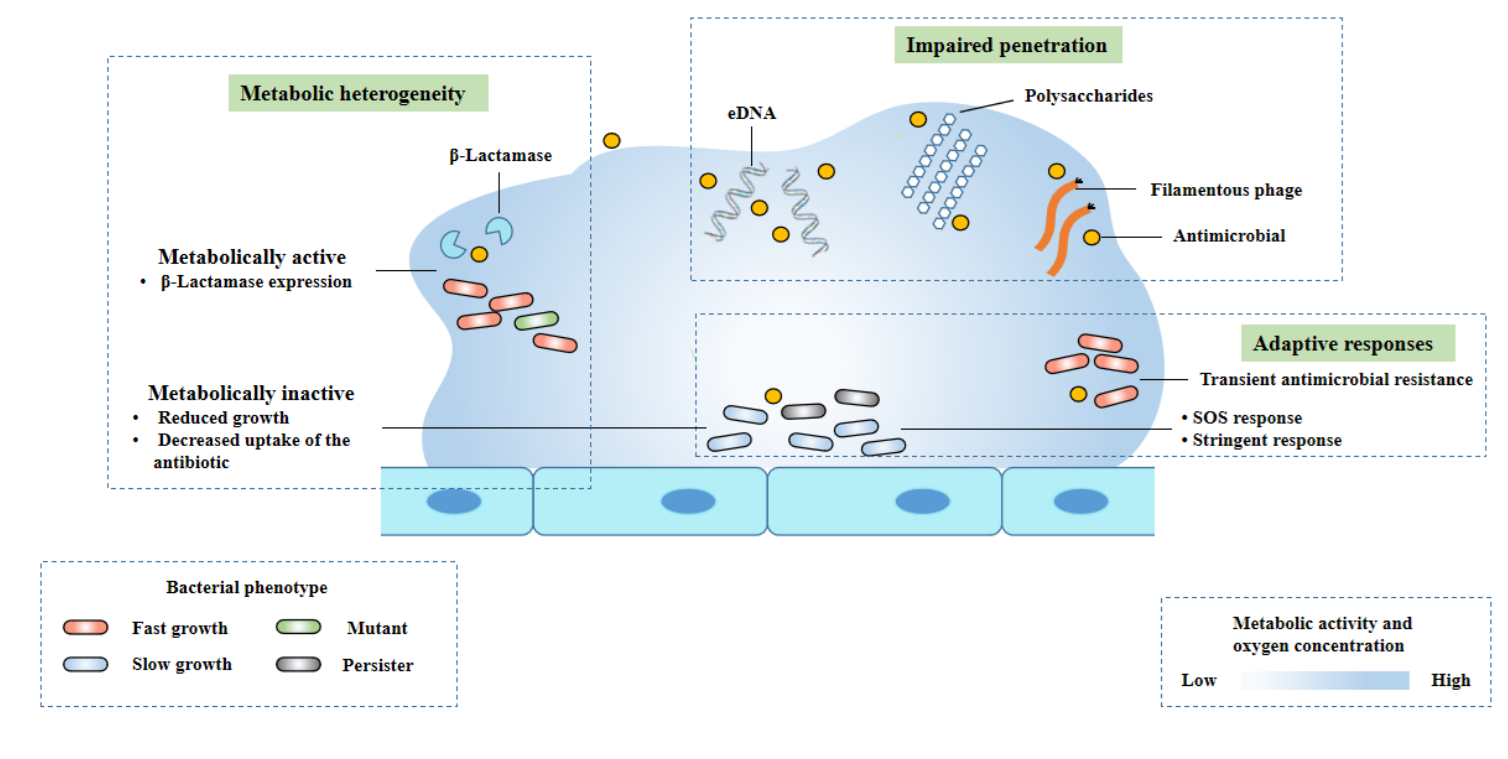
Biofilm tolerance, resistance and infections increasing threat of public health
Shanshan Yang1,3, Xinfei Li1,2, Weihe Cang1,2, Delun Mu1,3, Shuaiqi Ji1,3, Yuejia An1, Rina Wu1,2,3 and Junrui Wu1,2,3
The review explores the role of biofilms in the development of bacterial resistance mechanisms and proposed therapeutic intervention strategies for biofilm related diseases.

Infinity war: Trichomonas vaginalis and interactions with host immune response
Giulia Bongiorni Galego1 and Tiana Tasca1
Trichomonas vaginalis is the pathological agent of human trichomoniasis with an incidence of 156 million cases worldwide. This review highlights parasite strategies to activate and stimulate or evade variated and complex immunological mechanisms related to the symptoms and clinical complications observed here.
Effects of the intestinal microbiota on prostate cancer treatment by androgen deprivation therapy
Safae Terrisse1, Laurence Zitvogel2-5 and Guido Kroemer6-8
Prostate cancer (PC) can be kept in check by androgen deprivation therapy (ADT, usually with the androgen synthesis inhibitor abiraterone acetate or the androgen receptor antagonist such as enzalutamide) until the tumor evolves to castration-resistant prostate cancer (CRPC). The transition of hormone-sensitive PC (HSPC) to CPRC has been explained by cancer cell-intrinsic resistance mechanisms. Recent data indicate that this transition is also marked by cancer cell-extrinsic mechanisms such as the failure of ADT-induced PC immunosurveillance, which depends on the presence of immunostimulatory bacteria in the gut. Moreover, intestinal bacteria that degrade drugs used for ADT, as well as bacteria that produce androgens, can interfere with the efficacy of ADT. Thus, specific bacteria in the gut serve as a source of testosterone, which accelerates prostate cancer progression, and men with CRPC exhibit an increased abundance of such bacteria with androgenic functions. In conclusion, the response of PC to ADT is profoundly influenced by the composition of the microbiota with its immunostimulatory, immunosuppressive and directly ADT-subversive elements.
Occurrence and potential mechanism of holin-mediated non-lytic protein translocation in bacteria
Thomas Brüser1 and Denise Mehner-Breitfeld1
Holins are generally believed to generate large membrane lesions that permit the passage of endolysins across the cytoplasmic membrane of prokaryotes, ultimately resulting in cell wall degradation and cell lysis. However, there are more and more examples known for non-lytic holin-dependent secretion of proteins by bacteria, indicating that holins somehow can transport proteins without causing large membrane lesions. Phage-derived holins can be used for a non-lytic endolysin translocation to permeabilize the cell wall for the passage of secreted proteins. In addition, clostridia, which do not possess the Tat pathway for transport of folded proteins, most likely employ non-lytic holin-mediated transport also for secretion of toxins and bacteriocins that are incompatible with the general Sec pathway. The mechanism for non-lytic holin-mediated transport is (…)
Swimming faster despite obstacles: a universal mechanism behind bacterial speed enhancement in complex fluids
Bacteria constitute about 15% of global biomass and their natural environments often contain polymers and colloids, which show complex flow properties. It is crucial to study their motion in such environments to understand their growth and spreading as well as to design synthetic microswimmers for biomedical applications. Bacterial motion in complex viscous environments, although extensively studied over the past six decades, still remains poorly understood. In our recent study combining experimental data and theoretical analysis, we found a surprising similarity between bacterial motion in dilute colloidal suspensions and polymer solutions, which challenged the established view on the role of polymer dynamics on bacterial speed enhancement. We subsequently developed a physical model that provides a universal mechanism explaining bacterial speed enhancement (…)
Means of intracellular communication: touching, kissing, fusing
Anne Spang1
This work highlights different aspects of communication between organelles, including the importance of organellar contact sites.
Neuropathogenesis caused by Trypanosoma brucei, still an enigma to be unveiled
Katherine Figarella1
This Editorial addresses the meningo-encephalitic stage of Trypanosoma brucei infection and the resultig neuropathogenesis as well as the impact that the application of tools developed in the last years in the field of neuroscience will have on the study of neglected tropical diseases.
Lichens – growing greenhouses en miniature
Martin Grube1
This commentary article provides an overview on different aspects of lichen biology and the remarkable symbiotic association between fungi and algae.
Regulation of the mitochondrial permeability transition pore and its effects on aging
Damiano Pellegrino-Coppola1
Aging is linked to mitochondrial function, with the mitochondrial permeability transition pore (mPTP) playing a key role. Yeast is a useful model for studying how mPTP affects cell survival, aging, and related diseases.
Fungal infections in humans: the silent crisis
Katharina Kainz1, Maria A. Bauer1, Frank Madeo1-3 and Didac Carmona-Gutierrez1
This article highlights the growing global threat of fungal infections – exacerbated by rising drug resistance and medical practices – and emphasizes the urgent need for intensified research to develop more effective antifungal strategies.
Digesting the crisis: autophagy and coronaviruses
Didac Carmona-Gutierrez1, Maria A. Bauer1, Andreas Zimmermann1,2, Katharina Kainz1,
Sebastian J. Hofer1, Guido Kroemer3-7 and Frank Madeo1,2,8
This article reviews the multifaceted role of autophagy in antiviral defense and highlights how coronaviruses, including SARS-CoV-2, interact with this pathway, raising the possibility that targeting autophagy could offer novel therapeutic strategies against COVID-19.
Microbial Cell
is an open-access, peer-reviewed journal that publishes exceptionally relevant research works that implement the use of unicellular organisms (and multicellular microorganisms) to understand cellular responses to internal and external stimuli and/or human diseases.
you can trust
Can’t find what you’re looking for?
You can browse all our issues and published articles here.
FAQs
Peer-reviewed, open-access research using unicellular organisms (and multicellular microorganisms) to understand cellular responses and human disease.
The journal (founded in 2014) is led by its Editors-in-Chief Frank Madeo, Didac Carmona-Gutierrez, and Guido Kroemer
Microbial Cell has been publishing original scientific literature since 2014, and from the very beginning has been managed by active scientists through an independent Publishing House (Shared science Publishers). The journal was conceived as a platform to acknowledge the importance of unicellular organisms, both as model systems as well as in the biological context of human health and disease.
Ever since, Microbial Cell has very positively developed and strongly grown into a respected journal in the unicellular research community and even beyond. This scientific impact is reflected in the yearly number of citations obtained by articles published in Microbial Cell, as recorded by the Web of Science (Clarivate, formerly Thomson/Reuters):

The scientific impact of Microbial Cell is also mirrored in a series of milestones:
2015: Microbial Cell is included in the Emerging Sources Citation Index (ESCI), a selection of developing journals drafted by Clarivate Analytics based on the candidate’s publishing standards, quality, editorial content, and citation data. Note: As an ESCI-selected journal, Microbial Cell is currently being evaluated in a rigorous and long process to determine an inclusion in the Science Citation Index Expanded (SCIE), which allows the official calculation of Clarivate Analytics’ impact factor.
2016: Microbial Cell is awarded the so-called DOAJ Seal by the selective Directory of Open Access Journals (DOAJ). The DOAJ Seal is an exclusive mark of certification for open access journals granted by DOAJ to journals that adhere to outstanding best practice and achieve an extra high and clear commitment to open access and high publishing standards.
2017: Microbial Cell is included in Pubmed Central (PMC), allowing the archiving of all the journal’s articles in PMC and PubMed.
2019: Microbial Cell is indexed in the prestigious abstract and citation database Scopus after a thorough selection process. This also means that Microbial Cell obtains, for the first time, an official Scopus CiteScore as well as an official journal ranking in the Scimago Journal and Country Ranking.
2022: Microbial Cell’s CiteScore reaches a value of 7.2 for the year 2021, positioning Microbial Cell among the top microbiology journals (previously available CiteScores: 2019: 5.4; 2020: 5.1).
2022: Microbial Cell is indexed in the highly selective Science Citation Index Expanded™, which covers approx. 9,500 of the world’s most impactful journals across 178 scientific disciplines. In their journal selection and curation process, Clarivate´s editors apply 24 ‘quality’ criteria and four ‘impact’ criteria to select the most influential journals in their respective fields. This selection is also a pre-requisite for inclusion in the JCR, which features the impact factor.
2022: Microbial Cell is listed in the Journal Citation Reports™ (JCR), and obtains its first official Journal Impact Factor™ (JIF) for the year 2021: 5.316.Check Article Types and Manuscript Preparation guidelines. Submit online via Scholastica.




The long and winding road of reverse genetics in Trypanosoma cruzi
Miguel A. Chiurillo1 and Noelia Lander1
This Editorial provides a brief historic overview that highlights the strengths and weaknesses of the molecular strategies that have been developed to genetically modify Trypanosoma cruzi, emphasizing the future directions of the field.